For 40 years, IBM Maximo has led enterprise asset management by centralizing task, inventory, regulatory compliance, and reporting management.
IBM Maximo Application Suite (MAS), the next iteration of IBM Maximo, improves user experience, integration, AI analytics, and cloud deployment choices. IBM MAS is a powerful and modern asset management solution.
The Red Hat OpenShift-based IBM MAS integrated application suite supports hybrid and on-premises installations and is portable. An enterprise cloud-based asset management platform, it uses AI, IoT, and analytics to enhance equipment performance, extend asset lifecycles, and decrease operational downtime and costs. IBM MAS lets customers access important monitoring, maintenance, and reliability applications from a single platform for business-wide management.
The next-generation IBM MAS simplifies installation and administration and improves user experience with shared data, workflow, UX, and flexible application usage. You and your team will gain greater operational visibility of your assets through their lifecycle with faster ROI, increased productivity, and operational uptime with expanded access to CMMS, EAM, APM, and RCM.
IBM Maximo 7.x clients must switch to IBM MAS when it ends. IBM MAS is exclusively containerized for Red Hat OpenShift. Amazon Web Services (AWS) has worked with IBM and Red Hat to produce an IBM MAS on Red Hat OpenShift Service for AWS (ROSA) reference architecture to help customers inexperienced with production containerization.
This blog article will detail the recommended alternatives for running IBM MAS on AWS, the architecture, and how IBM, Red Hat, and AWS components work together to give a stable foundation. We will also discuss architectural options so you can choose the best one for your firm.
WHY ROSA for Maximo in AWS?
ROSA is a fully managed, turnkey application platform that offloads cluster lifecycle management to Red Hat and AWS, letting you focus on application deployment and innovation. Red Hat and AWS create and maintain Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS. It is native in the AWS console and connects with popular AWS services.
ROSA supports IBM MAS and manages Red Hat OpenShift Clusters. This means customers don’t need to establish, manage, or operate IBM MAS Red Hat OpenShift clusters. ROSA lets customers focus on business value rather than platform management.
Red Hat OpenShift runs Maximo Application Suite (MAS), according to its necessary software documentation. Therefore, a Red Hat OpenShift cluster must be running to install and configure Maximo Application Suite.”
This article covers three IBM MAS AWS deployment methods:
1.ROSA-powered MAS SaaS on AWS
2.ROSA-powered MAS Dedicated on AWS
3.Hosted by customers
1. ROSA-powered IBM MAS SaaS on AWS
For enterprises that want to use IBM Maximo Application Suite as a Service (IBM MAS SaaS) on AWS with the convenience of an IBM-managed SaaS model. This option allows browser-based access to software and its functions without managing hardware and infrastructure.
IBM MAS SaaS on AWS has many benefits. First, it’s fully managed and scalable, allowing resource modifications to meet demand. Second, the default high availability and fault-tolerance guardrails assure stability. Finally, IBM MAS SaaS on AWS clients can get the latest features via a scheduled update.
However, choosing a SaaS alternative has some risks. A shared platform limits customization, flexibility, and integration compared to dedicated IBM MAS at AWS choices.
MAS SaaS on AWS is a good choice for companies that want to simplify their MAS experience with cloud deployment:
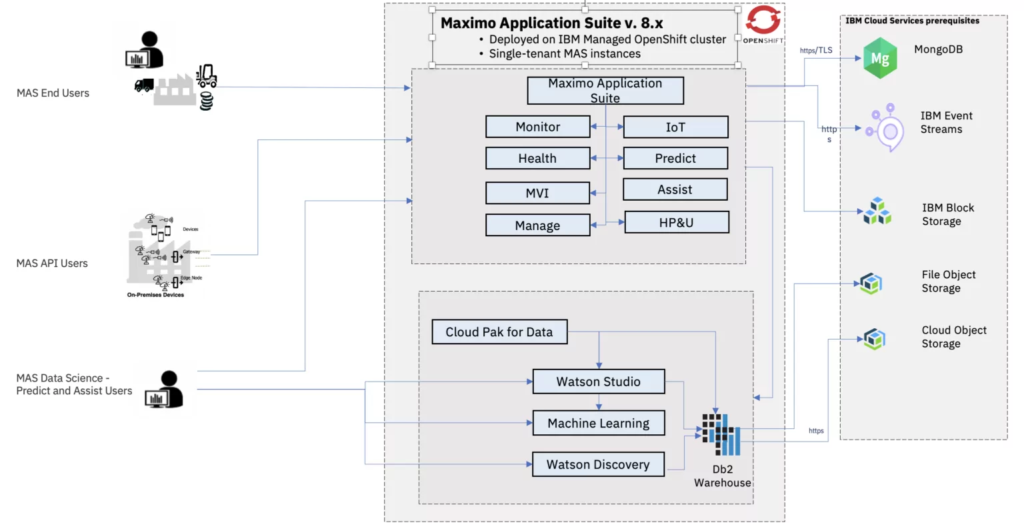
Figure 1: IBM Maximo Application Suite as a Service high-level architecture
2. ROSA-powered IBM MAS dedicated on AWS
For businesses searching for a customized MAS experience within AWS, the MAS Dedicated on AWS option offers a compelling alternative. This option places MAS on dedicated infrastructure that is only available to one company, assuring optimal performance and security that is overseen by IBM. In line with IBM’s supported version policy, this gives the customer more control over the infrastructure, updates, and upgrade plan. Better isolation and improved data privacy and protection are provided by the specialized infrastructure.
