Contents [hide]
Explore the importance of IoT security, key challenges, and effective solutions to protect smart devices and networks.
What is IoT Security?
IoT security protects networks and devices in the Internet of Things. IoT security protects these devices against network threats. Internet-connected devices will likely be attacked. Attackers may use remote access from Internet of Things devices using a number of techniques, such as vulnerability exploitation and credential theft, to steal data.
Types of IoT Security
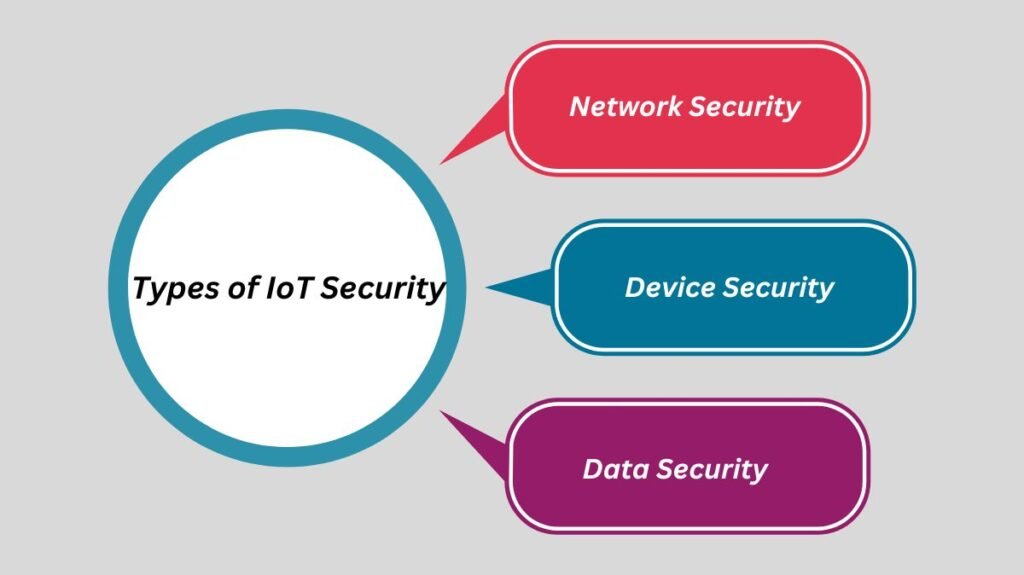
In order to safeguard devices, networks, and data, IoT security uses a multi-layered strategy. It has obligations for both the maker and the user.
Network Security
- This is about protecting the entire infrastructure of the Internet of Things network. This includes:
- Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls should be installed to secure the network.
- In a zero-trust architecture, all users and devices are considered harmful and require ongoing verification.
Network communication security measures include employing secure protocols and encrypting data being transferred between devices.
Device Security
The focus here is on safeguarding individual IoT devices:
- Using small, lightweight software to track device behaviour and identify irregularities is known as embedded security agents.
- Firmware hardening: Making sure that the software on a device is secure by updating and testing it thoroughly.
- Verifying the device’s operating system’s integrity prior to launch is known as the “secure boot process.”
Data Security
Thus, the data produced and sent by IoT devices is protected:
- Data encryption protects data in transit and at rest using strong encryption algorithms.
- Data privacy protects sensitive data against unwanted access.
- Data integrity: Checksums and other mechanisms ensure data accuracy and consistency.
How Does IoT Security Work?
- Devices with cloud storage capabilities are referred to as Internet of Things devices.
- The differences between IoT devices and traditional mobile devices necessitate a unique set of cybersecurity recommendations. The advantage of integrated security standards found in mobile operating systems such as iOS and Android is not present in them.
- In the event that an attacker gains access to a user’s account, the vast amount of data kept there could be used for identity theft or privacy violation.
- IoT security cannot be solved in a single way, but cybersecurity professionals have made it their goal to educate developers and manufacturers on safe coding techniques and how to fortify cloud activity defences.
Importance of IoT Security
- Due to the large amount of data that IoT devices process and the unique way they are made, cyberattacks are a constant worry.
- A few well-known events where a common IoT device was used to access and attack the wider network illustrate the importance of IoT security.
- We need excellent IoT security since vulnerabilities, data breaches, and other threats are always a concern.
- Businesses need IoT security, which involves a variety of methodologies, tactics, protocols, and actions to reduce their IoT vulnerabilities.
