AMD made several announcements at its Data Center and AI Technology Premiere event in San Francisco. The company provided more information about its 5nm EPYC Bergamo processors, designed for cloud-native applications, and stated that the chips are now shipping to customers.
AMD also unveiled its Instinct MI300 processors, featuring 3D-stacked CPU and GPU cores on the same package with HBM (High Bandwidth Memory). Additionally, they introduced a GPU-only model, the MI300X, which brings eight accelerators onto one platform with a remarkable 1.5TB of HBM3 memory. The EPYC Genoa-X processors, equipped with up to 1.1GB of L3 cache, were also announced. All three products are currently available. Furthermore, AMD revealed its EPYC Sienna processors for telco and edge applications, which are expected to launch in the second half of 2023.
AMD EPYC Bergamo:

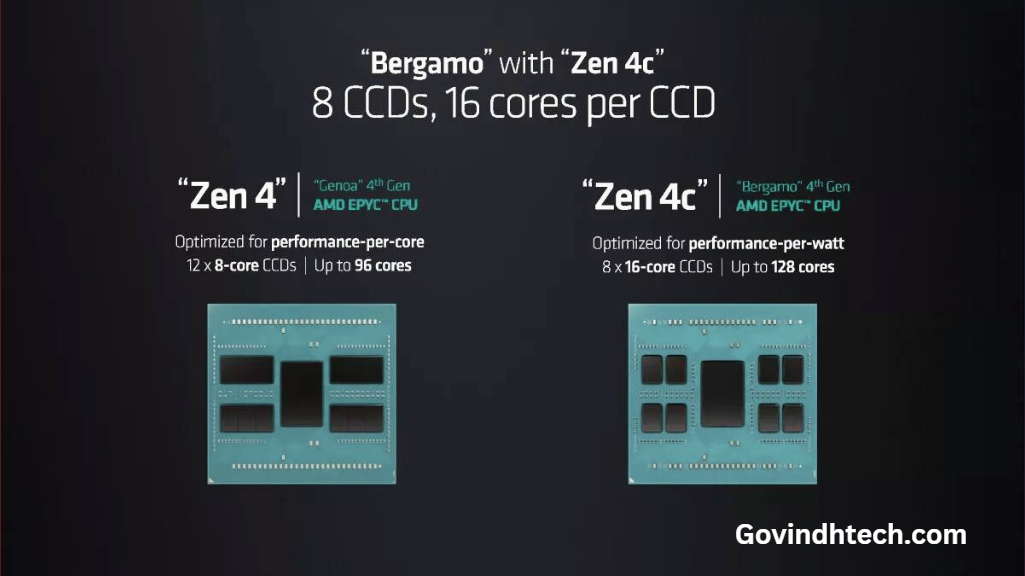
The EPYC Bergamo processors from AMD are the industry’s first x86 cloud-native CPUs, boasting 128 cores and an optimized Zen 4c core architecture that reduces the required area for each core. These processors will compete with Intel’s 144-core Sierra Forest chips and Ampere’s 192-core AmpereOne processors. They are specifically designed for power-efficient and highly-parallel workloads such as high-density virtual machine deployments, data analytics, and front-end web services. Despite having higher core counts than traditional data center solutions, the chips operate at lower frequencies and power envelopes.
The EPYC Bergamo processors are compatible with server platforms that use the same SP5 socket as the standard 96-core EPYC Genoa processors. They support 12-channel memory running at DDR5-4800. AMD combines chiplets with Zen 4c cores and the ‘Floyd’ central I/O die to produce the Bergamo chips, connecting compute chiplets to a memory and I/O chiplet based on an older process node.

Currently, AMD has announced two Bergamo processors: the EPYC 9754 with 128 cores and 256 threads, and the EPYC 9734 with 112 cores and 224 threads (with two cores per CCD disabled). Both processors feature 256MB of L3 cache and boast a 2.7 times increase in energy efficiency according to AMD.
The Bergamo architecture utilizes eight 16-core CCDs (Core Complex Dies) to achieve the maximum core count of 128 cores. Notably, AMD employs eight Zen 4C chiplets along with the central IO chiplet for the current configuration, whereas standard EPYC chips can utilize up to twelve Zen 4 chiplets. While it’s possible that AMD may introduce a future Zen 4C solution with twelve chiplets and 192 cores, no such design has been announced yet.