Advanced AI Security Measures
An AI PC, as cleverly described by Robert Hallock, is a brand-new computer equipped with parts made especially to run powerful AI-accelerated software.
Business is changing because of these incredible PCs. Nowadays, anybody using an AI PC for creation may do more tasks in less time. Are you altering a picture or writing a report? AI has caused a huge reduction in the time it takes people to create content, revolutionizing company efficiency.
Yet, AI PCs have benefits beyond significant boosts in productivity. These PCs’ AI capabilities, which are based on Intel Core Ultra CPUs, may also be used to improve security. To just a few advancements, AI security can automatically detect malware, interpret coding abnormalities, classify threats, run attack simulations, and compile vulnerability reports more quickly than a person can.
The use of AI security is crucial as malevolent actors are using novel strategies to get beyond established barriers: Currently, malicious malware is injected straight into computer memory, where it is difficult to differentiate it from legitimate system operations, accounting for 75% of fileless assaults. Artificial Intelligence has the capacity to swiftly identify and correlate previously unseen assaults and aberrant activity in systems. This blog article explains how organizations using AI security may be better protected by AI PCs. They will discuss how technologies like Intel Core Ultra CPUs’ neural processing units (NPUs) and Intel Threat Detection Technology (Intel TDT) improve security at the silicon level in this blog.
An overview of AI’s role in security advances
Researchers at Intel began investigating the possibility of fingerprinting malware six years ago. They did this by using machine learning (ML) techniques on telemetry data obtained from malware that was operating on the CPU microarchitecture. At the 2020 RSA conference, Intel presented an early proof of concept (POC) for this technology.
2018 saw the release of Intel TDT, a product of this technology. Intel TDT uses silicon-level telemetry and AI to detect targeted threats like ransomware and cryptojacking. Beyond deliberate assaults, research from 2022 by Intel and Microsoft shown the value of using CPU telemetry to model the appropriate behavior of system application processes and utilize this information as a starting point to detect attacks on the software supply chain. In the present day, Intel has enhanced defenses on over one billion PCs by scaling its AI security technologies with its security ecosystem!
Today, Intel TDT provides AI at scale
At its core, Intel TDT is a software development kit (SDK). Security ISVs may include AI-driven threat detection into endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems that operate on PCs with Intel Core processors starting with the 9th generation by using the SDK.
The use of dense performance monitoring unit (PMU) telemetry by Intel TDT to monitor specific application processes operating on the CPU microarchitecture is shown in Figure. Malware leaves a fingerprint on the CPU’s PMU while it runs in the operating system (OS) and on higher software layers. This fingerprint may be modeled in artificial intelligence (AI) to detect certain attack indications. The machine learning (ML) component of Intel TDT’s AI is made up of random forest classifier-based ML, which can be offloaded on the Intel integrated GPU. In order to preserve the user’s computing experience, AI security operates in the background.
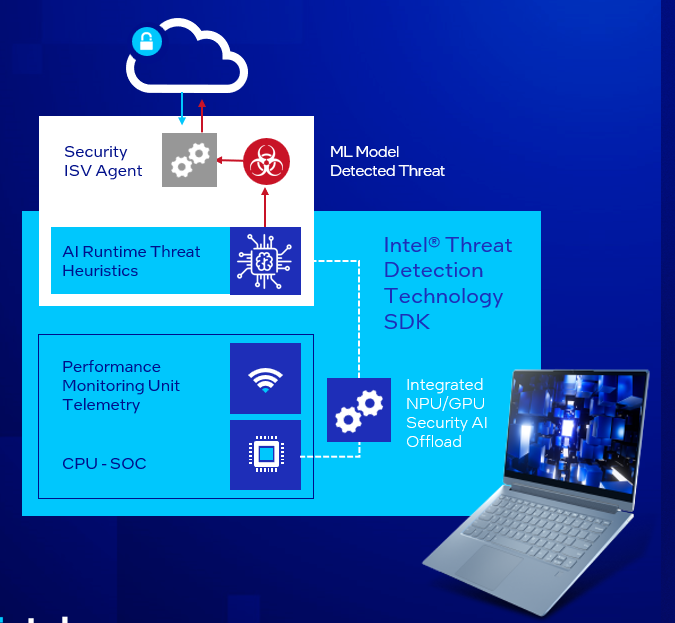
Many of the threats that Intel TDT can identify may go undetected by conventional file-based threat detection approaches because malware uses obfuscation and cloaking tactics. Nevertheless, ISVs may identify malware early when they include Intel TDT into their antivirus and EDR products.
IT fleet managers may strengthen defenses by combining AI PCs with EDR software from Microsoft, Acronix, Bytesatwork, CrowdStrike, Check Point, Trend Micro, Sequretek, Fidelis, Kingsoft, and ESET. This allows the PC hardware to assist in detections.
According to recent testing conducted by SE Labs, Intel TDT recognized 93% of the most common ransomware assaults. Because of the importance of these findings, security industry experts now score ISVs’ security solutions based on Intel TDT enablement.
Novel endpoint detection driven by AI
Another pillar of AI-powered threat detection on AI PCs is the NPU included in the latest Intel Core Ultra CPUs. Deep learning (DL) models may be executed on the CPU via the Intel NPU, a specialized low-power artificial intelligence engine. A subtype of machine learning called deep learning (DL) makes predictions by training artificial neural networks on data. These neural networks may perform very well at tasks including pattern recognition, image processing, natural language processing, and more because they are made up of layers of linked nodes which replicate the framework of the human mind.
EDR ISVs may transfer AI-based threat detection from the cloud to the AI PC endpoint by using the Intel NPU. There are multiple implications to this, like:
Reduced latency and real-time threat detection
Local data processing eliminates the requirement for round-trip communication to the cloud when DL models are used on the endpoint. Making choices in real time may help identify threats in real time, since it eliminates the need to wait for cloud-based processing.
Local data processing protects network bandwidth
Large data transfers to the cloud may put a pressure on network capacity. Data transmission is reduced when data is processed locally and only relevant insights or anomalies are transferred to the cloud. This improves threat detection by increasing the amount of data that can be handled at the endpoint.
Enhanced privacy
When working with personally identifiable information (PII) or sensitive corporate data, endpoint-based DL gives enterprises more control over their data. Check out the Bufferzone PR for information on new privacy-preserving anti-phishing technologies.
Novel security strategies
By enabling DL on the edge, new avenues for threat detection are made possible. Faster remediation may be achieved by solution providers via their innovative and dynamic local malware discovery capabilities. Check out the video and article from CrowdStrike on the possible AI on the endpoint.
The ideal selection when buying a new fleet
Businesses may increase productivity exponentially with the use of AI PCs. They are capable of more, however. They provide strong artificial intelligence (AI) improvement, providing security capabilities to support enterprises in advancing against dynamic ransomware attacks. AI PCs raise the bar for hardware-based security with their Intel TDT and Intel Core Ultra CPUs with the Intel NPU. AI PCs are the best option for new fleet purchases when security and productivity are top concerns.