IoT Security Benefits
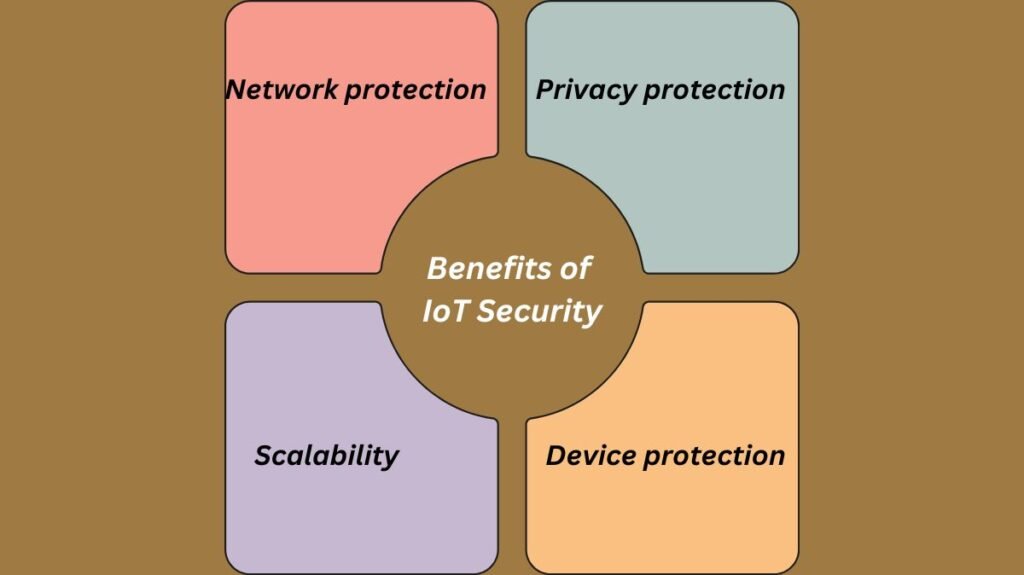
The following are some advantages of IoT security.
Network protection
In order to secure the Internet of Things overall, security solutions may help detect and stop threats like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) assaults, which have the potential to interrupt and damage the entire network.
Privacy protection
Through the protection of IoT devices, these solutions protect user privacy from illegal spying, data theft, and device tracking.
Scalability
Scalable IoT security ensures that security protocols continue to function as the number of connected devices increases and may grow with an organization’s IoT environment.
Device protection
By shielding devices against viruses, hacking, and unwanted access, IoT security guarantees the longevity and proper functioning of gadgets.
IoT Security Issues and Challenges
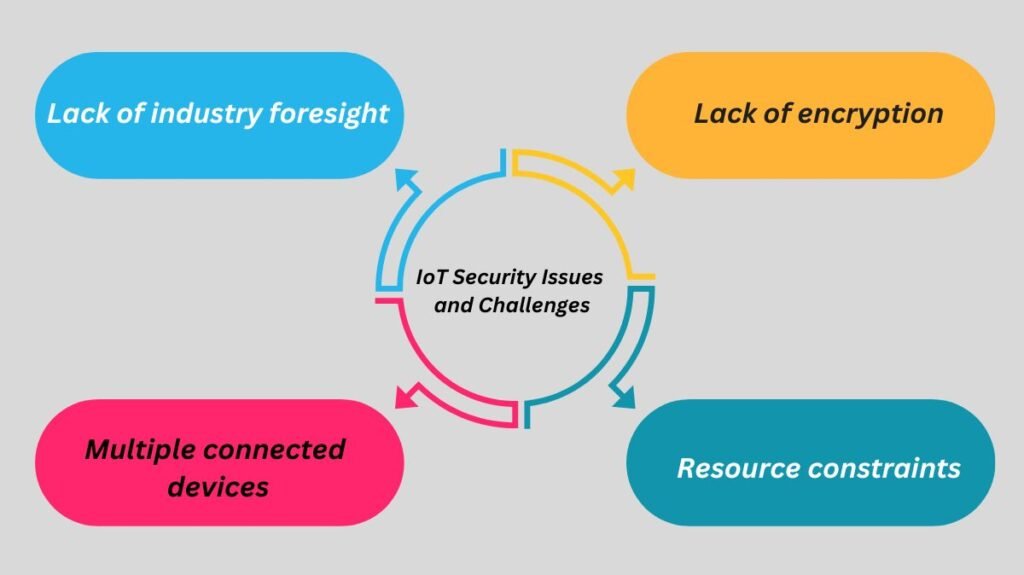
Here are a few IoT security issues.
Lack of industry foresight
The digital transformation of several industries and their goods has happened at the same pace as businesses. IoT devices have expanded in the automotive and healthcare industries in an effort to boost efficiency and reduce expenses.
