What is Software as a Service?
SaaS is cloud-hosted application software accessed by a web browser, mobile app, or thin client over the internet.
SaaS providers run, update, and manage software and infrastructure. The client only needs to set up an account, pay a charge, and start working.
Industry historians say SaaS began in the 1950s when mainframe software were transmitted to remote terminals. Salesforce initiated SaaS in 1999 by offering its CRM system as web browser software hosted in the cloud.
Software as a Service is the most prevalent software delivery mechanism and public cloud computing service today. The SaaS model is used to offer a large portion of the software used by workforces, ranging from essential business applications like enterprise resource planning (ERP) and human resources or workforce optimization platforms to commonplace tools like Slack (for messaging) and Dropbox (for file storage and sharing).
Businesses of all sizes, from startups to massive multinational corporations, can benefit from SaaS’s quick time to value, little or nonexistent administrative costs, and predictable prices as compared to traditional software deployed on-site.
How does SaaS works?
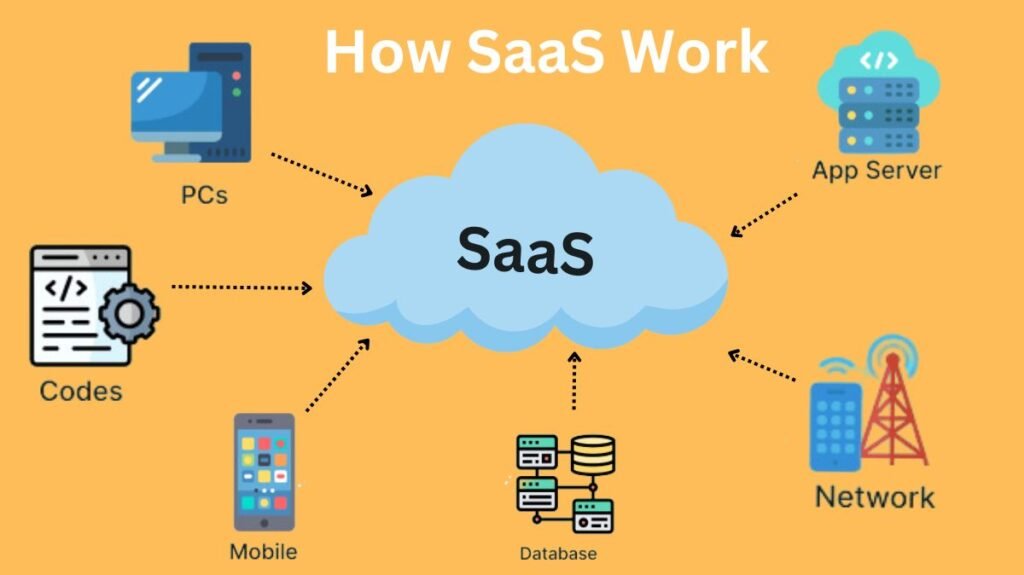
Utilizing economies of scale and cloud computing infrastructure, SaaS offers clients a more efficient way to purchase, use, and adapt software. Every SaaS application has these traits in common:
Cloud hosting is a feature of SaaS applications. Either the SaaS software supplier or a cloud service provider (like Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, or Amazon Web Services (AWS)) can host the application on its own cloud infrastructure. The SaaS provider can provide the scalability and worldwide accessibility that certain clients may need by hosting with a reputable cloud service provider.
Customers with an internet connection and a PC, smartphone, or tablet can use SaaS apps. SaaS apps can be used in any online browser, but they may work better or be required for smartphone or tablet apps on mobile devices. Users may need to download and install a specific thin client for certain SaaS apps, such Adobe Acrobat, on their computers.
Every customer is served by a single instance of the application with the multi-tenant architecture used by SaaS applications. The application, user, system, and custom configuration data of each client is isolated from that of other customers for security and privacy reasons.
The fundamental benefit of Software as a Service applications is that they require little to no client management or maintenance. The SaaS provider is accountable for
- Supplying, overseeing, and maintaining every server, networking device, storage device, and operating system needed to operate the program.
- When necessary, applying security patches and feature updates.
- supplying cloud security, data backup, load balancing, redundant infrastructure, and disaster recovery services in order to avoid failures and fulfill the service level agreement’s (SLA) requirements for performance, availability, and data protection.
An application programming interface (API), which is offered by many SaaS providers, allows users to combine their SaaS applications with other Software as a Service or conventional software programs.
SaaS software as a service benefits
When compared to traditional software that is installed and maintained on-premises infrastructure, the advantages and benefits of Software as a Service are most easily understood:
SaaS provides faster even instant adoption and time to benefit
SaaS programs are available for purchase and use right away, sometimes within minutes, for a small upfront fee (basically the cost of the first month’s subscription). As opposed to traditional software, which may necessitate investing in and setting up servers, installing software on each user’s device, and planning for and acquiring a complete license for each user.
