Blockchain databases were created to increase confidence in centralized ecosystems by introducing tamper-evidence characteristics into conventional databases. Compared to decentralized ledger systems, they are more user-friendly and can lower operational and development expenses. To regulate shared data on the ledger, numerous parties would need effective tools, which are now missing from blockchain databases.
Orion is an open source blockchain database that provides unique capabilities, such as multi-signature and proof functionalities, along with extensive key-level access control. These features empower parties to jointly control and validate values written to the database. Orion combines these capabilities with other blockchain properties, offering tamper evidence, provenance, data lineage, authenticity and non-repudiation, all while utilizing a standard data model and transactional APIs. Orion’s technology is highly valuable in enhancing system integrity and reducing errors, disputes and fraud.
In this article, we examine the need for trust in diverse business situations, pinpoint trust gaps, and discuss how Orion can successfully close such gaps. We examine Orion’s primary characteristics and consider its possible uses in several fields.
The significance of trust in business ecosystems
The development and success of business ecosystems depend on trust. But because so many different parties are involved, building confidence in complicated situations like global supply chains is extremely difficult. For instance, in response to sustainability trends, goods producers would have to show regulators and customers how much carbon their products emit. As a result, it is crucial to ensure accuracy and fairness when estimating the carbon footprint of every component along the whole supply chain. The use of technology that is mutually trusted can help companies, clients, partners, and government agencies confirm the existence, legitimacy, and integrity of interactions between parties. By doing this, it promotes a climate of trust and dependability as well as acting as a shield against potential disagreements and fraudulent actions.
Understanding the needs for trust
The level of trust among participants varies between business ecosystems, which affects the unique criteria for trust. In highly trusted contexts, it may be sufficient to assure independent, reliable, and crash-tolerant data recording, however in low-trust settings, we may also wish to confirm the accuracy of the data recorded, ensure authenticity, and offer tamper proof and data lineage.
Last but not least, in low-trust contexts, we might need to manage the transaction execution by providing multi-party approval and parallel smart contract execution, and even coming to an agreement in the face of nefarious parties.
Ecosystems can be divided into centralized and decentralized ecosystems from a topological perspective. Decentralized ecosystems lack a single entity that is trusted by all members, in contrast to centralized ecosystems where at least one party often enjoys some level of trust from all players. Currently, a centralized trust assumption governs the bulk of economic ecosystems. While other ecosystem players are not required to explicitly trust one another, a trusted party (such as a cloud provider, a government agency, or another powerful entity) plays a crucial role in these ecosystems. For instance, enterprises often rely on faith in the cloud provider, anticipating that despite having the power to do so, they won’t purposefully prevent client access to services.
The presence of a dependable party does not, however, entail unquestioning faith on the part of other players. Our experience shows that there is a lot of space to grow trust in centralized ecosystems. The ability to demonstrate data integrity and consistency as well as transparency across the data lifecycle are essential ingredients for progress. In environments with strict regulations, these components are especially important for expediting the auditing process. In order to avoid potential authorship conflicts in multi-party interactions, data authenticity must be guaranteed. To reduce the dangers of errors and fraud, even trustworthy parties frequently try to limit the authority of their privileged users. By filling in these trust gaps, centralized ecosystems can be enhanced even more, enabling more trust and dependability in commercial transactions.
Using technology to fill the trust gaps
Three main categories of technologies can aid in bridging the trust gap in corporate ecosystems. Typically, traditional databases with simple recording features are enough to ensure the smooth running of centralized ecosystems with high levels of trust. In contrast, blockchain databases are the greatest option for centralized ecosystems with low levels of trust since they expand the capabilities of traditional databases with verifications and proofs. Finally, decentralized ledger technologies are frequently utilized in low-trust decentralized systems and typically offer a full stack of trust features. It is important to keep in mind that supporting advanced trust features typically results in greater complexity, which might affect the solution’s performance and raise its operating costs. As a result, it’s critical to match the ecosystem’s requirements with the best technology available.
Figure 1 illustrates the topography of trust in the business ecosystems.
