Types Of Cloud Servers
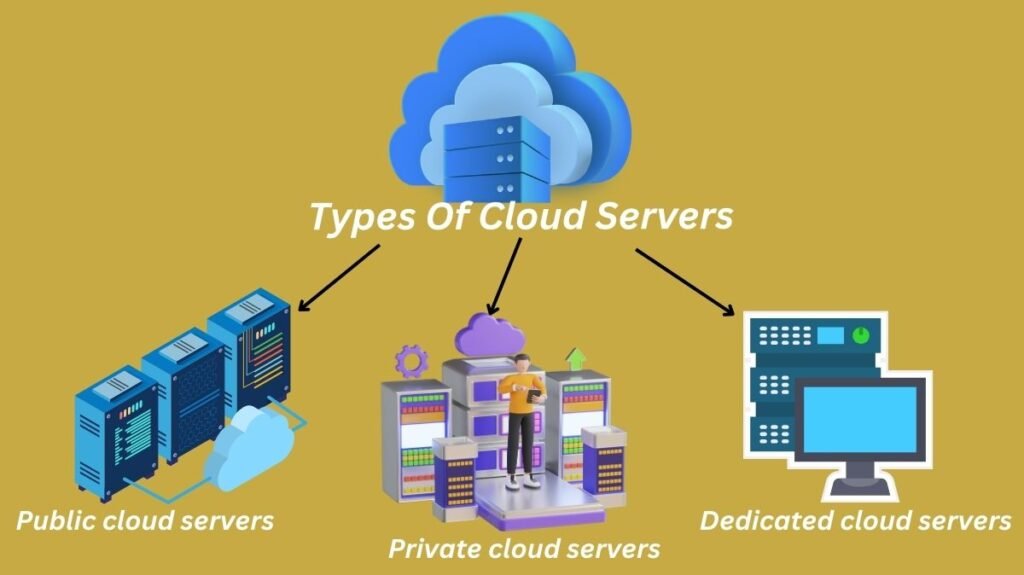
A business has a variety of cloud server options to select from. The following are three main models:
Public cloud servers
The most common type of cloud server is a virtual machine (VM), also known as a compute instance, housed on a public cloud provider’s infrastructure and delivered to clients via a web-based console or interface. This paradigm is IaaS.
Public cloud servers often employ prefabricated instances with specified vCPUs and RAM. Cloud servers include Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon EC2.
Private cloud servers
A computing instance in an on-premises private cloud can also be a cloud server. In this instance, an organisation uses a local area network (LAN) to distribute the cloud server to its internal users and, in some situations, to external users over the internet.
A private cloud server is located within an organization’s own infrastructure, whereas a public cloud server is owned and run outside of it. This is the main distinction between a private cloud server and a hosted public cloud server.
In addition to allowing customers to choose how much vCPU and RAM resources to utilize to run the instance, private cloud servers can also rely on preconfigured instances. Both private and public cloud servers can be found in hybrid clouds.
Dedicated cloud servers
Along with virtual cloud servers, cloud companies can also provide physical cloud servers, also referred to as bare-metal servers, which are essentially machines that are dedicated to a customer. When an organisation has to implement a bespoke virtualization layer or address the performance and security issues that sometimes come with a multi-tenant cloud server, they usually utilize these dedicated cloud servers, also known as dedicated instances.
Numerous compute choices with different processor and memory capacities are available on it. This makes it possible for a company to choose the instance type that best suits a given workload. One vCPU and four gigabytes of memory, for instance, might be found in a smaller Amazon EC2 instance, but 96 vCPUs and 384 GB of RAM are found in a bigger Amazon EC2 instance.
Additionally, cloud server instances that are customized to meet specific workload needs can be found. For example, compute-optimized instances, which have more processors than memory, or instances that use graphics processing units, or GPUs, for workloads requiring a lot of math.
The majority of public cloud servers lack storage resources, despite the fact that traditional physical servers frequently have some storage. Rather, cloud providers like Google Cloud storage and Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) usually provide storage as a stand-alone cloud computing service. In order to store information, including virtual machine images and application data, an organisation sets up and links storage instances with it.
Features of cloud servers
Cloud servers have several important features, including:
- Infrastructure that is varied: Cloud servers’ computing infrastructure can be either virtual, physical, or both, depending on the use cases and specifications of the cloud computing environment.
- Provisioning via self-service: In order to assist customers deploy and manage resources without requiring IT support, cloud servers usually provide self-service provisioning. Users may swiftly set up servers and apps on-demand with this simplified method, which also allows for quicker reaction times to shifting business requirements.
- Dependability: Since cloud servers are multi-server, the computing capabilities of a single server that fails are immediately transferred to the other servers in the pool.
- Provided via an API: Through an API that facilitates connection between various software programs and services, cloud server services may be accessed whenever needed. APIs make it simpler for developers and companies to create, launch, and maintain cloud applications by facilitating resource provisioning, scaling, and monitoring.
- PAYG model: Pay-as-you-go cloud services let companies only pay for what they consume. More money may be saved with the pay-as-you-go approach than with the maintenance and care of conventional physical servers.
- High accessibility: Cloud servers are very accessible. This is due to the fact that cloud providers utilise sophisticated failover methods to guarantee continuous uptime by distributing servers among several separate data centres and availability zones.
- Security and compliance: To protect sensitive data, cloud servers make significant investments in compliance and certifications as well as cutting-edge security features like firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, data encryption, and frequent audits.
Key differences between a cloud server and a traditional server
The particular requirements, available resources, and expansion goals of an organisation frequently influence the decision between a cloud server and a conventional physical server. Certain use cases may choose traditional on-premises servers, even if using cloud servers for computing operations can provide consumers several unique advantages over physical servers.
The following are the main distinctions between a cloud server and a conventional server:
Location and administration
A distant network or the internet can be used to access cloud servers, which are hosted and maintained by cloud server providers. The provider’s off-site data centres handle the management of its physical infrastructure. An organization’s in-house IT personnel is in charge of maintaining, upgrading, and troubleshooting traditional or dedicated servers, which are physically situated on-site.
Scalability
Businesses may scale processing capacity up or down in real time by dynamically adjusting cloud server resources based on demand. Scaling conventional servers sometimes involves investing in and setting up extra gear and infrastructure, which may be expensive and time-consuming.
workloads. While traditional servers are better suitable for businesses with steady, high-demand workloads, cloud servers are often best for organizations with changeable workloads.
Dependability
Reliability is increased by cloud servers’ inherent redundancy, load balancing, and failover features. The infrastructure of the company determines the dependability of typical servers, and extra configurations are frequently needed to provide redundancy.
The cost structure. Businesses just pay for the resources they use using cloud servers, which usually operate on a PAYG approach. Conventional physical servers need a one-time hardware investment as well as continuing maintenance expenses.


[…] Cloud servers are accessible from any internet-connected device. Laptops and mobile devices can access your cloud server. […]