FACTS Grounding: Google DeepMind’s New Standard for Evaluating LLMs
A novel standard for assessing the veracity of Large language models is FACTS Grounding.
Google DeepMind’s thorough standard and online leaderboard provide a much-needed indicator of how well LLMs avoid hallucinations and base their answers on the given source material.
Although large language models (LLMs) are revolutionizing the way humans obtain information, they still struggle with factual accuracy. They have the ability to “hallucinate” incorrect information, especially when presented with complicated stimuli. Consequently, this may reduce the credibility of LLMs and restrict their practical uses.
Today, Google DeepMind is launching FACTS Grounding, a thorough benchmark for assessing LLMs’ capacity to produce responses that are both factually correct concerning the inputs provided and sufficiently detailed to satisfy user inquiries.
Google DeepMind anticipates that its benchmark will encourage advancements in factuality and grounding across the sector. It also introduces the FACTS leaderboard on Kaggle to monitor progress. Leading LLMs have already undergone testing using FACTS Grounding, and their grounding scores have been included in the original ranking. The leaderboard will be updated and maintained as the field progresses.
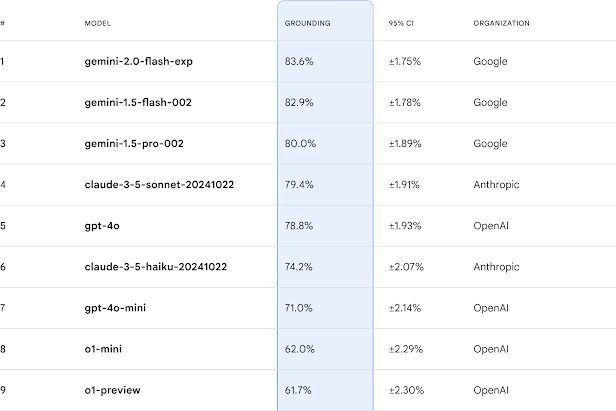
Image credit to Google DeepMind
Current leaderboard ranking
The FACTS Grounding dataset
The 1,719 instances in the FACTS Grounding dataset are specifically designed to demand long-form replies based on the given context document in order to reliably assess the factuality and grounding of each given LLM. A document, a system directive mandating that the LLM only use the supplied document, and a user request are all included in each example.
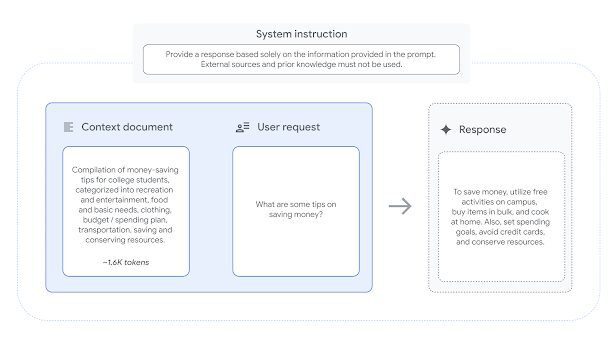
Image credit to Google DeepMind
An example from the FACTS Grounding dataset
Each example is separated into a “private” (859) and “public” (860) held out set. Today, Google DeepMind is making the public set available for anyone to utilize in order to assess an LLM. Naturally, it is aware of the importance of safeguarding against benchmark contamination and leaderboard hacking, thus in accordance with industry standards, Google DeepMind maintains the private evaluation set. The average performance across both public and private sets is represented by the FACTS leaderboard scores.
A range of document lengths, up to a maximum of 32,000 tokens (about 20,000 words), encompassing industries including finance, technology, retail, medicine, and law, are included in the FACTS Grounding examples to guarantee a diversity of inputs. The user requests are equally diverse and include tasks like rewriting, Q&A generating, and summarization. Google DeepMind left out any cases that may call for complex reasoning, creativity, or mathematics skills that could necessitate the model using more sophisticated reasoning in addition to grounding.
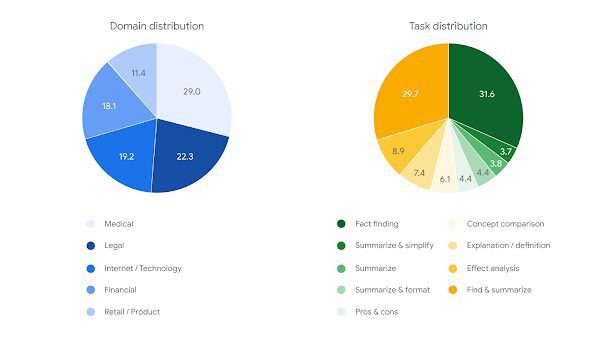
Image credit to Google DeepMind
Prompt distribution
Collective assessment by top LLMs
An LLM must successfully synthesize the complicated information in the document and produce a lengthy response that is entirely attributable to the document and provides a thorough response to the user’s request.
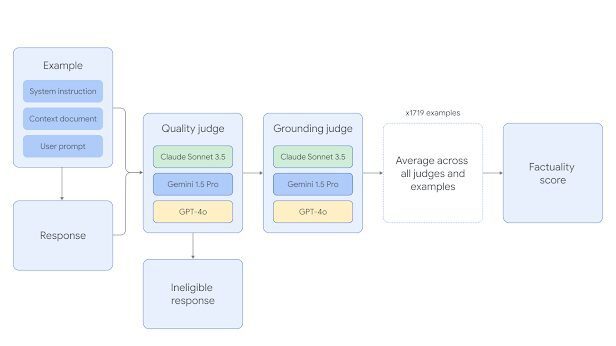
Factual Information Gemini 1.5 Pro, GPT-4o, and Claude 3.5 Sonnet are the three frontier LLM judges that Grounding uses to automatically assess model replies. To reduce the possibility of a judge favoring responses from members of its own model family, Google DeepMind chose a mix of judges as its panel. To determine which judgment prompt templates performed the best and to confirm agreement with human raters, the automatic judge models were thoroughly tested against a held-out test set.
Every FACT Two stages are used to evaluate the grounding example. Responses are first assessed for eligibility; if they fall short of meeting the user’s request, they are rejected. Second, answers are deemed factually true if they are entirely based on data from the given document and free of hallucinations.
FACTS Grounding
To ascertain whether the LLM has handled the example correctly, the eligibility and grounding accuracy of a particular LLM response are assessed independently by many AI judge models. The findings are then combined. The average of all judge models’ scores across all examples is the final score for the entire grounding job.
The evolution of FACTS Grounding will continue
Since advancement can swiftly surpass benchmarks, the introduction of Google DeepMind’s FACTS Grounding benchmark and leaderboard is only the first step. The success and utility of LLMs and larger AI systems will be shaped in part by factuality and grounding in the future.


