Contents [hide]
We go over the definition of IoT architecture, architectural traits, the 5 layers of IoT architecture, and the 4 stages of IoT architecture in this blog.
IoT architecture diagram
What is IoT architecture?
IoT architecture defines how devices, networks, sensors, and apps interact in an IoT environment. An IoT architecture includes physical devices, data gathering systems, network devices that send IoT data to data processing applications, and IoT data storage.
Read more on IoT Platform Features: Scalability, Security & Analytics
IoT Architecture Perspective
The characteristics of an architectural include:
- The architecture is used as a guide for IoT applications in corporate operations and services.
- A collection of intelligent sensors that collect data, analyze and transform data elements as needed in accordance with the device application architecture, and link straight to a communication manager.
- A gateway with independent data collection, processing, communication, and capturing capabilities is coupled to a group of sensor circuits. One end of the gateway receives the data in one format, and the other end receives it in another.
- Message caches, message routers, and protocol handlers make up the communication-management subsystem.
- The device identification database, device identity management, and access management features are all included in this management subsystem.
- Information travels from the gateway to the application server or enterprise server that receives it via the Internet and data centre.
- Subsystems for organisation and analysis make it possible for services, business operations, enterprise integration, and intricate procedures.
5 layers of IoT architecture
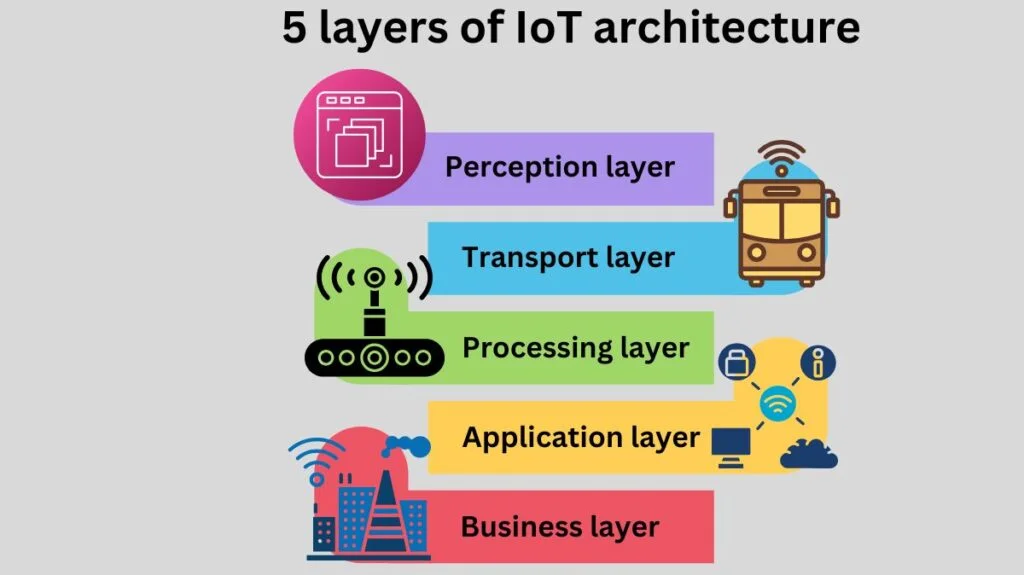
In order to identify the best IoT solutions for a company, it is essential to comprehend the IoT layer architecture. A five-layer Internet of Things architecture will be discussed here as an example.
Perception layer
To collect raw data, the perception layer engages with the physical world. Sensors, cameras, and other IoT-connected devices passively collect data and images that are then transmitted through the transport layer (such as the network layer), whereas actuators in IoT systems give devices instructions to carry out specific activities depending on sensor data or other commands. (Hardware tools called actuators transform energy into motion.)
Transport layer
The data flow and transfer between the sensors in the perception layer and the processing layer via different networks are handled by the transport layer, also referred to as the network layer (e.g., data transfer between IoT devices and backend systems utilising WiFi, Bluetooth, etc.).
Processing layer
The transport layer’s data is stored, examined, and pre-processed by the data processing layer, also known as the middleware layer. To prepare data for the application layer, this involves tasks including data aggregation, protocol translation, and security enforcement. This layer may also contain edge computing nodes, message brokers, and IoT platforms.
Application layer
Software programs that utilize the processed data acquired in the perception layer to accomplish tasks or obtain insights through sophisticated analytics are found at the application layer. The application layer includes databases, data warehouses, and data lakes.
Business layer
Since most businesspeople are used to using dashboards, user interfaces, and data visualization tools on a regular basis, the business layer is likely the most frequently seen IoT architecture layer. The business layer is where all of the data that has been gathered and analyzed adds value by influencing business choices and offering insights.
Note: The names “7-layer IoT architecture,” “5 layer IoT architecture,” and even “3-layer architecture” are frequently used when talking about the levels of IoT architecture. Simply put, these disparate explanations indicate that the same essential ideas of IoT design are being covered in more or lesser detail (e.g., five-layer architecture versus three-layer architecture).
Read more on What Are The Characteristics Of IOT (Internet Of Things)?
The stages of IoT architecture
A four-stage method is another way to explain the architecture of an IoT solution. The different components that make up Internet of Things solutions are described in this architecture. Note: Compared to the previous suggested ideas for IoT solutions, edge computing is given more weight in this scenario.
4 stages of IoT architecture
- Devices: The sensors or actuators in the perception layer are among the devices in IoT solutions that are covered in this stage. The internet gateway stage receives the data generated by these IoT system devices.
- Internet gateways: Before transmitting the raw data from the IoT devices to the cloud, the internet gateway stage pre-processes it. The internet gateway that receives the data can be a standalone device that can connect to sensors via low-power networks and send the data to the internet, or it can be directly connected to the IoT device. The IoT architecture’s transport layer is located here.
- Edge computing: The goal is to complete data processing as fast as possible after receiving pre-processed data from the internet gateway. An IoT system will frequently use a technique known as edge computing to accomplish this successfully. Edge computing processes data near its source, such as a network’s edge, rather than cloud servers. In an IoT system, local processing of sensor, IoT, and edge device data reduces latency, bandwidth consumption, and cloud data centre dependency. It supports local decision-making, real-time processing, and faster reaction times, making it ideal for low-bandwidth, latency applications.
- Cloud or data centers: This last step involves storing the data for further processing. This stage is home to the application and business layers, from which dashboards and management software can be accessed using cloud-stored data. At this point, resource-intensive processes like developing machine learning algorithms and conducting in-depth analysis take place.
Read more on Internet of Things History: Overview of Key Developments

