This article covers the following topics: the mechanics of the Internet of Things infrastructure, the Importance of sensors in IoT, present and upcoming challenges, and the cost of IoT sensors.
Mechanism of the IoT Infrastructure
Often called the IoT ecosystem’s eyes and ears, the sensor functions best when coupled with other crucial elements. This is a brief summary of the entire infrastructure:
Read more on Components Of IoT Ecosystem : Devices, Gateways And Cloud
- The main component of the infrastructure is the sensor. It might target tangible objects like pressure transducers and smoke alarms, or it might have several uses, like RFIDs and QR codes.
- The data gathered by the sensor is processed and managed by microcontrollers, which frequently carry out operations including filtering and calibration.
- The data is sent to devices (such as tablets, laptops, or desktop PCs) or the cloud by the communication module. Satellite, WiFi, and Bluetooth are a few examples of them.
- The user interface of the majority of IoT devices transforms the data for consumption. It might be a notification when certain limitations are reached or a live monitoring display.
Read more on Examples Of IoT Devices In Business & IoT Devices Security
- People who work in sectors that depend on these IoT sensors and related systems should understand how they operate since it facilitates effective troubleshooting, solution customization, and data accuracy.
Importance of sensors in IoT
Sensors used in IoT
Given their many benefits, smart gadgets are unlikely to decline in use.
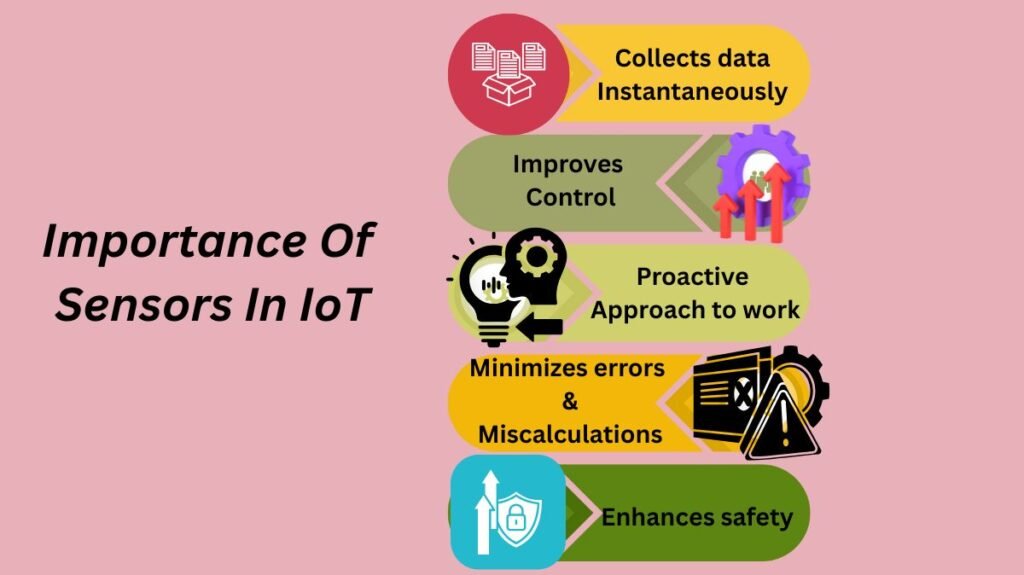
Collects data instantaneously
The sensor collects real-time data to improve operational decisions. CCTV, air quality monitors, and automated traffic signals are used in smart cities including Singapore, London, and New York.
Improves control
Previously, operational problems were difficult to resolve since staff were alerted slowly. Because these tools notify users during emergencies, mitigating measures are implemented right away. The Internet of Medical Things, or IoMT, can remotely monitor patient conditions and notify workers in case of an emergency, which is particularly true in the healthcare industry.
Enhances proactive approach to work
Predictive maintenance is made easier by IoT sensors, which tell operators about the output and physical state of their equipment. Because their jobs heavily rely on working machinery, the manufacturing and construction industries would especially benefit from this.
Read more on What Is An IoT Sensor? How Do IoT Sensors Work Explained
Minimizes errors and miscalculations
Automated environmental monitoring and measurement is synonymous with accuracy and precision. Issues brought on by even the smallest change in temperature or humidity, particularly in the agriculture industry and the rest of the supply chain, can be resolved right away, guaranteeing efficient operations and superior final goods.
Enhances safety
There are many risks in the world, from home invasions to chemical spills. Installing proximity detectors next to high-energy zones in the factory or security cameras on your property not only keeps people safe from damage but also improves their wellbeing and gives them more confidence to complete any task.