SaaS provides access to new features and versions as soon as they’re available
Without clients even realizing it, SaaS companies frequently add functionality and update features multiple times per week. They can even improve the user experience and interface without interfering with the clients’ work. In contrast, consumers may have to wait months for the capability in a new version of traditional on-premises software due to the frequent, disruptive, and expensive upgrades (assuming they don’t decide to forego some upgrades entirely).
SaaS enables cost-effective, on-demand scalability
By simply upgrading or downgrading tiers or purchasing additional capacity, customers can scale Software as a Service applications up and down as needed, allowing for cost-effective, on-demand scalability. In contrast to typical software, which needs users to buy more capacity in advance of demand surges, this program wastes empty space until it is needed.
SaaS offers predictable costs and dramatically lower overhead
Software as a Service eliminates the need to budget for internal IT professionals to install, update, and maintain the program, as well as for periodicupdating software and supporting infrastructure. Nearly 80% of the cost is directly related to the software.
Software as a Service Disadvantages
Data security and delivery speed are the main obstacles to Software as a Service adoption. Since data is kept on external servers, businesses need to make sure that it is secure and inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. SaaS business users in the aerospace and defense industries place a high value on security.
Performance can be negatively impacted by slow Internet connections, particularly if cloud servers are accessible from a distance.Internet connections are slower than internal networks. Because Software as a Service solutions are distant, they also suffer from a lack of customization and a loss of control.
- Enhanced security threats
- Reduced velocity
- Loss of command
- Absence of personalization
Software as a service saas architecture
Software as a Service (SaaS) architecture delivers software to consumers via the internet from a vendor’s remote server. This concept lets numerous organizations share a single application that they can use as needed.
Here are some Software as a Service architecture highlights:
Cost
Subscriptions allow businesses to use the product without installing or maintaining it.
Technical work
Data storage, upgrades, and security are handled by the Software as a Service provider.
Customization
The software can be used as-is or customized with an API and third-party tools.
Architecture with many tenants
One instance of the software serves each customer on a host server. Quick management and upgrades are possible.
Security
SaaS security can be achieved via multifactor authentication, regular upgrades, and data encryption.
SaaS differs from PaaS and IaaS. PaaS lets developers and enterprises construct software, while IaaS provides network infrastructure.
CRM, communication, accounting, and design tools are popular SaaS platforms.
Software as a service examples
Software as a Service is a cloud-based software distribution paradigm that lets customers access software online rather than install it.
For Work
- Google Workspace includes Google Sheets, Docs, and Gmail.
- Microsoft 365: Teams, Word, and Excel.
Interaction
- Zoom: Video conferences and calls.
- Slack: Group conversations and cooperation.
Internet Retailers
- Create an online store with Shopify.
- Squarespace: E-commerce and websites.
Task Management
- Asana: Plan out assignments and projects.
- Trello: Task boards that are visual.
Keeping
- Dropbox: File sharing and storage.
- Cloud file storage is provided by Google Drive.
Cash
- Manage your finances using QuickBooks Online.
- Xero: Accounting online.
Software as a Service pricing
Software as a Service programs come in a wide range of subscription pricing plans, all of which differ from traditional software licensing, which offered access to the program and its associated services for a set price (or a set of fixed rates) for a certain amount of time.
Free or ‘freemium’ pricing
Most software as a service (SaaS) providers provide a week- or month-long free trial. Free trials usually offer all program features but limit how often or much users may use it. Some even don’t require a credit card.
Some software as a service (SaaS) providers provide “freemium” versions of their apps, which are always free but only include a useful fraction of the full product’s functionality, or they are completely unrestricted but occasionally ask users to click on displays before they can continue using the app. Freemium customers are expected to eventually switch to a premium version of the software, according to Software as a Service vendors.
Monthly or annual tiered subscription pricing
Software as a Service products usually offer price “tiers” for small and mid-sized organizations according to feature set or consumption level. SaaS email marketing solutions may offer a “standard” tier for up to 5,000 contacts for $250 per month, a “pro” tier for 20,000 contacts for $500, and a “business” tier for 100,000 contacts plus hosting and landing page design for USD 600 per month.
Large businesses can benefit from a more comprehensive feature selection, priority support, unique SLA terms, and even negotiable price through the “enterprise” tier that SaaS vendors can offer.
Scalability is as simple as going up to the next tier with tiered pricing, which enables users to select the plan that best suits their functional needs and budget. Customers who pay for a complete year at once typically receive a reduction from most tiered subscription pricing, while customers who switch tiers mid-subscription receive a prorated price adjustment.


[…] SaaS, IDaaS is an application delivery model that lets customers employ cloud-based identity management […]
[…] NaaS is linked to Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service. […]
[…] IDaaS often offers the previously described advantages and allows SSO into Software as a Service (SaaS) programs, making it ideal for small and medium-sized enterprises as well as those that were […]
[…] SaaS, or cloud application services, are the most common cloud services. SaaS is popular with organizations because it reduces IT stress and improves customer experiences through information exchange and services. SaaS delivers programs and services online, eliminating the need for clients to download software. With SaaS, a cloud vendor manages applications, data, runtime, middleware, operating systems, services, storage, networking, and virtualization. […]