As organizations modernize and shift workloads to IBM Cloud, they typically need some application workloads to function on other cloud service provider networks. Enterprises, especially in regulated industries like insurance, banking, and healthcare, struggle to establish safe and dependable communication across multicloud application components and services due to these requirements.
This blog article answers common questions by summarizing important principles and ways organizations use to link IBM application workloads to other clouds to assist overcome the problems. Use the article to choose the optimal connectivity options for your use case:
1.Why are regulated workload components in several clouds?
2.What workloads typically demand multicloud connectivity?
3.How do IBM Cloud regulated workloads link to other clouds?
4.What are multicloud workload communication methods?
1. Why do regulated workload components span across clouds?
Complex business processes (insurance underwriting, claims processing, payment processing, fraud detection, medical data processing, etc.) and automated and semi-automated workflows drive business functions in regulated sectors. Modernizing these procedures usually needs a mix of best-of-breed vendor services or applications that may not be on the same cloud.
Homegrown tailored applications run on private cloud networks, apart from dependent components on other clouds. Enterprises also work with managed service providers that have a central cloud but access resources from different clouds. To meet compliance standards, decrease disruptions, and reduce vendor lock-in, workloads are commonly operated on various clouds.
2. What workloads often demand multicloud connectivity?
Multicloud workloads can be characterized by high-level use cases and data shared across clouds. General categories include:
Application data exchange: RESTful APIs allow application components across clouds to exchange data and conduct synchronous or asynchronous transactions.
Batch data transfer: Asynchronous or planned batch data transfers between clouds for analytical processing, archiving, AI training, or data migration.
Administration access: Remote access and communication between cloud hosts and managed systems on other clouds, generally part of managed services and third-party administration contracts.
Monitoring and tooling data transfer: Automatic or manual transfer of logs and performance and security monitoring data from several clouds to a centralised collection and management system on another cloud.
Data replication: Real-time or non-real-time batch sharing of data between systems and components for HA, DR, etc.
Enterprise implementations combine the above workloads depending on application complexity. Knowing use cases and data interchange characteristics across clouds are crucial for analyzing workload component connection alternatives.
3. How do IBM Cloud regulated workloads connect to other clouds?
Insurance and banking companies on IBM Cloud use the VPC-based reference design from IBM Cloud for Financial Services. Security and controls are embedded into IBM Cloud for Financial Services, which automates security and compliance posture and simplifies regulatory compliance risk management.
IBM Cloud for Financial Services multicloud application workloads Applications and services on VPCs or SaaS offerings on other clouds exchange data with VPCs. Enterprises choose from the cloud provider’s services to connect VPCs to other clouds or networks.
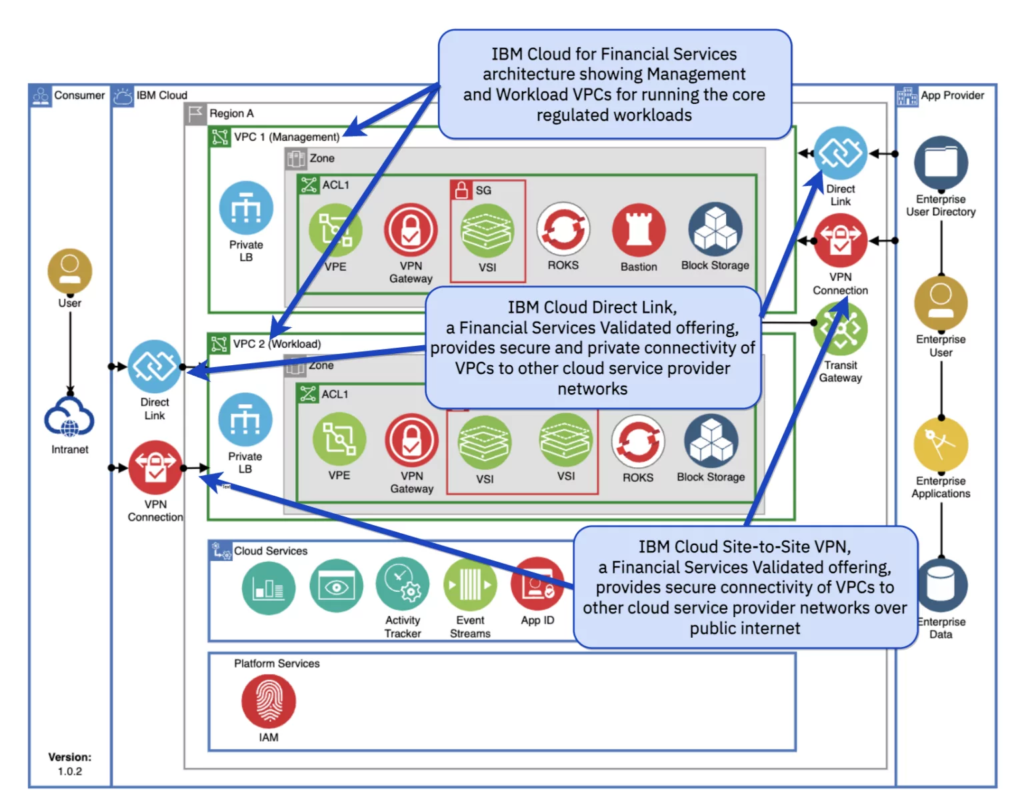
Offerings for IBM Cloud VPC connectivity services are Financial Services Validated, ensuring compliance with the framework’s rules. The Site-to-Site VPN product offers safe internet access while the Direct Link Connect and Direct Link Dedicated offerings offer secure and private internet connectivity by utilizing pre-existing alliances with more than 45 international service providers. With the features for security, compliance, and resiliency that financial and other regulated institutions demand, these IBM Cloud capabilities enable a transparent public cloud environment and foster a culture of trust.
