Data center architects at cloud service providers and OEMs are increasing their investment in NVMe and NVMe-oF into their IT infrastructures as consumers demand quick responses from increasingly huge volumes of data.
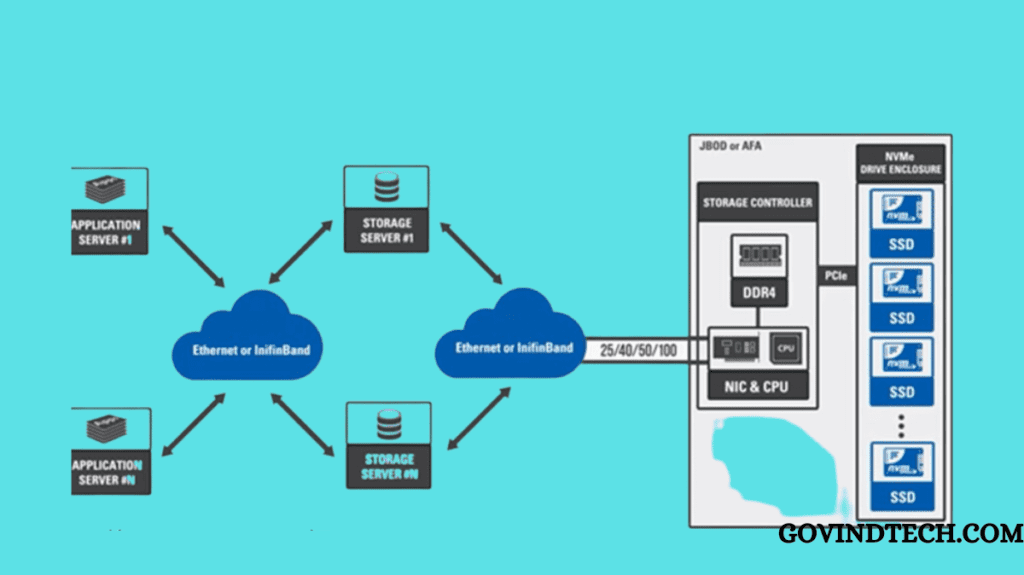
With improved versions of its OpenFlex Data24 NVMe-oF storage platform, subsequent-generation RapidFlex A2000 and C2000 NVMe-oF fabric bridge devices (FBDs), and the new Ultrastar DC SN655 PCIe Gen 4.0 dual-port NVMe SSDs, Western Digital unveiled its next step in NVMe and NVMe-oF.
According to a June 2023 report by Gartner® titled Block Storage Trends: NVMe Over Fabric, “the NVMe-oF protocol accelerates the adoption of next-generation storage architectures, such as disaggregated storage-compute to scale capacity and compute independently, use of software-defined storage, and hyperconverged and composable infrastructures.”
According to Scott Hamilton, senior director of product management at Western Digital, “we’re seeing increased adoption and movement in NVMe-oF among our customers, initially with the cloud titans’ proprietary architectures.” We are now offering CSPs and XSPs our tested, vertically integrated solutions so they can maximize usage without compromising performance.
Hamilton also thinks Ethernet will be the preferred storage fabric in the future.
“CSPs and XSPs are moving away from SAS and toward Ethernet, starting with flash,” claimed Hamilton. Ethernet was the fabric of choice when we first created our disaggregated architecture because it is the most widely used in the world. Additionally, it will be the most economical.
NVMe/NVMe-oF: Why?
High-speed storage media were not intended for legacy protocols like SAS. Due to its speed and proximity to the CPU, PCI Express (PCIe), on which NVMe is based, became the next logical storage interface. By distributing flash resources among servers, NVMe-oF extends the advantages of NVMe in terms of performance, availability, and flexibility.
Wasabi, a pure-play provider of cloud storage, is one of the businesses using NVMe and NVMe-oF because of their speed. Fast access to customer data is provided through Wasabi’s Hot Cloud Storage.
