Contents [hide]
- 1 Hardware Based Virtualization
- 2 Features of hardware based virtualization are:
- 3 Advantages of hardware based virtualization
- 4 Disadvantages of hardware-based virtualization
- 5 Operating system based Virtualization
- 6 Features of operating system-based virtualization are:
- 7 Advantages and disadvantages of Operating System-Based Virtualization
- 8 Advantages of Operating System-Based Virtualization
- 9 Disadvantages of Operating System-Based Virtualization
Hardware Based Virtualization
Hardware based virtualization in computing refers to a platform virtualization technique that enables effective full virtualization with the aid of hardware capabilities, mostly from the host CPU. whole virtualization, in which an unaltered guest operating system (using the same set of instructions as the host machine) runs in sophisticated isolation, is used to replicate a whole hardware environment, or virtual machine.
The many logical layers of operating system-based virtualization, where virtual machines are created by first installing the virtual machine (VM) into a full host operating system.
Hardware-level virtualization is the phrase used to describe an abstract execution environment in terms of computer hardware where guest operating systems can be run. An operating system serves as the guest in this scenario, while the host is represented by the actual computer hardware, the virtual machine is represented by its emulation, and the virtual machine manager is represented by the hypervisor. Hardware based virtualization is typically more effective when virtual machines can communicate with hardware without the host operating system having to take any additional steps. The hypervisor, often known as the virtual machine management (VMM), is a key element in hardware virtualization.
Basically, there are two types of Hypervisors which are described below:
Type-I hypervisors:
Type I hypervisors operate directly on the hardware. They therefore act as operating system substitutes and interact directly with the ISA interface provided by the underlying hardware, which they mimic to enable the management of guest operating systems. This type of hypervisor is also referred to as a native virtual machine since it operates natively on hardware.
Type-II hypervisors:
Type II hypervisors need an operating system to let them provide virtualization services. This indicates that they are operating system-managed apps that mimic the ISA of virtual hardware for guest operating systems and interact with it through the ABI. This type of hypervisor is also referred to as a hosted virtual machine since it is contained within an operating system.
The basic user interface of a hypervisor requires some storage space. It is a thin software layer that performs hardware management functions to create a virtualization management layer. Device drivers and associated software are designed for virtual machine provisioning, but many common operating system features are left unimplemented. This kind of virtualization system is essentially intended to improve the performance overhead that comes with coordination, which enables numerous virtual machines to communicate with the same hardware platform.
Another issue with hardware based virtualization is hardware compatibility. All related drivers and support software must be compatible with the hypervisor because the virtualization layer communicates directly with the host hardware. Drivers for hardware devices that are compatible with other operating systems might not be compatible with hypervisor platforms. Furthermore, the variety of sophisticated functionality shared by operating systems may not be included in host management and administration features.
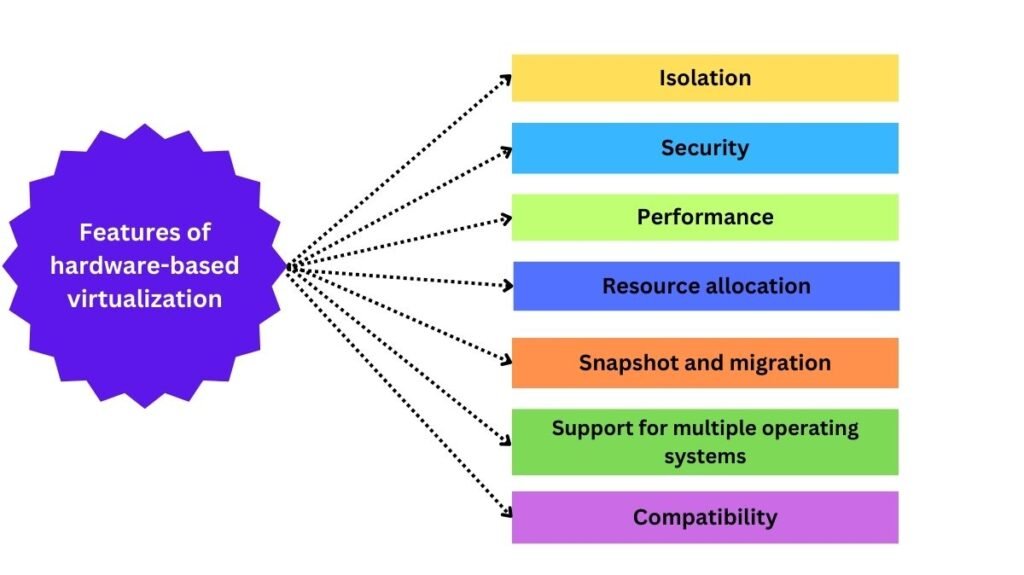
Features of hardware based virtualization are:
Isolation
Hardware based virtualization isolates virtual machines, so errors in one won’t affect others on the same physical host.