4. How can multicloud workloads connect to one another and communicate?
There are three basic methods for connecting workloads that are spread across various cloud providers:
- Over the general internet.
- Partner networks are connected.
- At the data center, there is direct connectivity.
Connectivity over public internet using public interfaces: Application-to-application communication and connection using secure public interfaces on the internet is one of the most popular methods (e.g., public API endpoints or TCP host/ports exposed from custom applications, SaaS public API endpoints, etc.). This method, however limited in the use cases it can handle, is straightforward and often employed because it only needs access to the public internet to connect to and from the VPC. Offerings from IBM Cloud Public Gateway and API Connect give users the ability to connect to services on another peer cloud and use public interfaces.
Connectivity over the open internet using virtual private networks (VPNs): Virtual private network-to-network connectivity, also known as VPNs, is another option for internet connectivity. A host running on any cloud can connect to an IBM Cloud VPC using IBM Client-to-Site VPN. An IBM Cloud VPC can connect to a VPC on a different peer cloud using an IBM Site-to-Site VPN.
Connectivity through provider networks: A connectivity provider partner network connects cloud VPC networks for private network-to-network communication. The IBM Cloud Direct Link Connect offering has collaborations with network service providers that connect to other clouds. It provides secure and private connectivity between IBM Cloud VPCs and other peer cloud VPCs and is multi-tenant.
Co-location data center facility: Direct physical connectivity of the networks at a data center facility provider that co-locates IBM Cloud and another peer cloud is the most direct choice for linking workloads. IBM Cloud Direct Link Dedicated enables direct, secure, private single-tenant physical connectivity to other cloud networks through pre-established co-location relationships.
Evaluation of IBM Cloud and peer cloud providers’ services is crucial to adopting one or more of the above options for a business multicloud workload. Selecting a viable solution includes assessing short- and long-term strategic goals and technical needs.
Wrap up
Finally, IBM Cloud for Financial Services’ VPC-based reference design can securely connect multicloud application workloads on IBM Cloud to other clouds and on-premises networks for regulated industries. Enterprises can choose from IBM Site-to-Site VPN for public internet connectivity or IBM Direct Link for private network connectivity with over 45 global service providers to meet their business and technical needs.



[…] data exchange across applications using IBM Cloud Pak for Data and standardized integration using IBM Cloud Pak for Integration […]
[…] Dell’s Multicloud Solutions […]
[…] cloud banking application deployment best practices for IBM Cloud and Satellite security and […]
[…] moving from IBM Cloud Functions, IBM Cloud Code Engine is a deployment target. Choose from apps, jobs, and (recently) […]
[…] systems: Most companies have resource explosions. Multicloud and adaptive cloud deployments, operational edge servers, and IoT devices can be overwhelming. […]
[…] are using multicloud deployments for contemporary containerized programs to improve user experiences, increase […]
[…] catalog. Other cloud providers call them marketplace images. Each catalog image will include an IBM Cloud Catalog tile. Only virtual servers support catalog images; bare metal servers are not […]