Contents
What Is A Cloud Infrastructure?
Cloud infrastructure is the cloud’s hardware and software. In their worldwide data centers, cloud companies manage thousands of servers, physical storage devices, and networking equipment. They use a variety of operating system settings to set up the actual devices. In order for a program to function, they also install other software. Pay-as-you-go cloud infrastructure leasing allows your company to save a lot of money on the expense of buying and maintaining separate components.
How Does Cloud Infrastructure Work?
Resources from physical hardware are separated and pooled into clouds using an abstraction technology or process like virtualization; automation software and management tools distribute these resources and create new environments so users can access what they need when they need it.
Why Use Cloud Computing Infrastructure?
Providing customers with on-demand services at any time and from any location is known as cloud computing, and the cloud infrastructure is what activates the entire cloud computing system. Cloud infrastructure is more capable of offering consumers the same services as physical infrastructure. It is accessible for low-cost, more flexible, and scalable private, public, and hybrid cloud systems.
Role Of Cloud Infrastructure
By breaking down the characteristics and capabilities of those hardware and software components, cloud infrastructure supports cloud computing. After that, the virtualized resources are hosted by a cloud service provider (or, in the case of a private cloud, an IT department) and made available to customers over a network or the internet. These resources consist of servers, RAM, network switches, firewalls, load balancers, storage, and virtual machines (VMs). Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), two broad and task-specific services, are frequently supported by these resources.
Requirements For Building Cloud Infrastructure
A public cloud provider, which has far greater resources and experience to design, create, and operate cloud infrastructure, is what most enterprises looking for a cloud computing model rely on. Customers choose different degrees of abstracted resources, including computation, scaled virtualized instances, and storage, and these providers occasionally purchase infrastructure components with design input. To just a few, they also provide higher-level services for self-service, billing, security, integration, orchestration, and reporting.
Nonetheless, some businesses may need their own private cloud and decide to take ownership of the entire stack, including the hardware, administration, and workloads and apps that use it. According to them, constructing an on-site private cloud architecture necessitates the following:
- A standardized architecture that guarantees policy-based settings and control, offers scalability and flexibility for workloads, and allows for the sharing of IT resources.
- Resources like computation, virtualization and containers, storage, and networking may be abstracted from on-premises hardware and software.
- Other management tasks, include chargeback, security, orchestration, integrations, and reporting.
- The provider of choice determines the particular tech stack for a private cloud. A company can choose to use a vendor to supply both the software and hardware components, or it can use its own hardware and software to create a private cloud.
As an alternative, a business can use the services of the following cloud providers to establish an off-premises private cloud:
- A service provider uses specialized hardware, networking, and software to host and manage cloud services for a single client in a hosted private cloud.
- The hosted option is expanded by a managed private cloud, in which the provider also handles other services, including identity management.
- Workloads are separated from other clients in a virtual private cloud, which is a walled-off setting within a public cloud that nevertheless uses multi-tenant servers. This idea is expanded to include cloud provider-controlled on-premises infrastructure.
Components of cloud infrastructure
The computational needs of a cloud computing paradigm are supported by several cloud infrastructure components. There are several essential elements that make up cloud infrastructure, including but not limited to servers, software, networks, and storage devices. In general, cloud infrastructure may be divided into three categories, namely.
- Computing
- Networking
- Storage
The most crucial aspect is that cloud infrastructure needs to adhere to certain fundamental infrastructure requirements, such as security, scalability, transparency, and intelligent monitoring.
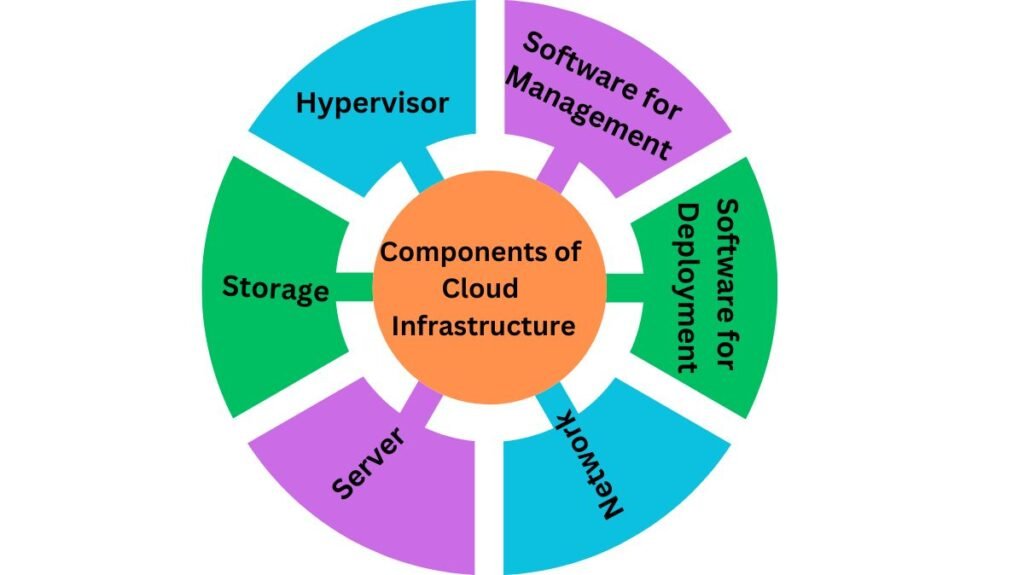
Hypervisor
A firmware or low-level application called a hypervisor is essential for enabling virtualization. It is employed to split and distribute cloud resources across several users. The hypervisor is known as a virtual machine monitor, or virtual machine manager, since it keeps an eye on and controls cloud services and resources.
Software for Management
Infrastructure configuration and maintenance are aided by management software. Data, apps, services, and resources are all monitored and optimized via cloud management software.
Software for Deployment
Cloud application integration and deployment are facilitated by deployment software. Therefore, it usually aids in creating a virtual computer environment.
Network
It is one of the essential parts of the cloud architecture that connects cloud services to the internet. A network is necessary for the internal and external transfer of resources and data.
Server
The server, which stands for the computational component of the cloud infrastructure, is in charge of administering and providing cloud services for different partners and services, keeping security, and other things.
Storage
Storage is the term for the facility that is offered to various organizations for the purpose of managing and storing data. Because it maintains several copies of storage, it offers the ability to extract another resource in the event that one fails.
In addition, virtualization is regarded as a crucial element of cloud infrastructure. Because customers interact with their cloud infrastructure through a graphical user interface (GUI), it abstracts the available processing power and data storage away from the real hardware.

