A quantum register is a collection of qubits, analogous to a classical register but operating under quantum mechanics. A register with n qubits can represent 2n basis states simultaneously due to the principle of superposition. These states are described in a 2ndimensional Hilbert space and can have quantum properties like entanglement, which makes it possible to do very complicated quantum computations.
Quantum gates manipulate the qubits within a register to execute quantum computations. Quantum gates are unitary matrices that operate on qubits, analogous to the logical gates in classical computers.
- A sequence of quantum gates applied to a quantum register constitutes a quantum circuit.
- In their most basic form, quantum circuits are made up of a multi-qubit system that is set to a classical value, a set of quantum gates that work on the system, and measurements of certain qubits.
Measurement plays a critical role in extracting information from a quantum register. Measuring qubit forces it to collapse from its superposition into a single classical state, either 0 or 1.
Unitary evolution governs the behavior of quantum registers. Unitary transformations ensure that the evolution of a closed quantum system is reversible and deterministic. This property guarantees that the total probability of the system remains constant throughout the computation.
How Quantum Registers Work in Quantum Computing: Step-by-Step
A quantum register enables the storage and handling of quantum information. Here is a step-by-step explanation of how quantum registers function:
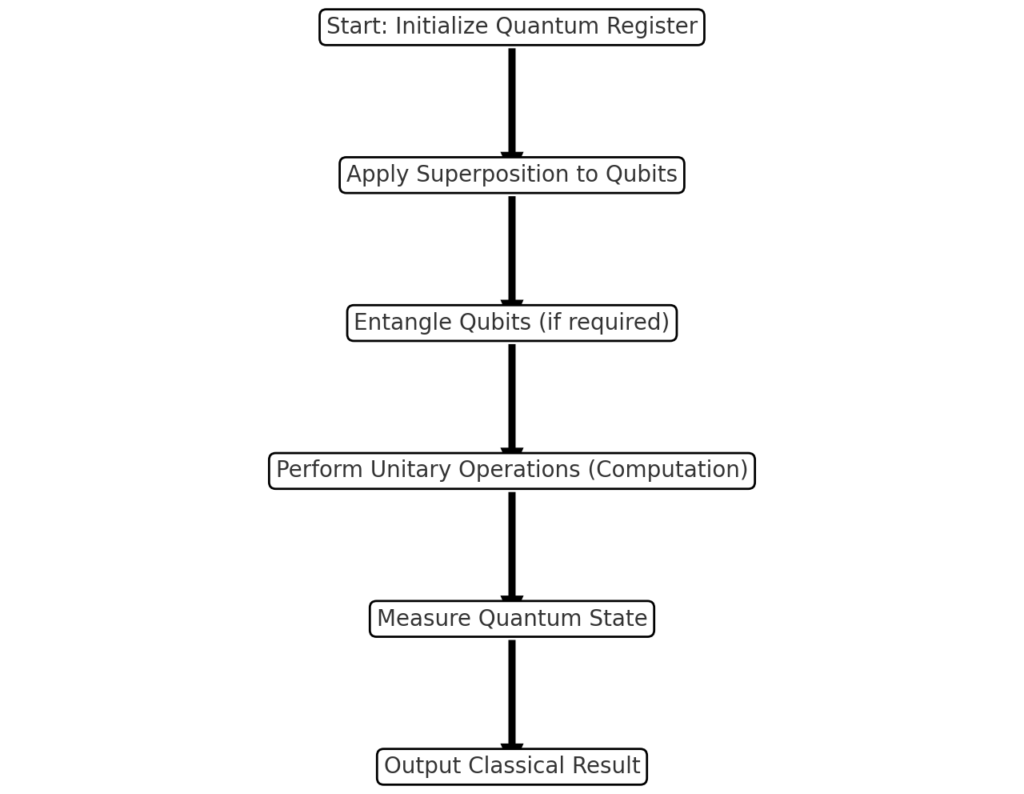
1. Initialization
- What Happens?
- Quantum registers start with all their qubits initialized in a standard state, typically ∣0⟩ (zero state).
- For an n-qubit register, the initial state is represented as ∣00…0⟩ in the computational basis.
- Mathematical Representation:
- For a 3-qubit register, the state is ∣000⟩|.
2. Superposition
- What Happens?
- Quantum gates (e.g., the Hadamard gate) are applied to individual qubits, placing them in a superposition of ∣0⟩ and ∣1⟩.
- This allows the quantum register to represent multiple states simultaneously.
- Mathematical Representation:
- For a single qubit, after applying a Hadamard gate: 1/√2 (∣0⟩+∣1⟩)
- For an nn-qubit register, superposition allows the representation of
1/√2∑i=12n ∣i⟩3. Entanglement
- What Happens?
- Quantum gates, such as CNOT or controlled gates, create entanglement between qubits.
- Entanglement ensures that the state of one qubit is dependent on the state of another, enabling quantum correlations.
- Example:
- Two qubits in an entangled state: 1/√2 (∣00⟩+∣11⟩)
- Measuring one qubit immediately determines the state of the other.
4. Unitary Operations (Computation)
- What Happens?
- Quantum gates (e.g., Pauli-X, Y, Z, and multi-qubit gates) are applied to the register to perform computations.
- These gates evolve the quantum state while preserving the probabilities (unitarity).
- Purpose:
- Perform operations like addition, multiplication, or solve specific problems using quantum algorithms such as Grover’s or Shor’s algorithms.
5. Measurement
- What Happens?
- When a measurement is made, the superposition collapses to one of the basis states.
- The result is probabilistic, governed by the amplitudes of each state’s wavefunction.
- Example:
- A register with equal superposition over ∣00⟩and ∣11⟩ collapses to ∣00⟩ or ∣11⟩ with a 50% probability each.
6. Error Correction (if needed)
- What Happens?
- Quantum error correction codes (e.g., Shor or Steane codes) detect and correct errors without measuring the quantum state directly.
- This ensures the integrity of the quantum state throughout computations.
7. Output (Classical Result)
- What Happens?
- After measurement, the quantum register outputs a classical result corresponding to the collapsed state.
- The result is then used for further classical or quantum computations.
This sequence enables quantum computers to leverage phenomena like superposition and entanglement to solve problems exponentially faster than classical systems in certain scenarios.
Uses for Quantum Registers in Quantum Computing
1. Data Representation in Quantum Algorithms
2. Superposition for Parallel Computation
3. Entanglement for Quantum Communication
4. Implementation of Quantum Gates
5. Simulation of Quantum Systems
6. Error Correction and Fault-Tolerant Computation
7. Quantum Machine Learning
8. Cryptographic Applications
9. Quantum Optimization
10. Physical Implementation of Quantum Computers