When selecting this option, there are a few things to keep in mind. When compared to the customer-owned alternative, customizations are constrained, and the IBM MAS Dedicated on AWS option has higher infrastructure expenses than the IBM MAS SaaS services. Overall, the IBM MAS Dedicated on AWS option provides enterprises desiring an exclusive and tightly managed IBM MAS environment within AWS with a solid and secure solution:
Figure 2: IBM MAS Dedicated on AWS high-level reference architecture
3. IBM MAS on ROSA hosted by the customer
A potent option for hosting IBM MAS in a customer’s virtual private cloud (VPC) with ROSA is the customer-hosted ROSA option. ROSA is the best option for a MAS deployment since it is a container application platform that offers smooth containerized application deployment, scaling, and management.
This choice offers a number of benefits. In order to better customize and adapt the environment to their needs, organizations have complete control over the infrastructure while still being subject to the organization’s monitoring, controls, and governance standards. This control also includes the option to establish more MAS integrations and to enforce current cloud security and governance guidelines. Additionally, ROSA fees are combined into a single AWS payment and are deducted from any AWS enterprise agreement, easing financial administration.
Customers can benefit from savings for the underlying infrastructure enabling the MAS implementation if they have an AWS enterprise agreement or a compute savings plan. The customer also has the option of purchasing upfront ROSA contracts and receiving either 33%off (one year) or 65%off (three year) the ROSA service charge because the ROSA cluster runs in their AWS account.
Customers can use this option to monitor and maintain their MAS platform while giving Red Hat site reliability engineers (SREs) control over the lifecycle management of the underlying OpenShift cluster.
There are a few further considerations to take into account, though. While Red Hat SREs are controlling the ROSA cluster in this option, there is still an additional operational overhead cost for configuring and operating the IBM MAS application on ROSA. This option requires separate purchases of ROSA and IBM MAS, increasing the financial expenditures.
Red Hat OpenShift and IBM MAS can be hosted on AWS with the customer-hosted ROSA option since it gives enterprises complete control and customizability:
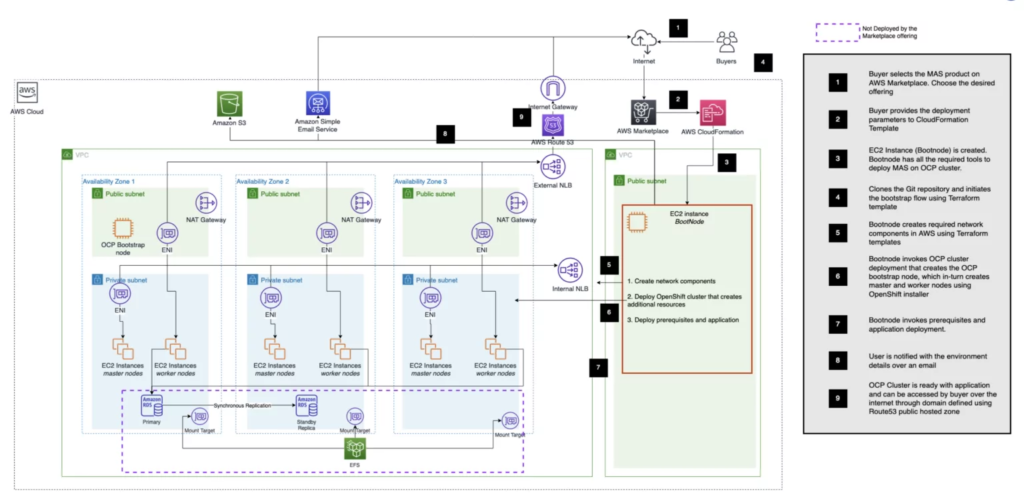
Figure 3: Customer-owned ROSA reference architecture
Conclusion remarks
There are various benefits and drawbacks to each IBM Maximo Application Suite deployment option, including MAS SaaS on AWS, MAS Dedicated on AWS, and IBM MAS on customer-hosted ROSA. In order to match their deployment with particular business goals and requirements, customers should have a look at these variables. In addition to ease and controlled scalability, IBM MAS SaaS on AWS offers enhanced control and isolation, IBM MAS Dedicated on AWS offers enhanced control and isolation, and customer-hosted ROSA enables complete customization, flexibility within the customer’s VPC, and the capacity to take advantage of current AWS Enterprise Agreements.
To achieve a successful and effective IBM MAS deployment, customers should evaluate their infrastructure, customization needs, and pricing concerns. Customers can select the deployment option that best serves their business goals by being aware of the advantages and disadvantages of each option.
Contact your IBM, Red Hat, or AWS account team to discuss your unique requirements if you’d like to learn more about integrating AWS and Red Hat with IBM Maximo to migrate and modernize the software. Consider joining the IBM Maximo community as well to participate in discussions, ask questions about this topic, and share your insightful experiences with other professionals.



[…] established IBM as a hardware, software, and services provider. Its early success and IBM WebSphere in the 1990s […]
[…] AI created a “automated visual inspection” presentation for Red Hat Summit 2023. In comparison to TFLite, they were able to process 62% more frames per second utilizing OpenVINO […]
[…] do this in one environment and reduce the development lifecycle for new AI models for end users. Red Hat OpenShift Data Science (RHODS) and the newly launched Red Hat OpenShift AI enable quick development and deployment of […]
[…] do this in one environment and reduce the development lifecycle for new AI models for end users. Red Hat OpenShift Data Science (RHODS) and the newly launched Red Hat OpenShift AI enable quick development and deployment of […]
[…] RedHat, IBM, and Docker joined Kubernetes, an open-source version of Borg, in 2014. The software tool has […]
[…] measures change over time. Applications come and go. Every change requires DNS adaptation. Thus, IBM maintain contact after migrations. The authoritative DNS IBM construct for you should fulfill your […]