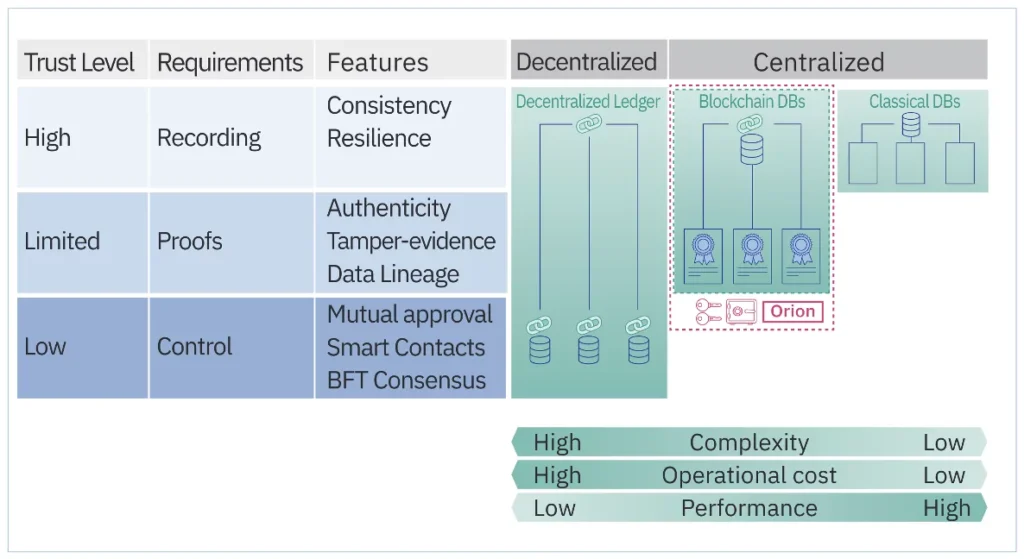
Although the usage of current blockchain database technologies can help close some trust gaps in centralized contexts, they fall short in terms of facilitating effective control of shared data among numerous parties. These features are provided by decentralized blockchain ledger technologies and can be employed in centralized systems, however this is frequently ineffective and doesn’t make up for the added expense and complexity. Herein lies the role of Orion, our cutting-edge open-source blockchain database. By providing a wide range of blockchain features and enabling various parties to control access to shared data, Orion sets itself apart from other centralized blockchain databases. This is done by offering a wide range of read/write access controls at the key level as well as multi-signature capabilities, which makes sure that database transactions are only accepted when they are jointly signed by specified parties.
Orion: A centralized blockchain database with multi-party data access control is called Orion.
With the strength of blockchain technology and the dependability of conventional database features, Orion is a powerful open-source blockchain database. It offers a complete answer for reliable, transparent, and secure data management. Orion provides a wide range of blockchain functions, including a highly available, secure, replicated distributed database with an immutable tamper-proof ledger, by layering a cryptography-based layer on top of a conventional database. The ledger provides tamper evidence, making it possible to identify any data updates, including those performed by privileged users. This extra security measure guarantees data integrity while boosting credibility and dependability.
The blockchain capabilities that Orion offers are shown in Figure 2.