Security
Because each virtual machine is isolated from the host operating system and other virtual machines, hardware-based virtualization makes it harder for malicious malware to spread.
Performance
Because the hypervisor has direct access to the real hardware, virtual machines running on hardware-based virtualization can attain performance levels that are nearly identical to native ones.
Resource allocation
Including CPU, memory, and I/O bandwidth, to virtual machines is made flexible by hardware-based virtualization.
Snapshot and migration
Hardware-based virtualization makes it possible to take snapshots, which are useful for recovery and backup. Additionally, it permits real-time virtual machine migrations between physical hosts, which can be applied to load balancing and other scenarios.
Support for multiple operating systems
By enabling the consolidation of workloads onto fewer physical machines, hardware-based virtualization lowers maintenance and hardware expenses by supporting numerous operating systems.
Compatibility
Hardware-based virtualization is simple to integrate into current IT infrastructure because it works with the majority of contemporary operating systems.
Advantages of hardware based virtualization
Because it minimizes (preferably, completely removes) the need to modify the guest operating system, it lowers the maintenance burden associated with paravirtualization. Achieving improved performance is also quite convenient. Virtual Iron and VMware engineers have noted a useful advantage of hardware based virtualization.
Disadvantages of hardware-based virtualization
The host CPU must explicitly enable hardware based virtualization, which not all x86/x86_64 CPUs may have. The scalability and effectiveness of server consolidation are limited by the numerous virtual machine (VM) traps that come with a “pure” hardware based virtualization strategy, which includes the whole unaltered guest operating system. The introduction of para-virtualized drivers helps lessen this performance impact; this combination has been dubbed “hybrid virtualization.”
Operating system based Virtualization
Based on an operating system An operating system technology known as virtualization allows many separate user-space instances to exist thanks to the kernel. Operating system-based virtualization is another term for the installation of virtualization software. The host operating system is the one that is put on top of an already-existing operating system.
In order to run and create different virtual machines, a user installs the virtualization software into his system’s operating system, just like he would with any other program. In this case, the user can directly access any of the virtual computers that have been generated thanks to the virtualization software. Even when the hardware driver is not assigned to the virtualization software, operating system virtualization may impact hardware compatibility concerns since the host OS can offer hardware devices the necessary support.
Hardware IT resources that need special software to function can be transformed into virtualized IT resources using virtualization software. Numerous OS-based services are accessible as organizational management and administration tools can be used for the virtualization host management because the host OS is a full operating system in and of itself.
Some major operating system-based services are mentioned below
- Recovery and backup.
- Management of Security.
- Directory Services integration.
Various major operations of Operating System Based Virtualization are described below:
- Hardware features like the CPU and network connection can be used.
- peripherals that are connected and that it can communicate with, like scanners, printers, webcams, and keyboards.
- Files, folders, and network shares are examples of data that can be read or written.
Depending on the program’s request and the user account it is running on, the operating system may be able to grant or refuse access to certain resources. Additionally, OS may conceal certain resources, preventing them from showing up in the enumeration results when a computer program computes them. However, from the standpoint of programming, the operating system has controlled an act of interaction, and the computer program has interacted with those resources.
Programs may run inside containers when operating systems are virtualized or containerized, with only a portion of these resources allotted to them. When operated inside a container, a software that is supposed to see the entire computer can only see the resources that have been allotted to it and assumes that’s all there is. Each operating system allows for the creation of several containers, each of which is given a portion of the computer’s resources. Numerous computer programs may be included in each container. These programs may operate alone or in simultaneously, and they may even be related to one another.
Features of operating system-based virtualization are:
Resource isolation
High resource isolation: Operating system-based virtualization gives each container its own CPU, memory, and I/O bandwidth.