Current Challenges and Future Advancements
Since its growth over the last 20 years, the Internet of Things has had a big impact on how people live, engage, and do business. However, it has also created new challenges for individuals who depend on these. Additionally, these difficulties become more noticeable as the infrastructure becomes more accessible and broad.
Read more on Internet of Things Software Development: Trends And Tools
- Miniaturization to lower power consumption: It’s imperative to replace batteries often because many IoT devices run on batteries that deplete quickly. And it’s pretty expensive.
- Energy consumption will decrease if the device’s components are made smaller or more compact. Smaller tools are simpler to incorporate into different pieces of equipment and, some claim, increase the device’s longevity.
- Interoperability is resolved via edge computing and AI. Occasionally, a single piece of equipment needs multiple sensor types (such as an engine control unit’s (ECU) coolant thermostat, exhaust oxygen sensor, and ignition crankshaft), which makes data sharing and integration difficult. This issue is lessened when anomalies are detected instantly with AI, machine learning, and edge computing.
- Networks of wireless sensors improve scalability. It is quite difficult to manage several devices; reliable network performance and effective data management are necessary. Even when workloads and user counts rise, LoRaWan and other low-power, long-range communication technologies keep the IoT device connected to the network, guaranteeing dependability.
Read more on IoT Device Management Protocols: Choosing The Right Protocol
- Integrating blockchain enhances privacy and data security. Critical IoT infrastructure concerns, security and privacy, are frequently targeted and susceptible to theft, damage, and illegal access. Data integrity is guaranteed by including a decentralized, tamper-resistant ledger in addition to putting strong security measures like firewalls and encryption into place.
Cost of IoT sensors

Many people could benefit greatly from the IIoT as a result of the declining cost of sensors:
- Given that sensors are becoming more sophisticated and affordable, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), which makes it possible for new digital services and business models based on intelligently connected machines and devices, is anticipated to significantly accelerate growth in developed markets.
- Since networks are present almost everywhere, sensor data may be transferred effectively.
- The design of cloud computing has enabled inexpensive data storage.
As data science continues to advance, it will be possible to obtain the key insights in the data more quickly and consistently.
Prominent businesses have already fully embraced the IIoT and are starting to reap its rewards:
- More in-depth performance analysis
- Lower predicted maintenance costs
- Enhanced effectiveness of operations
Since sensor prices are declining, businesses can now attempt to accomplish the aforementioned goals at a significantly reduced cost.
Read more on Different Types Of Sensors In IoT & Examples Of IoT Sensors
| Category | Details |
| Definition of IIoT | IIoT is IoT implemented in the industrial and manufacturing space. It’s about connecting smart sensors to the internet and using the information to make better business decisions. IIoT holds a major subset of IoT. |
| Key Difference between IoT and IIoT | The greatest difference is that the IIoT is designed to be a relatively closed environment focused on communicating with a company. |
| Estimated Spending on IIoT Technology | It has been estimated that manufacturing companies worldwide will spend $500 billion a year on IIoT Technology. |
| Estimated Value Generated by IIoT | Furthermore, the value generated by IIoT will reach $15 trillion per year by 2030. |
| Core Components of IIoT | It mainly involves connections, things, and data1 . IIoT in actuality involves a network of smart sensors collecting data. |
| Trend in Sensor Costs | The cost of sensors is drastically reducing; in 2004 the average cost of sensors was $1.30 and in the year 2020, it is expected to come down to $0.38. With the decrease in the cost of sensors, now more data can be collected, and more intelligent decisions can be made at a lower cost. |
| Current Applications of IoT in Manufacturing | Manufacturers are currently using IoT solutions to track assets in their factories, consolidate their control rooms, and increase their analytics functionality through predictive maintenance. |
| Smart Manufacturing | Smart manufacturing is the use of IoT devices which typically involves retrofitting sensors to existing manufacturing equipment, whereas new manufacturing equipment comes with IoT sensors pre-installed. With the fitting of sensors, there is a drastic improvement in the efficiency and productivity of manufacturing operations. |
| Benefits of IIoT | Industrial IoT will help manufacturers to increase their productivity by 30%. Also, with the sensors fitted, the manufacturers can predict when the machines will fail and hence they can fix the problem before it becomes huge. Real-time data tracking can also be achieved now at a lower cost as the sensor prices are slashing. Manufacturing operations achieved more efficiently and with more productivity will also have a good return on investment. |
| Current Adoption in US Manufacturing | Today, 35% of US manufacturers are currently collecting and using data generated by smart sensors to enhance manufacturing and operating processes. 38% currently embed sensors in products that enable end users/customers collect sensor generated data. |