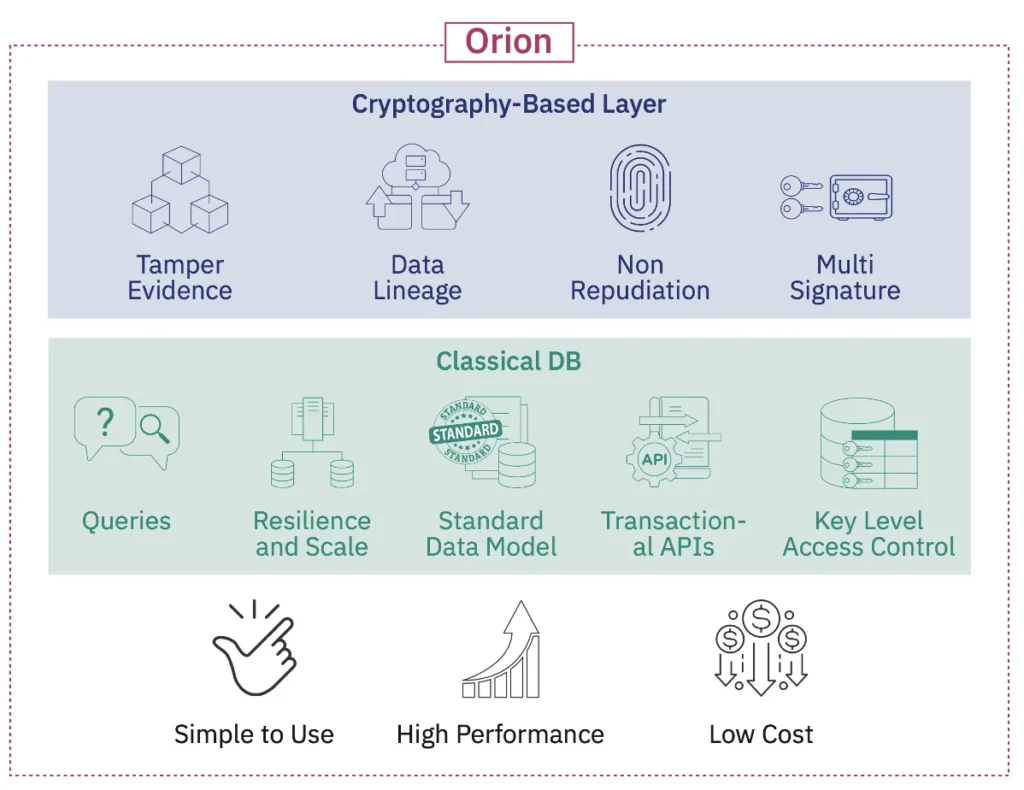
Orion’s ability to enable multi-signature (multi-sig) transactions, made possible by a special read-write key-level access control mechanism, is a fundamental differentiator. For several parties to engage in reliable ways, this functionality is essential. In order to ensure a secure and dependable environment for multi-party interactions, transactions are only considered committed when signed by many designated participants.
Orion’s capability to facilitate provenance and data lineage is one of its most significant characteristics. Data transformations are tracked, allowing historical searches to determine when, how, and by whom changes were made to the data. Utilizing a graph-DB-based provenance engine, Orion can offer insightful information about the background and source of the data, encouraging accountability and openness.
Orion offers users with authenticity and non-repudiation features that offer conclusive proof that the information received is exactly the same as that sent by the original source. The server creates a digital receipt that may be used to confirm the accuracy of the data and signs each transaction. This skill eliminates authorship conflicts and raises trust levels even higher.
Orion also smoothly incorporates blockchain capabilities with traditional database features. It delivers scalability, reliable resilience, and effective queries. Orion ensures the execution of a group of read/write operations as an atomic transaction, maintaining consistency and data integrity, using a common key-value JSON store and transactional APIs.
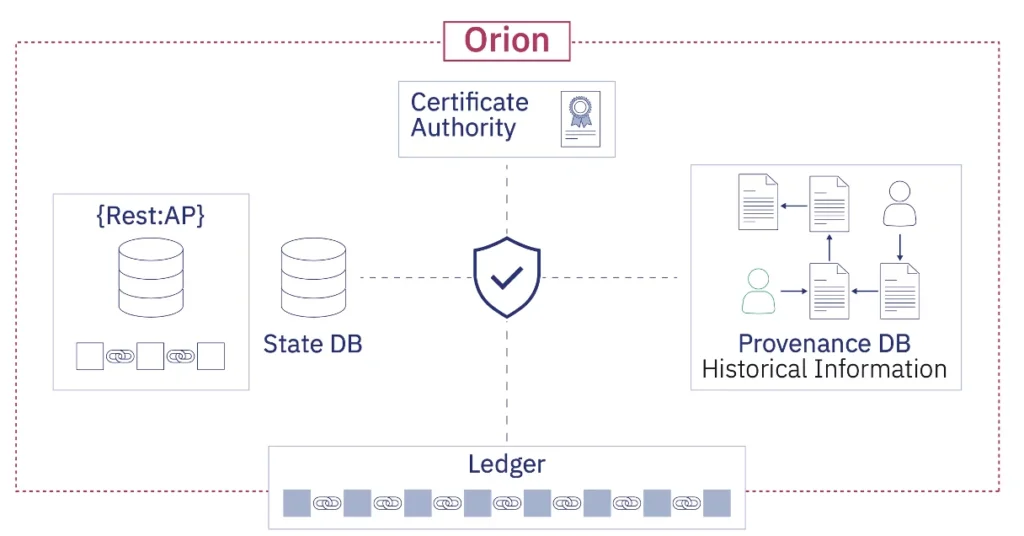
The design of Orion offers open insights that guarantee responsibility, as shown in Figure 3.
