Contents
- 1 What is multicloud architecture?
- 2 What are the future trends in multicloud architecture?
- 3 What constitutes the multicloud architecture elements?
- 4 What advantages does multicloud architecture?
- 5 What are the challenges of implementing multicloud architecture?
- 6 How is business agility enhanced by multicloud architecture?
- 7 What security factors are taken into account when designing a multicloud system?
- 8 What are the use cases of multicloud architecture?
- 9 How can the effectiveness of multicloud architecture be measured?
- 10 Which multicloud architecture trends will emerge in the future?
What is multicloud architecture?
Cloud computing services from multiple vendors are combined into a single infrastructure through multicloud architecture. Workloads are optimised using this technique to improve vendor independence, flexibility, and robustness. It ensures smooth administration and integration while deploying apps, services, and data across several public or private cloud, depending on the particular business objectives of each organisation.
What are the future trends in multicloud architecture?
Several factors make multicloud architecture crucial, including:
- Through flexibility and the avoidance of vendor lock-in, multicloud architecture enables enterprises to take advantage of the advantages and special qualities of several providers.
- Workload distribution among several cloud providers improves availability and resilience by lowering the chance of service interruptions.
- By choosing the most economical services and distributing workloads among suppliers, it makes cost optimisation possible.
- By allowing data processing and storage in particular geographic areas, multicloud configurations aid in complying with regulatory standards.
- Innovation is accelerated and organisational agility is enhanced when a wider range of services and technology are available.
- Cloud provider diversification reduces the chance of outages, security lapses, or problems that only affect one provider.
What constitutes the multicloud architecture elements?
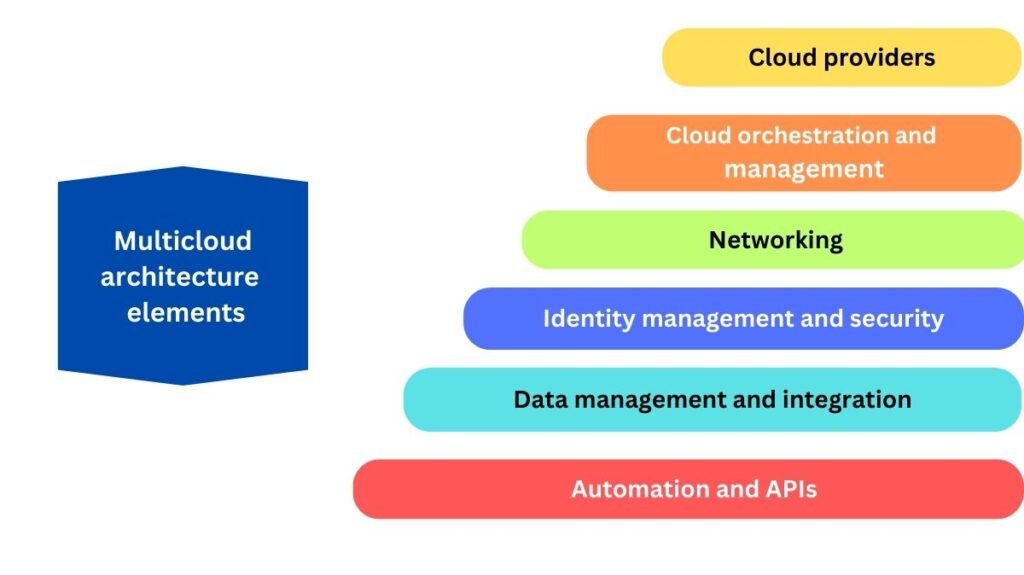
Cloud providers
A variety of private and public cloud platforms that offer storage, processing, and other services.
Cloud orchestration and management
Centralised solutions for provisioning, automating, and streamlining processes across various clouds are known as cloud management and orchestration.
Networking
A dependable network for cloud provider integration and secure, low-latency communication.
Identity management and security
Cloud-wide security frameworks for threat detection, encryption, compliance, and access control.
Data management and integration
Cloud consistency, backup, migration, and storage tools.
Automation and APIs
APIs and automation systems that maximise multicloud efficiency, application deployment, and process optimisation.
What advantages does multicloud architecture?
The utilisation of multicloud architecture has the following benefits:
- Avoiding vendor lock-in lets firms choose the best services from multiple sources. This method increases overall flexibility and helps prevent reliance on a single source.
- Diversifying workloads among many cloud providers helps boost uptime and reduce disruptions.
- Businesses can choose the cheapest cloud provider and adjust their cloud usage to their needs and budget by using multiple providers.
- Businesses can reduce latency and improve performance by choosing cloud providers with data centres in specified areas.
- By selecting specific providers and geographical areas for data processing and storage, multicloud configurations enable enterprises to meet regulatory requirements and data sovereignty.
- Organisations may employ the newest tools and technology from several platforms and innovate more quickly when they have access to a variety of cloud services.
- Utilising many cloud providers can help lower hazards. By distributing workloads and data across many environments, it aids in addressing problems like outages, security breaches, or service interruptions.
What are the challenges of implementing multicloud architecture?
Multicloud architecture implementation has unique difficulties.
- Because it involves navigating different tools and APIs to make sure that services function properly together, managing numerous cloud environments can be difficult.
- Maintaining uniform security rules across many cloud environments for varying regulatory requirements might be difficult.
- Dealing with data fragmentation, high transfer costs, and consistency across several platforms can make effective data management difficult.
- Cost monitoring and optimisation across multiple cloud providers might be difficult. This is because each supplier has a distinct pricing structure and they may overpay on wasted resources.
- It is challenging to maintain application performance and improve user experience due to cross-cloud latency issues and the need for continuous network optimisation.
- A broad range of skills are required to handle different cloud platforms efficiently, which can lead to knowledge gaps and increase IT teams’ training costs.