Lack of encryption
Most network communication from Internet of Things devices is not encrypted, increasing the possibility of security issues and data breaches. By ensuring that all devices are secure and encrypted, these threats can be avoided.
Multiple connected devices
These days, most houses have multiple connected devices. This simplicity of use has the drawback that if one gadget malfunctions because of a security bug, all connected devices in the same house will also malfunction.
Resource constraints
Not all Internet of Things devices possess the computing power to run sophisticated firewalls or antivirus software. Certain devices have very limited connectivity.
Which Industries Need IoT Security?
IoT security is important in many businesses since they are becoming more interconnected. Here are a few industries that require robust IoT security:

Healthcare
Cyberattacks have the potential to kill people, even on medical devices like insulin pumps, pacemakers, and remote patient monitoring systems.
Manufacturing
Cyberattacks bring with them significant financial losses, safety risks, and the paralysis of critical infrastructure’s ICS/OT settings.
Energy and Utilities
Power grids and water treatment facilities, among other important infrastructure, are being powered by a large number of IoT devices in this sector, which makes them highly desirable targets for cyberattacks that could have disastrous results.
Transportation
Due to their extensive data usage, connected cars, autonomous vehicles, and smart traffic systems are all very susceptible to hacking and subsequent data breaches.
Financial Services
Strong security measures against fraud and data theft are necessary for IoT-related devices used in banking, payments, and financial transactions since they handle sensitive financial data.
Retail
If Internet of Things devices are compromised, customer data, inventory management data, and point-of-sale systems are all at danger.
Government
National security, citizen data, and key infrastructure all require IoT security.
Agricultural
The production and supply chain of food can be impacted by cyberattacks on smart farms and IoT-enabled equipment.
Building Automation
For smart buildings with IoT-enabled equipment, security is necessary to prevent data breaches and unwanted access.
How to protect IoT systems and devices?
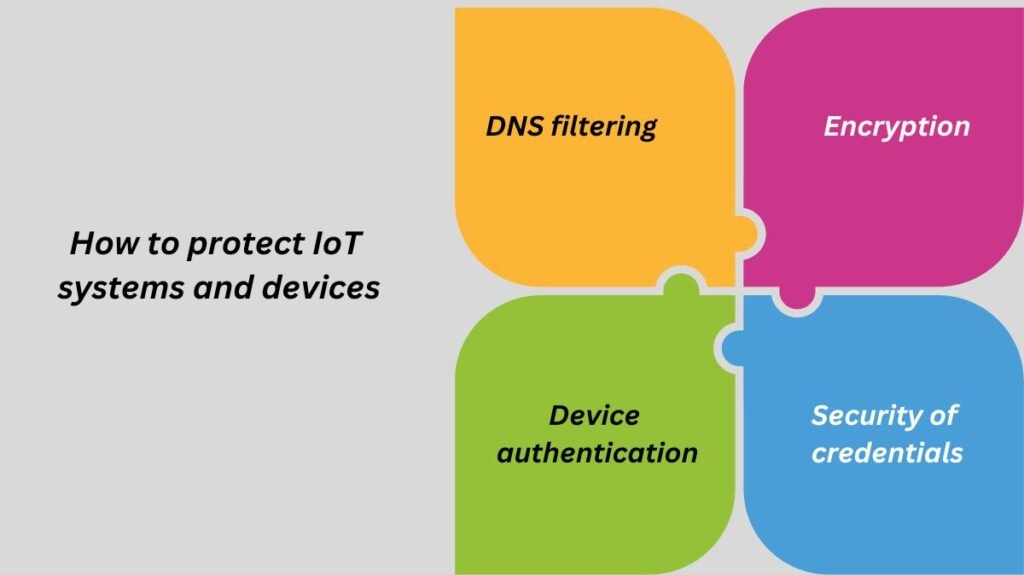
Here’s how to safeguard Internet of Things devices.
DNS filtering
DNS filtering blocks harmful websites. IoT devices are prevented from connecting to unauthorised domains when DNS filtering is implemented on a network that includes these devices.
Encryption
Data flows across the network between IoT devices are vulnerable to both external and on-path attackers if they are not encrypted. Like an envelope, a letter can be encrypted to safeguard its contents while it is being transported by the postal service.
Device authentication
Networked devices, servers, and other devices are all connected to Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets. Authentication is required for all connected devices in order to stop unauthorised input or requests from outside parties.
Security of credentials
IoT device admin credentials should be updated whenever possible. It is advised that each device have its own password and that login information not be shared across apps and devices. Credential-based assaults become less frequent as a result.

