CodeRabbit GitHub
By securely and effectively running untrusted code, CodeRabbit, a quickly expanding AI code review tool, is using Google Cloud Run to reduce code review time and errors by half.
By comparing changes to the whole codebase and producing scripts for more in-depth analysis, CodeRabbit enhances code quality and automates code reviews. Pull requests are automatically responded to through integration with code hosting sites.
CodeRabbit required an execution environment that was scalable, affordable, and secure enough to examine and run their clients’ code in order to safely execute untrusted code.
In this article, we’ll explain how CodeRabbit used Google Cloud Run to create an AI code review agent that can expand dynamically and effectively and securely manage large quantities.
CodeRabbit offers automated code reviews that are triggered by pull requests and connects directly with platforms such as GitHub and GitLab. Its interaction with the basic models evaluates the effects of the modifications on the whole codebase, not simply the modified files. This calls for an advanced system that can:
- The user’s repository should be cloned.
- Install the required dependencies in a build environment (think npm install, go mod download, etc.).
- Static analysis using security scanners and 20+ linters.
- Run programs created by Artificial Intelligence. Things start to become extremely intriguing at this point. To browse the code, look for certain patterns (using tools like cat, grep, and even ast-grep), and extract pertinent information, CodeRabbit’s AI agent writes shell scripts. For analysis, it can even produce Python code.
- Engage with outside services. In order to interface with services like Slack, Jira, and Linear, for instance, CodeRabbit can also generate and run curl instructions.
Above all, any solution must be safe, affordable, and scalable. By definition, the code being examined and run is not reliable. It could have bugs, be unfinished, or even be harmful.
The solution: Cloud Run
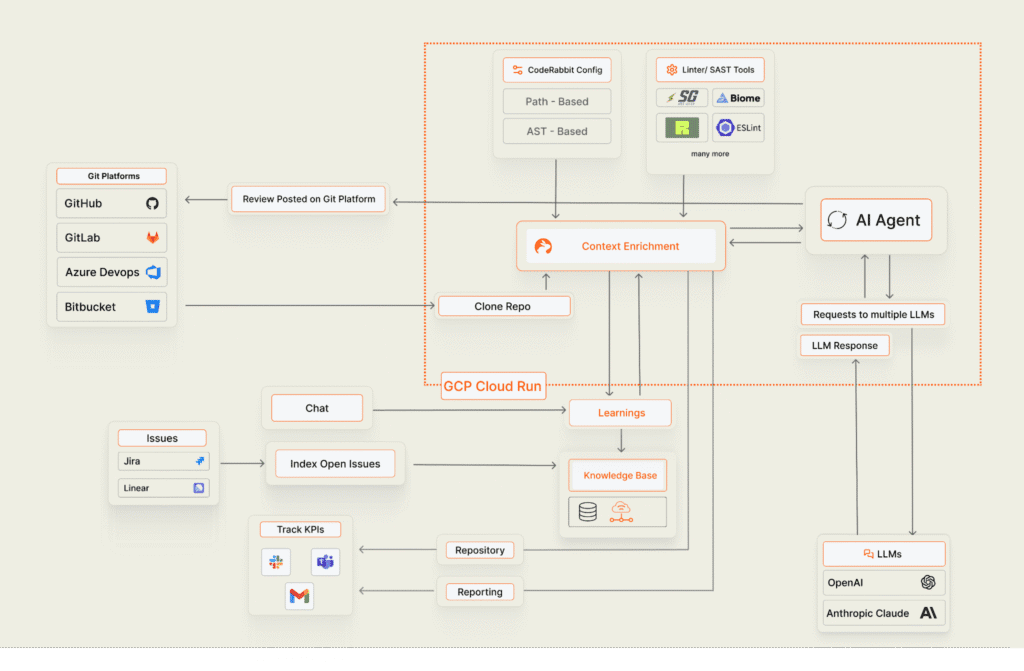
The design of CodeRabbit deftly blends a number of technologies to produce a stable and segregated execution environment:
Cloud Run services: Cloud Run services serve as the foundation for CodeRabbit. First, a lightweight Cloud Run service handles incoming webhook events (from GitHub, GitLab, etc.) and verifies subscriptions and billing. After then, a task is pushed to Google Cloud Tasks using this service.
Google Cloud tasks: By serving as a queue, this separates the handling of webhooks from the actual execution of code. CodeRabbit can now manage spikes in pull requests without overloading the system.
Cloud Run execution service: This is the system’s core component. Tasks are pulled from the Cloud Tasks queue by a different Cloud Run service. Every job is a request for a code review. This service may scale according to CPU utilisation because it is set up with a 3600 second request timeout and 8 requests per instance. Because code reviews are drawn-out processes that frequently take 10 to 20 minutes to finish, this configuration is essential. The whole repository, build artefacts, and temporary files are kept in an in-memory volume mount used by the Execution Service.
Sandboxing: By using a dedicated service identity, it is possible to set all Cloud Run instances to have minimum IAM rights. All instances are sandboxed with two levels of sandboxing. CodeRabbit uses Cloud Run’s second-generation execution environment, a Linux cgroup-capable microVM. CodeRabbit employs cgroups to further limit the rights of the jailed process and Jailkit to establish isolated processes within each Cloud Run instance.
For CodeRabbit, sandboxing is particularly important in situations when running untrusted code is necessary, like:
- Static analysers that accept unique, unreliable plugins (like Rubocop and ESLint).
- Verification scripts produced by LLM for a more thorough examination of the complete codebase.
- CLI activities generated by LLM, including creating Jira or GitHub problems.
- Advanced analysis based on Python.
Cloud Run lets CodeRabbit scale dynamically. Over 200 Cloud Run machines send up to 10 queries per second to CodeRabbit’s Agentic PR Reviewer service during peak hours. Each instance of Cloud Run is really large and uses 32GiB of RAM and 8vCPUs. When using Cloud Run to run their PR reviewer service, CodeRabbit observes high CPU utilisation, substantial network traffic (downloading repositories and dependencies), and high memory consumption.
Try this on your own
An excellent illustration of how to create a safe, scalable, and reasonably priced platform for doing AI-powered code analysis is CodeRabbit’s usage of Google Cloud Run. Their experience demonstrates the developing potential of serverless technologies, and their architecture offers a model for developers addressing related issues. As Cloud Run keeps adding new features.


