IBM Promontory
Functioning at the nexus of risk management, technology, strategy, and legislation.
By creating and carrying out strategic initiatives, controlling operational, financial, and regulatory risks, and carrying out essential tasks, IBM Promontory assists clients in reaching their objectives.
Companies face significant risk and compliance problems in an environment of changing regulations, technology advancements, and shifting business practices. With its understanding of these overlapping themes, IBM Promontory helps its clients think more strategically and reshape their companies for the future. IBM bring exceptional value to our clients by fusing carefully selected competencies with top-notch assets. IBM can deliver this value at scale and with the help of cutting-edge technology and innovation because IBM have access to IBM platforms and experience. Promontory, a dependable partner of regulatory agencies and financial institutions, collaborates with senior management, business-line executives, boards of directors, and compliance specialists to enhance operations and boost profitability.
Third-party risk management programs are improved and strengthened by IBM team of subject matter specialists. IBM’s consultation services can assist your company in evaluating its third-party risk management guidelines and practices. In order to make sure that your organization’s risk tolerance is met, IBM may also evaluate how well your AML program addresses third-party risk management.
To ensure that third parties acting on your company’s behalf comply with AML requirements, IBM Promontory can assist you in creating an AML due diligence and continuous monitoring program. To make sure they address AML regulations, IBM Promontory can evaluate the contract templates you employ with third parties. Additionally, for outside parties involved in the administration of AML controls, IBM Promontory can provide procedures for risk mitigation, governance, and reporting.
Working with IBM, IBM Promontory is in a unique position to offer AI-powered reporting, AI-generated summaries and clustering, and automated data analysis. IBM WatsonX Discovery is capable of analyzing vast volumes of third-party data, including transaction records, organizational documents, and due diligence data. Patterns, anomalies, and linkages that human analysts would not notice can be found by the tool. Summaries and infographics are also possible using it. This feature makes it possible to identify important components of risk assessment and due diligence.
Third parties’ data, risk ratings, and other pertinent considerations can be used to summarize and group them using IBM Cloud Pak for Data. Additionally, the tool can offer suggestions for improving monitoring or offboarding in order to solve the underlying problems. Senior management, regulators, and other stakeholders can benefit from the comprehensive reports that IBM Cognos Analytics can produce on trends and patterns observed by third parties.
Authorities are clearly concentrating on how banks handle threats related to financial crime that come from third parties. To perform due diligence on third parties and to continuously monitor, evaluate, and manage the risks arising from these partnerships, financial institutions require the implementation of efficient and effective processes.
TPRM
What is Third party risk management?
A procedure used by companies to recognize, evaluate, and reduce risks related to their dealings with other parties, including suppliers, contractors, business partners, and vendors, is known as third-party risk management.
US federal and state authorities continue to place a high premium on third-party risk management; enforcement proceedings against financial institutions have been brought forth recently. Millions in civil money fines were imposed as a result for the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) infractions and for the inadequate third-party risk management procedures.
Recent events demonstrate how regulators are increasingly making financial institutions answerable for their dealings with third parties, particularly fintech companies. In order to perform sufficient due diligence on these third parties and to continuously monitor, evaluate, and manage the risks associated with these connections, regulatory agencies anticipate that institutions will be implementing risk-based practices.
Higher risk management requirements must be met by financial organizations
Third-party risk management has received more consent orders, thorough guidelines, and other resources in the previous 18 months.
The Federal Reserve Board, OCC, and FDIC released third-party risk management rules for financial institutions in June 2023. This directive sets regulatory expectations.
It attempts to handle third-party connections and best practices risks in an efficient manner.
After finding flaws in the south Atlantic regional bank’s third-party risk management program, the OCC filed a consent decree against it less than a year later.
The FDIC found that a fintech company in the northeast was using risky and unethical banking practices. Among other reasons, it issued a consent order regarding the bank’s lack of information systems and internal controls suitable for its scale. The directive also covered the kind of its third-party relationships—their extent, complexity, and risk.
The FDIC also ordered a midwestern regional bank to establish third-party risk management measures in a consent decree. Enhancing due diligence and managing third parties that meet AML and CFT rules were also advised.
Compliance with financial crimes requires effective third-party risk management (FCC)
To manage its FCC controls, institutions frequently depend on outside service providers. Traditionally, third-party services were restricted to transaction monitoring, sanctions screening, and bad news identification. These services now encompass procedures like electronic data proofing, alert investigations, risk assessments, generative artificial intelligence in enhanced due diligence case management, and customer identification verification.
Organizations may have strict, continuous internal process monitoring. It is possible for businesses to onboard the incorrect consumer, close the incorrect alert, or forget to file a suspicious behavior alert if they do not extend these standards and practices to other parties. Organizations can prevent compliance risks brought on by outside partners by performing sufficient due diligence or regular vendor risk assessments.
