Understanding Hybrid Cloud Architecture And Advantages
Contents
What is a hybrid cloud architecture?
In order to provide a unified, adaptable managed IT infrastructure, hybrid cloud architecture blends on-premises, private cloud, public cloud, and edge settings.
The hybrid cloud architectural model is essential to digital transformation because it gives companies an adaptable, portable, and affordable means of updating legacy applications, deploying data, and distributing workloads among several computing environments.
The evolution of modern of hybrid cloud architecture
Prior to cloud computing, enterprise companies had their own on-premises data centres, which were made up of servers, networking infrastructure, and enterprise software applications, to store data and run software programs. Compared to cloud-based infrastructure, this conventional infrastructure configuration usually needs more electricity and physical space. Organisations started using hybrid cloud solutions to reduce costs and boost overall agility as cloud computing for business gained traction and the demand for digital transformation grew.
A hybrid cloud model’s main objective is to provide the flexibility required to shift workloads and apps to the cloud and use cloud services in accordance with compute requirements and other situations. For example, in reaction to unforeseen increases in traffic, public cloud computation and storage resources can scale up fast, automatically, and affordably without affecting workloads in private cloud. Cloud bursting is a crucial hybrid cloud function that helps businesses with unexpected spikes in computing demand, such as online retailers, who frequently employ it to handle spikes in traffic during flash deals.
Hybrid cloud architecture diagram
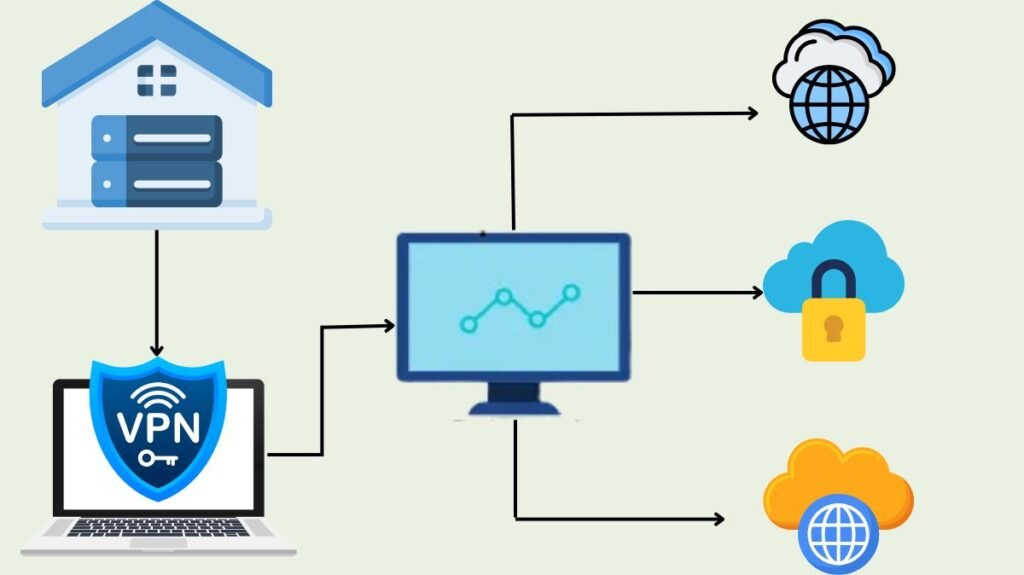
The building blocks of hybrid cloud architecture
A company can benefit from high-performance computation and storage capacity, low-latency network connectivity, virtualisation, and strong security with the right hybrid cloud architecture.
In addition to integrating applications that utilise various resources (private and public cloud infrastructure, as well as on-premises), hybrid cloud architecture includes several additional essential elements.
Network connectivity
An essential part of hybrid cloud architecture is network connectivity. Multiple sites can share resources thanks to network connectivity.
The following technologies are essential for hybrid cloud connectivity:
- VPNs safeguard point-to-point connections between network nodes. A VPN encrypts a user’s identity, access credentials, and internet data. On-premises and private cloud infrastructure can connect securely over public networks using private, secure connections by using a virtual private network (VPN).
- Wide area networks, or WANs, link computers across large distances, including continents or even regions. With billions of computers connected globally, the internet is the biggest WAN. A wide area network (WAN) links offices, data centres, cloud apps, and cloud storage in an enterprise setting. Businesses can connect on-premises networks at their offices and data centres with cloud-based storage, apps, and other resources by using a cloud-based wide area network (WAN).
- Application programming interfaces, or APIs, are a collection of established guidelines that facilitate communication between various programs and serve as a layer of intermediary processing data transfers between systems. Through APIs, businesses may make their application data and functionality available to internal departments, business partners, and external third-party developers. APIs are HTTP requests made between clouds to link networks, databases, and applications in a hybrid cloud architecture.
Virtualization
Virtualization technology, which creates an abstraction layer over the physical hardware to a virtual compute system using software, is the foundation of modern hybrid cloud architecture. This technology effectively creates many virtual computers, or virtual machines (VMs). A key element of enterprise cloud computing is virtualisation, which was initially created for commercial use by VMware. It allows businesses to use a single physical server to operate numerous virtual computers, operating systems, and applications. Additionally, it enables customers to buy computer resources as needed and expand them effectively and economically as their workloads increase.