Important applications produce worthwhile solutions.
Orion supports a broad range of essential applications that cater to different industrial needs and offer beneficial solutions for companies and organizations. The supply chain industry is one notable application. Orion can operate as a reliable repository for all carbon footprint information provided by component manufacturers regarding all product components. It can also keep the written, jointly-signed conditions of the contracts between buyers and sellers of these components. . Furthermore, Orion enables the inclusion of the formula used to compute the carbon footprint of the product, along with links to the carbon consumption data of its individual parts, which can be updated by the product owner. By leveraging Orion, organizations can ensure the authenticity, non-repudiation and integrity of this critical data. Moreover, key-level access control mechanisms guarantee data privacy between the involved parties. If necessary, privacy-preserving techniques like zero-knowledge proofs can be employed to conceal sensitive details, even from the central party. In such cases, Orion can retain only the necessary metadata required to demonstrate the accuracy of the records, which can be kept outside the system for third-party auditors.
Orion offers a wide range of extremely advantageous use cases that our clients have recognized in addition to the supply chain application. By providing evidence of authenticity, data integrity, and tampering for corporate documents, for instance, Orion can help auditing processes in the financial sector and other regulated sectors. With the help of our multi-signature capabilities, diverse company contracting procedures can be automated, and we can assist notary services in numerous industries. Orion can also be used to preserve the veracity and integrity of data gathered over the course of insurance claims processes. For government entities, it can make it easier to handle rights to property ownership, certificates, licenses, and educational records. Orion can also be used as a safe digital platform for keeping track of immunization procedures, records, and statuses. It also makes it possible to maintain supply chain maintenance standards and confirm the provenance of commodities. In order to maintain data integrity in hybrid contexts, Orion can also act as an off-chain store for decentralized ledger ecosystems.
Several EU-funded programs have already used Orion as a blockchain platform with success. Traceability, provenance, and non-repudiation characteristics from Orion were used in the C4IIoT project to track changes in machine and production line configurations, increasing the level of confidence in an IoT cybersecurity platform. Orion is being used in the COPA EUROPE project to monitor the creation and lifecycle of media assets, enabling reliable and secure exchange of sports films, rights, and participant incentives. Orion is used in the i4Q project to protect the integrity of industrial IoT data, including device access policies and crucial location data, supporting use cases for smart manufacturing. These initiatives showcase Orion’s adaptability and dependability as a blockchain database system in practical applications.
Hyperledger Labs offers the Orion server, its documentation, and client SDK. Read our paper “Orion: A Centralized Blockchain Database with Multi-Party Data Access Control,” which we presented and published at ICBC 2023, to learn more about Orion’s capabilities.
Across corporate ecosystems, the Orion blockchain database provides a solid solution that improves openness, authenticity, and integrity. By enabling various parties to control access to shared data, Orion distinguishes itself from other centralized blockchain databases. Organizations may exercise fine-grained control over data governance and guarantee confidence in multi-party interactions thanks to its comprehensive key-level read/write access control and multi-signature capabilities.


[…] Blockchain technology has completely changed the banking industry by making peer-to-peer transactions possible without the use of middlemen. Blockchain technology has gained a new dimension with the launch of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), which is revolutionizing how people and businesses will make payments in the future. […]
[…] is used by end users to access to both the VSIs in their IBM Cloud VPC and the instances and databases in their on-premises […]
[…] is the database […]
[…] which we extended with six more in 2019, Google Cloud collaborated with the community to democratize blockchain data at the beginning of 2018. Eleven more of the most popular blockchains have been added to the […]