“NVMe offers a standardized protocol for accessing storage and provides a reliable, high-performance transport,” said Pramod Kalyanasundaram, SVP, engineering and operations at Wasabi. “NVMe and NVMe-oF are a key component of our service delivery and fit into our infrastructure at the storage layer in environments that demand higher throughputs and IOPs.”
For its cloud-native solutions, object storage company Cloudian is going toward disaggregation.
According to Glenn Haley, senior director of product management at Cloudian, “as our customers’ workloads become more performance-intensive, they require increasingly faster media to support them.” AI, data lakes, and data warehouses are some of the workloads that are causing object storage to move from backup and recovery to primary storage. This move to accommodate mainstream workloads needing analytics is made possible by NVMe and NVMe-oF.
On-demand resources
No matter how much of either is needed, storage and computation both reside in the same server in a typical SAS-based hyper converged infrastructure (HCI). Storage may consequently become locked in that server. Resources can be pooled together, utilised as needed, and then released for use by another application thanks to NVMe-oF’s disaggregation of resources.
The OpenFlex technology from Western Digital is used by the ICM Brain and Spine Institute to dynamically expand and allocate storage volumes to support the institute’s efforts to combat neurological diseases.
The IT staff at ICM is adaptable enough to expand and reallocate storage volumes as needed and to swiftly and simply allocate storage to satisfy any researcher’s needs. ICM is able to future-proof its IT architecture and investment because to its ability to smoothly add new resources as technology develops.
keeps from over-provisioning
The avoidance of overprovisioning resources is another advantage of shared storage. If extra capacity is needed, storage and computing are added in equal amounts in a hyperconverged architecture, regardless of whether more of either is needed. Because they don’t want to run out of capacity when they need it, organizations frequently overprovision.
For its content delivery network, Telefónica, which has more than 345 million consumers in Europe and Latin America, switched to a disaggregated architecture. Depending on whether multiple subscribers are accessing the same event concurrently or if subscribers are selecting from a huge archive of various content, livestreaming and video-on-demand (VOD) have different storage needs. Combining computing and storage on one server reduces efficiency and raises costs. The servers at Telefónica can share a pool of storage capacity among themselves by using NVMe-oF, which lowers costs while retaining good performance.
Utilization optimization
Because storage and servers don’t always run at the same time, keeping them separate prevents underutilization of resources. Customers can use flash on demand rather than loading the server with five to seven years’ worth of flash storage at initial deployment and expecting the flash would be used up over the course of a server’s lifetime by disconnecting the SSD refresh from the server refresh and sharing outside via Ethernet.
“If you’re not adequately utilizing resources or when a server needs to be retired and (both storage and compute are trapped in that server), you end up with wasted resources,” added Hamilton. “TCO adds up when maximizing usage with a shared pool of resources available on demand.”
Data Restoration
Disaggregation, in addition to being flexible, offers quicker recovery time goals (RTO) because data is kept on shared drives rather than servers, claims Barrett Edwards, CTO of Western Digital Platforms.
“With a disaggregated infrastructure, you take the drives out of those servers and put them in a remote storage enclosure or a shared storage enclosure,” Edwards explained. The servers have no state. Data does not live on a server, therefore if it crashes, nothing is lost.
A top data protection provider offers cloud and on-premises backup, recovery, and archiving services. To enable rapid data recovery, they are implementing flash-based NVMe-oF using Western Digital’s OpenFlex Data24 NVMe-oF storage technology.
Assisting the ecosystem
Flash and NVMe are being used in data centers for workloads that demand better performance and lower latency. By maximizing resources and utilization, NVMe-oF reduces TCO.
Western Digital makes it simple to share flash storage among workloads and is a dependable partner for businesses using NVMe-oF. As CSPs and OEMs choose these speedier protocols for their cutting-edge infrastructures, the company’s improved solutions expand the NVMe and NVMe-oF ecosystem by offering more flexibility and options.

[…] November 2022 and March 2023, the tests were carried out in Intel and Dell performance labs with NVMe drives made by Solidigm. The ultimate objective was to determine how much faster vSAN 8.0 ESA performed […]