In the CPU, the Core virtual version is called a Processor threads, which divides the physical core of a CPU into virtual multiple cores. A thread is also known as a lightweight process. which is typically a part of the Operating System. A single CPU core can have up to 2 threads per core. hyper-threading and multithreading technologies are used for breaking up physical cores into virtual cores it means threads increase performance. Intel CPUs use hyper-threading to create a thread, and AMD CPUs use simultaneous multithreading(SMT)To create a thread.
For example, AMD processors with 8 cores use simultaneous multithreadingto provide sixteen threads, and Intel processors with sixteen cores use hyper-threading to provide thirty-two threads. These methods have a huge effect on complete processor performance, as you can understand check any CPU benchmark.
How threads work in CPU
The threads are always generated by the core(operating System gives instructions to the CPU) for the execution of a task of a specific application. several times you open one application, the core creates a thread that will handle all the tasks of that specific application. If you use more applications it creates more threads for handling more applications.
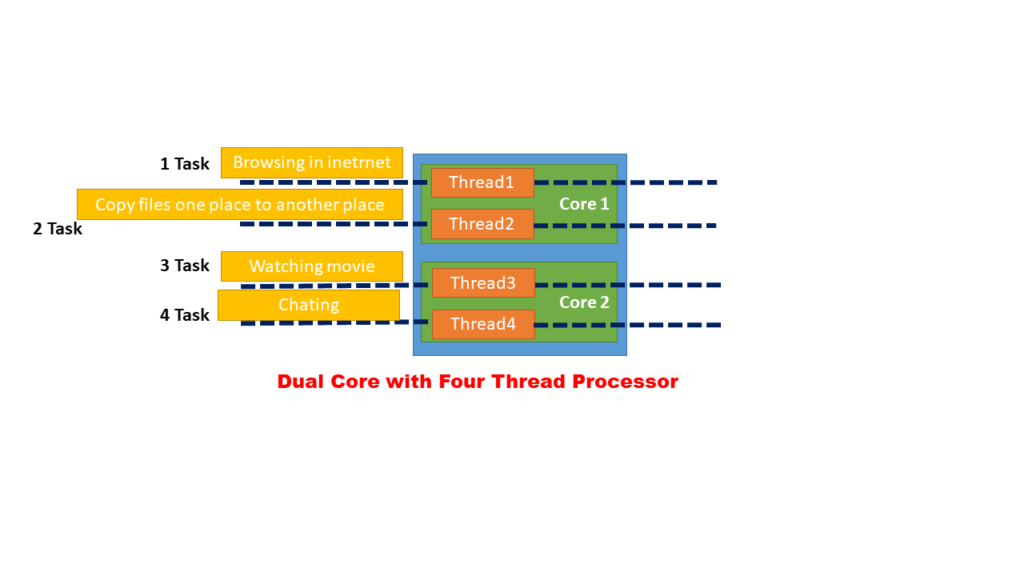
If you want to browse for some information on the internet a core creates a thread that allocates the task to it. when a core gets the task(Copy file from one place to another place) from the user, creates another thread, allocates the task to it. Similarly If you want to watch a movie it forms the third thread and allocates the task to it. If it gets another instruction chating,it forms the fourth thread and allocates the task to it. The Totally dual-core processor creates four threads for complete four tasks.
Advantages of Threads in CPU
- Approachability: If the process is broken up into several threads, each thread’s output can be returned right away when it has finished running.
- Throughput of the system: When a process is split up into numerous threads, with each thread function being treated as a separate task, the number of jobs performed in a given amount of time increases, boosting the system’s throughput.
- . If a process contains many threads, we can schedule those threads to run on different processors. As a result, processes will run more quickly. It will make the process completing faster
- Resource sharing: All threads inside a process may share resources like code, data, and files.
- Communication: The fact that numerous threads share an address space makes communication between them simpler.
- Faster context switch



[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 1900X has 8 cores and 16 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 1920X has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 1950X has 16 cores and 32 Threads […]
[…] The Athlon 240GE has 2 cores and 4 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 PRO 3900 has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 5900 has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 3900XT has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 3900X has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 3900 has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 7 5800 has 8 cores and 16 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 PRO 2600 has 6 cores and 12 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 5600 has 6 cores and 12 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 4500 has 6 cores and 12 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 3600X has 6 cores and 12 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 3400G has 4 cores and 8 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 3 PRO 5350GE has 4 cores and 8 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 3 3200GE has 4 cores and 4 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 3 3200G has 4 cores and 4 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 7600 has 6 cores and 12 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 7900 has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D has 8 cores and 16 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 7 7700 has 8 cores and 16 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D has 16 cores and 32 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 3 7330U has 4 cores and 8 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 7530U has 6 cores and 12 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 7 7730U has 8 cores and 16 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 7 7736U? has 8 cores and 16 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 7845HX has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 7945HX has 16 cores and 32 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 7645HX has 6 cores and 12 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 3 PRO 7330U has 4 cores and 8 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 9 PRO 7945 has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 7 PRO 7745 has 8 cores and 16 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 5 PRO 7645 has 6 cores and 12 Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 2990WX has 32 cores and 64 Threads […]
[…] The Athlon Silver PRO 3125GE has 2 cores and 4 Threads […]
[…] The Athlon 3000G has 2 cores and 4 Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Threads […]
[…] Max will eventually be eclipsed by the M3 Ultra, which is rumored to have a considerable increase in CPU and GPU cores above the M2 […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 3 2300X has 4 cores and 4 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen 3 3100 has 4 cores and 8 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 5975WX has 32 cores and 64 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 5965WX has 24 cores and 48 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 5995WX has 64 cores and 128 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 3975WX has 32 cores and 64 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 3955WX has 16 cores and 32 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 3970X has 32 cores and 64 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 2970WX has 24 cores and 48 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 2950X has 16 cores and 32 Threads […]
[…] The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 2920X has 12 cores and 24 Threads […]