Contents [hide]
Machine learning, especially data mining and association rule learning, relies on the Apriori algorithm. It finds patterns, correlations, and associations in massive databases. This method is best known for market basket analysis, which identifies commonly purchased products. It was introduced by Rakesh Agrawal and Ramakrishnan Srikant in 1994, and since then, it has become an essential tool in understanding customer behavior, generating recommendations, and supporting decision-making processes across various industries.
The Apriori algorithm’s purpose, operation, and machine learning applications are explained in this article. We will also examine its pros and cons and how it has influenced data mining techniques.
What is the Apriori Algorithm?
The classic Apriori Algorithm is used for frequent itemset mining and association rule learning in data mining. It seeks interesting linkages or correlations in transactional databases, where each transaction contains a set of items. Apriori’s main objective is to locate frequent itemsets in the database, which are groups of items that come together in a transaction more often than a minimal support.
After discovering common itemsets, the Apriori algorithm can build association rules that describe how one thing may affect another. In retail, an association rule may illustrate that customers who buy bread also buy butter.
How Does the Apriori Algorithm Work?
The Apriori algorithm generates itemsets “bottom-up”. It finds larger itemsets by merging frequent smaller itemsets after identifying commonly purchased items. The algorithm employs breadth-first search to examine larger itemsets and prune those that don’t fulfill the support criterion.
The primary Apriori algorithm steps are:
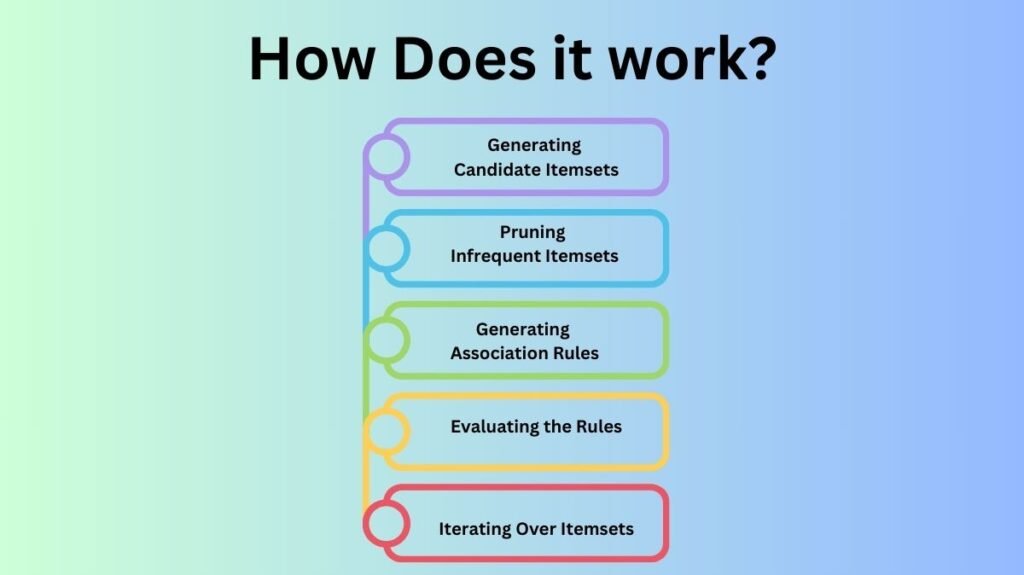
Generating Candidate Itemsets
In the beginning, the algorithm counts the frequency of each database entry. These items are candidate 1-itemsets. After this, the algorithm removes items with frequency below the user-defined minimum support threshold. The remaining items are common 1-itemsets.
Next, the system creates candidate 2-itemsets, pairings of items that may appear in transactions. For 3-, 4-, and higher-order itemsets, this process is repeated. Only candidate itemsets that fulfill the minimum support criterion are processed each time.
Pruning Infrequent Itemsets
At each level, the algorithm analyzes candidate itemsets for minimum support. Itemsets with support below the threshold are eliminated. This pruning phase reduces search space by removing infrequent itemsets.