Lightweight
Containers are lighter than virtual machines since they share the same host operating system, speeding startup and reducing resource utilization.
Portability
Because containers are so portable, moving them from one environment to another is simple and doesn’t need changing the underlying application.
Scalability
Applications can be highly responsive to shifts in demand thanks to containers’ easy scaling up or down based on application requirements.
Security
By separating the containerized program from the host operating system and other containers running on the same system, containers offer a high degree of security.
Reduced Overhead
Because containers don’t have to simulate an entire hardware environment, they have lower overhead than conventional virtual machines.
Easy Management
Containers are simple to start, stop, and monitor, making them easy to manage.
Operating system-based virtualization may result in additional performance overhead requirements and issues, including:
- CPU, memory, and other physical IT resources are used by the host operating system.
- Performance is reduced when guest operating systems make hardware-related calls because they must traverse multiple layers to and from the hardware.
- In addition to separate licenses for each of their guest operating systems, licenses are often necessary for host operating systems.
Advantages and disadvantages of Operating System-Based Virtualization
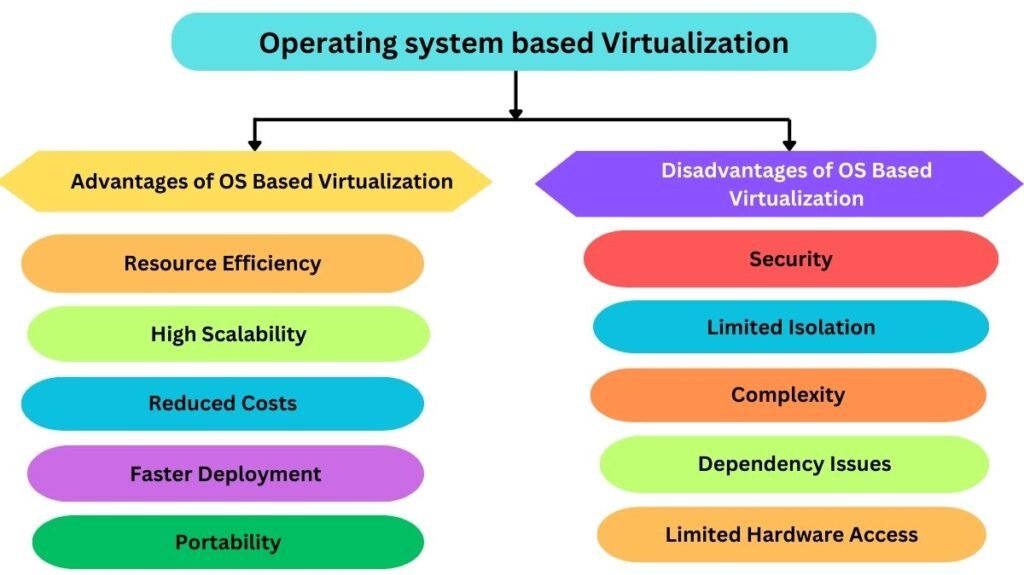
Advantages of Operating System-Based Virtualization
Resource Efficiency
Because containers do not have to simulate an entire hardware environment, operating system-based virtualization saves resource overhead and enables higher resource efficiency.
High Scalability
It is simple to adapt to changes in the workload because containers may be swiftly and simply scaled up or down in response to demand.Simple Commands: Deploying and maintaining a large number of containers is made simple by the ease with which containers may be managed.
Reduced Costs
Because operating system-based virtualization uses less infrastructure and resources than traditional virtual machines, it can drastically lower expenses.
Faster Deployment
Because containers can be set up rapidly, it takes less time to update or start new apps.
Portability
Because containers are so portable, transferring them between environments is easy and doesn’t need application changes.
Disadvantages of Operating System-Based Virtualization
Security
Operating system-based virtualization may provide security risks because containers share the host OS. This is because a security vulnerability in one container may affect all others on the same system.
Limited Isolation
Containers’ inability to totally segregate programs may cause performance degradation or resource contention.
Complexity
Setting up and maintaining operating system-based virtualization can be challenging and call for specific expertise and abilities.
Dependency Issues
Dependencies between containers and the host operating system or other containers may cause incompatibilities and impede deployment.
Limited Hardware Access
Certain operations or applications that call for direct hardware access may not be able to be carried out by containers due to their limited access to hardware resources.