How is business agility enhanced by multicloud architecture?
The following are some ways that multicloud architecture increases business agility:
- Companies can choose the best tools and services from a range of cloud providers, which improves productivity and performance for a variety of workloads.
- Businesses can reduce their reliance on a single vendor and prevent vendor lock-in by using many sources.
- Businesses can modify their workloads and increase resilience by spreading risk by using several cloud services, which reduces downtime.
- Access to specialised services from many clouds expedites the creation and introduction of new products.
- Businesses can better control their spending by choosing the most cost-effective cloud services for specific needs.
What security factors are taken into account when designing a multicloud system?
The following are important security factors for multicloud architecture:
Uniform security regulations and governance
Establish a single governance structure to supervise and enforce the uniform security regulations for every cloud environment.
Identity and access management (IAM)
Use a centralised IAM system to manage user roles and permissions and a zero trust strategy to check individuals and devices.
Data encryption and protection
All cloud services should use end-to-end encryption for transmission and storage. Install data loss prevention (DLP) solutions to protect against any leaks and illegal access.
Compliance management
Use automated monitoring technologies for continuous compliance tracking and reporting to ensure that different cloud providers are adhering to regulatory regulations.
Business continuity and disaster recovery
To ensure data availability and resilience, develop a solid disaster recovery plan that covers several cloud services. Put into practice business continuity plans that monitor events in real time and react to them promptly. This will ensure a speedy recovery from disturbances and assist minimise downtime.
What are the use cases of multicloud architecture?
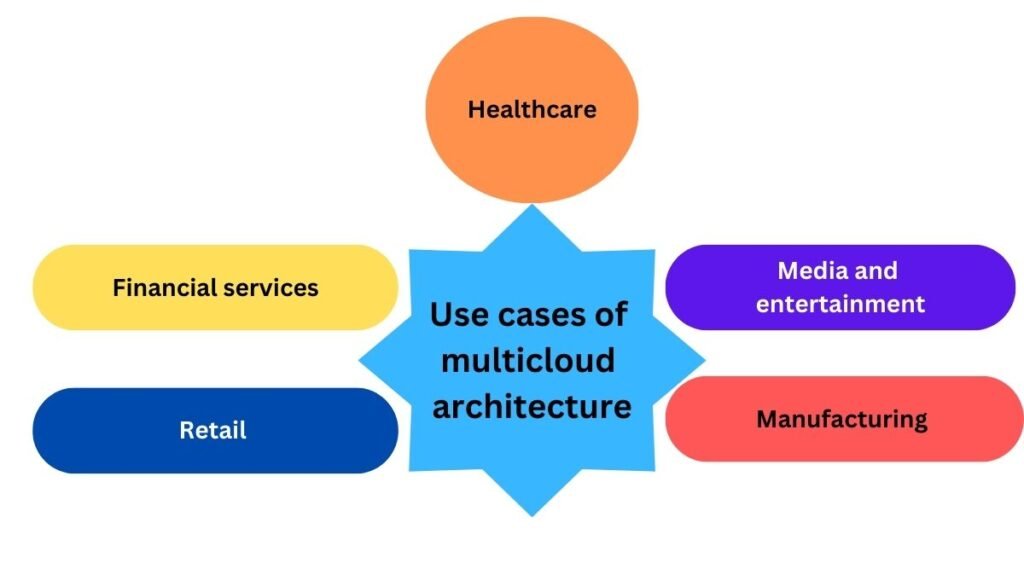
Healthcare
By selecting providers with superior security and local data residency, multicloud solutions enable healthcare organisations to store sensitive patient data in compliance with HIPAA.
Financial services
By distributing apps across clouds and offering high availability and fast recovery during outages to maintain essential transaction services, multicloud architecture assists financial organisations in managing risk.
Retail
To manage traffic spikes during peak shopping seasons and cut expenses during slower times, retailers employ multicloud typologies to scale resources according to seasonal demand.
Media and entertainment
To increase delivery speed and latency for audiences around the world, media organisations distribute content over several clouds using the best CDN services from different suppliers.
Manufacturing
Using specialised cloud services for machine learning and big data processing, multicloud architecture offers real-time analytics and insights from IoT devices.
How can the effectiveness of multicloud architecture be measured?
Cost effectiveness
Compare many cloud providers’ TCO and resource consumption rates to maximise spending and uncover underutilised resources.
Performance and availability
Monitor application latency, response times, end-user satisfaction, and uptime/downtime to meet SLAs.
Scalability
Assess the architecture’s capacity to quickly scale resources to meet demand to ensure peak and off-peak performance.
Security
Track regulatory compliance and security incident response time. Well-designed architecture reduces incidents and meets rules.
User satisfaction and business agility
To ensure that the multicloud strategy satisfies business needs and innovation, gauge user satisfaction with application performance and speed.
Which multicloud architecture trends will emerge in the future?
The following are the multicloud architectural trends of the future:
Automation and AI
AI-powered solutions will handle more cloud management responsibilities, improving performance, anticipating possible issues, and reducing operating expenses through predictive analytics.
Integration of edge computing
Multicloud configurations will increasingly include edge computing, enabling distributed computing models that manage data closer to consumers and speedy processing for IoT devices.
Zero-trust unified security
Consistent security and compliance across cloud environments can be achieved by using automated Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solutions and zero-trust security paradigms.
Kubernetes and serverless adoption
Kubernetes will be the preferred alternative for executing containerised apps that are portable across various cloud environments.
Sustainability and green cloud
As companies use “green cloud” tactics to reduce their environmental impact in multicloud environments, cloud providers are giving priority to energy-efficient operations.
These patterns highlight how multicloud architecture is moving towards automation, security, portability, and sustainability.