Generating Association Rules
After finding frequent itemsets, the Apriori algorithm develops association rules for item connections. These rules divide common itemsets into two subsets, one for the antecedent (the “if”) and the other for the consequent (the “then”). The algorithm then determines the rule’s confidence, which quantifies how likely the consequent item is given the antecedent.
Evaluating the Rules
The association rules are then assessed for support and confidence. Support is the percentage of transactions with antecedent and consequent. Confidence is the percentage of antecedent-consequent transactions. These measurements eliminate weak rules to identify the most intriguing associations.
Iterating Over Itemsets
The method generates candidate itemsets, prunes, and generates rules until no more frequent itemsets are identified. Once the final collection of frequent itemsets is selected, the Apriori algorithm stops and the user sees the most relevant association rules.
Applications of the Apriori Algorithm
Market basket analysis is the most popular usage of the Apriori algorithm. Some of its main uses:
- Market Basket Analysis:
Retailers acquire massive volumes of transaction data that can reveal client buying trends. The Apriori algorithm finds frequently purchased combinations. Customers who buy a certain bread may also buy butter or jam. Store promotions, product bundling, and sales methods benefit from this data. - Recommendation Systems:
E-commerce companies, streaming services, and social media sites employ recommendation systems to propose products, movies, and content based on user preferences. By employing the Apriori algorithm, systems can reveal which things are frequently purchased together, leading to more tailored and relevant recommendations. - Fraud detection:
In the banking business, the Apriori algorithm can detect anomalous transaction patterns that may imply fraud. Banks and financial organizations can indicate fraudulent transactions by examining transaction frequency. - Bioinformatics:
In bioinformatics, the Apriori method finds recurrent patterns in genomic sequences and protein interactions. Researchers can use these patterns to study biological processes and find novel therapeutic targets. - Customer Behavior Analysis:
The Apriori algorithm helps companies understand client behavior. Businesses can target specific consumer categories and improve customer satisfaction by discovering typical client buy itemsets.
Advantages of the Apriori Algorithm
The Apriori algorithm has several advantages that make it a popular choice for association rule learning:
- Simple and Easy to Implement: The algorithm is basic and quick to implement, making it ideal for data mining beginners.
- Scalable: It handles large datasets well if they are not too large.
- Efficiency : The bottom-up technique gradually expands the search field and considers only frequent itemsets, enhancing algorithm efficiency.
- Useful for Rule Generation: The Apriori algorithm may build association rules that reveal item linkages, letting organizations base decisions on data.
Limitations of the Apriori Algorithm
Although beneficial, the Apriori method has numerous drawbacks:
- Computationally Expensive: When working with huge datasets, the Apriori approach might be computationally expensive. Each loop generates and checks numerous candidate itemsets, which might use a lot of memory and processing.
- Difficulty with Large Itemsets: The number of potential itemsets expands exponentially as itemsets grow, causing inefficiencies and excessive processing times. This is the “curse of dimensionality.”
- Limited to Binary Data: The Apriori method assumes data is binary, meaning transactions have either present or absent components. It is less effective for continuous or categorical datasets.
- Threshold Sensitivity: Support and confidence thresholds greatly affect the Apriori algorithm’s performance. If the thresholds are too high, the algorithm may overlook essential patterns, while too low may create too many useless rules.
Conclusion
The Apriori Algorithm is important in data mining, machine learning, and predictive analytics because it reveals hidden patterns and relationships in large datasets. The Apriori method is used in market basket analysis, recommendation systems, fraud detection, and bioinformatics to identify common item groupings and create association rules.
Despite its popularity and usefulness, the Apriori technique suffers from computing efficiency and scalability concerns when dealing with huge datasets. Because of such concerns, more complicated methods have been made to make things work better, like FP-growth.
The Apriori algorithm is an important part of data mining because it helps businesses and researchers make choices based on data.