Financial institutions must identify, retain, and manage FCC risks imposed by third parties notwithstanding the advantages of doing business with them. In order to accomplish this, companies have to put in place a program for managing third-party risks, which makes it easier to monitor third parties’ actions and help guarantee that they are adhering to their regulatory duties.
Best practices for programs managing third-party risks
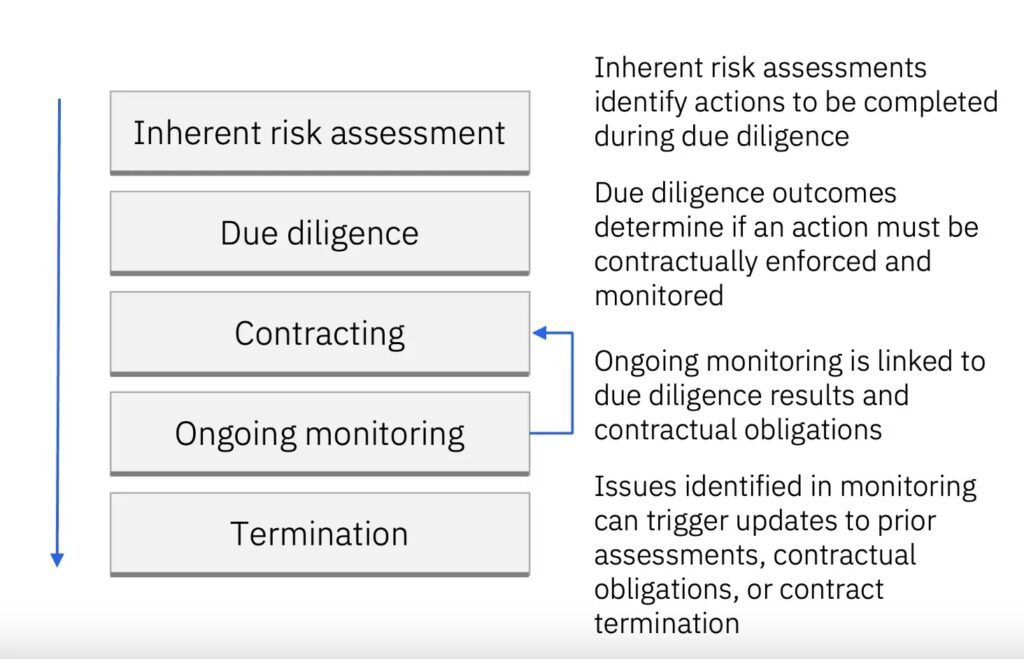
The three main risk management components of due diligence review, continuous monitoring, and risk assessments are all incorporated into the lifecycle for assisting in ensuring proper oversight and management over third parties.
Review of due diligence (before enrolling third parties):
As part of their due diligence throughout the contract process with a new third-party partnership, many financial institutions improve their standard compliance evaluation. This involves assessing how well a third party manages risk generally, including internal controls, procedures, and policies, as stated in recent interagency recommendations. Additionally, it entails confirming that they are in line with the rules and guidelines pertaining to the activity.
In order to confirm whether the party is possibly adding new or other hazards, due diligence should also involve an evaluation of the technology they use. The compliance unit of the financial institution might carry out preliminary testing to verify the caliber of the services rendered. Additionally, by doing this, the third party is made sure to operate inside the institution’s risk tolerance threshold.
Continuous observation:
The interagency guidelines set forth requirements for data security, stability, and safety in order to provide continuous observation of optimal procedures. Financial institutions are required by regulators to keep an eye on the performance of third parties during the entire partnership. This helps guarantee they meet expectations, finds any relationship adjustments that are needed, and permits the ensuing adjustments to hazards and their controls. Important risk-management tasks during the continuous monitoring stage consist of:
- To ensure the quality of ongoing third-party services, key performance indicators (KPIs) and risk indicators (KRIs) are being watched.
- Providing regular metrics reports to the relevant BSA officer or governance committee.
- Carrying out the necessary testing.
- Looking into and figuring out the underlying cause and keeping an eye on the remedial process in case KRIs or KPIs are violated.
- Keeping an eye on potential threats, third-party problems and complaints, and service level agreement compliance.
Evaluations of risks:
Enhancing current yearly AML and BSA risk assessments can help a financial institution better understand its risk profile and uncover financial crime compliance risks. They are able to recognize dangers imposed by outside parties and implement risk-reduction measures. Along with documenting important third-party data points, they can also connect linkages to regulatory obligations.
An institution can identify the best risk-based strategy by evaluating the total third-party risks; not all third parties can justify the same level of monitoring and due diligence.