Network virtualisation is one of the numerous forms of virtualisation used in hybrid cloud architecture in addition to virtual servers. Software-defined networking (SDN), a component of network virtualisation, virtualises the hardware that manages network traffic routing . By virtualising one or more hardware appliances that perform a particular network function (such a firewall, load balancer, or traffic analyser), network function virtualisation (NFV) makes it simpler to setup, provision, and manage those devices.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC), which automates infrastructure provisioning and helps developers to create, launch, and grow cloud applications more quickly, with lower risk, and at a lower cost, is another benefit of virtualisation.
Containerization
A key component of contemporary hybrid cloud architecture are containers, which are lightweight, executable application components that bundle application source code with all the operating system (OS) libraries and dependencies needed to run the code in any environment. Containers virtualise the operating system (often Windows or Linux) instead of the underlying hardware, like virtual machines (VMs) do.
Containers have emerged as the de facto compute units of contemporary cloud-native apps due to their superior mobility and resource efficiency over virtual machines (VMs). Microservices, also known as microservices architecture, are the building blocks of cloud-native apps, which are created to run exclusively in the cloud and are scalable by DevOps and other teams. This indicates that numerous smaller, loosely linked, and independently deployable components or services make up a single application.
Because each service can be developed and deployed independently, microservices expedite software development and deployment. Many top companies have switched from creating monolithic apps to creating microservices apps. For example, Amazon employs microservices to collect user history, actions, and other data in order to provide real-time suggestions for improved customer experiences.
Hybrid cloud management that is unified
A unified platform for finding, using, and managing on-premises, private, and public cloud data and resources is part of today’s hybrid cloud computing strategy. In order to maintain consistency and dependability throughout the diverse hybrid cloud environment, a variety of hybrid cloud platforms and technologies combine compute, storage, networking databases, analytics, and security services.
AWS Outposts, Google Cloud Platform, VMware Hybrid Cloud, and Red Hat OpenShift are examples of popular hybrid cloud platforms that come with pre-configured hardware, software, and services. In order to orchestrate container-based services and other software-based capabilities, each platform usually integrates common cloud technologies such as Kubernetes. Multiple monitoring tools and data feeds can be combined into a single interface with the help of these unified management solutions for monitoring, allocating, and managing those resources from a single pane of glass.
The following summarises the essential features of a hybrid cloud management platform:
Management of resources
Depending on the needs of the application, stakeholders can reallocate and distribute resources across on-premises and cloud environments with the use of hybrid-cloud-managed service tools. For example, a company such as a financial institution can test new apps, such mobile banking apps, on the public cloud while maintaining critical customer data on the private cloud.
Orchestration of workload
Container orchestration systems, like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm, are used in hybrid cloud architectures to automate workloads that are containerised. Developers may swiftly deploy, run, and sync their containers on clusters of servers located in multiple locations with the aid of these technologies. Additionally, they improve containerised workloads’ scalability, allowing DevOps and other teams to automatically create Kubernetes clusters that run containerised apps as needed, leading to optimal performance and reduced downtime.
Integration of data
Data integration the process of merging data from several source systems to provide a single view is necessary in hybrid environments because they collect and process data from a variety of distinct sources.
Data analytics software platforms that use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to gather, organise, and analyse data are examples of data management solutions for hybrid clouds. The architectural idea of a data fabric, which operates on top of the many technologies in a hybrid environment and combines data from several source systems to produce a single view, is incorporated into many of these data integration solutions.
Data management
In hybrid cloud architecture, data governance solutions offer an additional technological layer that enables enterprises to establish and uphold policies and procedures that specify how their data must be handled, kept, and utilised in accordance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Safety
The technologies and best practices used to safeguard sensitive data in an environment where data and apps move across on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud platforms are known as hybrid cloud security. Technical safeguards including network authentication, encryption, and management software are part of the hybrid cloud architecture’s security layer.
Encrypting data
- In hybrid cloud environments, data encryption is utilised to shield private information from ransomware and malware attacks and other cyberthreats.
- Management of identity and access (IAM): All users are given digital identities via IAM management tools, a standard authorisation technique that allows for active monitoring and restriction of all data transactions.
- Information and event management for security (SIEM): Along with a complete security orchestration system that automates threat monitoring, real-time threat detection, and response, SIEM management solutions offer security monitoring and observability consoles.
- Recovery from disasters (DR): To speed up the recovery of lost data and return to regular business activities, disaster recovery hybrid-cloud-based solutions offer data security for data backup, retention, and retrieval.
Advantages of hybrid cloud architecture
Among the many advantages of a hybrid cloud architecture are the following:

Agility and scalability
By quickly allocating and de-allocating resources stored on-premises or in public or private clouds, hybrid cloud architecture increases agility and facilitates quick responses to shifting business requirements. Thanks to on-demand cloud resources, hybrid cloud also provides nearly infinite scalability up or down.
Continuity of business
By moving mission-critical data to the cloud and allowing scalability during demand surges, hybrid cloud deployment maximises business continuity by minimising downtime.
Cost savings
By moving workloads to the public cloud and avoiding the continuous costs associated with maintaining and updating outdated hardware, a hybrid cloud strategy can assist reduce capital expenditures.
Modernisation of applications
The process of modernising outdated programs to scalable, cloud-native app environments is made possible by the flexibility and security provided by a hybrid cloud environment. This eliminates waterfall development processes by enabling applications to be developed rapidly, deployed automatically, and updated often.
Adoption of generative AI
Because hybrid cloud infrastructure offers limitless storage capacity, compute power, and quick scaling, it speeds up generative AI and its significant reliance on massive volumes of data and large language models (LLMs).