Contents
What is Desktop as a Service?
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) provides cloud-based virtual desktop environments with data, operating systems, programs, and user preferences.
The cloud provider manages the network, storage, and computing infrastructure in which the PCs operate as virtual machines. Users can access their desktop environment from PCs, laptops, tablets, and even cellphones.
A lot of businesses are searching for an alternative to the conventional desktop deployment paradigm, which involves IT managers setting up an operating system and apps on each employee’s device. Administrators frequently waste too much time and money using that strategy to secure the devices, handle updates and upgrades, and install software.
Additionally, a workforce that is becoming more mobile and remote makes the traditional desktop deployment strategy unsuitable. Today’s workers utilize a wide range of devices, including PCs, laptops, and mobile devices, and they regularly work remotely and while on the go. To optimize remote and mobile productivity, organizations need to offer a robust and consistent user experience across all of those devices. Regardless of the device they use, employees can effortlessly access the same apps and data with this method.
Security needs to be a primary concern as businesses decide on new methods for providing data and apps. Even if a device is lost or stolen, organizations still need to make sure that data doesn’t end up in the wrong hands.
A DaaS model might be the answer. With the correct DaaS solution, your company can protect sensitive data, simplify management, lower costs, and provide users with consistent, easy access to apps and data across devices.
Benefits of Desktop as a Service
Provide a powerful and flexible user experience
- Boost mobile and remote productivity by enabling workers to access their work environments from nearly any device, whether they are at home or on the road. They can access data, desktop settings, programs, and more safely.
- Handle numerous devices: Desktops, laptops, tablets, and even some smartphones are among the many devices that a DaaS approach can handle.
Reduce administrative burdens and control costs
- Quicken onboarding: Your admins won’t have to waste time installing software on every new machine. DaaS allows you to quickly connect a user’s device to a virtual desktop that has already been set up.
- Profit from the newest hardware: A reputable cloud provider ensures that your desktop computers are powered by the newest data center systems. You can prolong your device’s refresh cycle because your users are utilizing the data center’s processing and memory capabilities.
- Remove hardware management: Your IT managers won’t have to spend time on infrastructure resource scalability, patching, maintenance, or upgrades. Your administrators can concentrate on other duties because your DaaS supplier handles that work for you.
- Reduce infrastructure expenses: By using the DaaS paradigm, you may provide virtual desktops without having to pay for or maintain the underlying network, storage, and computing infrastructure.
- Adopt a model of flexible consumption: You can quickly and affordably add or delete users using a pay-as-you-go or annual pricing plan.
Bolster security and promote compliance
- Protect data: Sensitive information is less likely to be compromised if an employee’s laptop or tablet is stolen. Data remains safe in the cloud as long as authentication measures are in place. The worker can use another machine to resume work in the interim.
- Simplify compliance: You can store your data and apps in a data center that complies with HIPAA and ISO standards without having to deal with the hassle of setting up or maintaining compliance if you choose the correct service provider.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) disadvantages include:
Dependency on the Internet
DaaS is accessible only with an internet connection and is hosted in the cloud. Employees won’t be able to access their desktop computers in the event of an internet outage. Performance problems might also be caused by slow internet connections.
Security issues
There may be security hazards while storing private information on the cloud. Companies should confirm that the security measures implemented by their DaaS supplier are sufficient.
Lock-in of vendors
Switching cloud providers might be challenging because DaaS requires the use of a certain provider.
Unexpected expenses
Additional expenses for DaaS could include fees for data transfers, storage, and system integration.
Minimal personalization
Compared to on-premises configurations, certain DaaS options provide less customization.
Variations in performance
Variations in server resources and internet connection quality might cause performance to fluctuate.
Concerns about compliance
Regulations pertaining to data sovereignty may make compliance difficult.
Making the switch from current systems
There may be challenges associated with switching from current systems.
DaaS provides virtual desktop environments on the cloud. It distribute desktop operating systems and software online so consumers may access them on any suitable device from anywhere. This is how it operates:
How Desktop as a Service Works
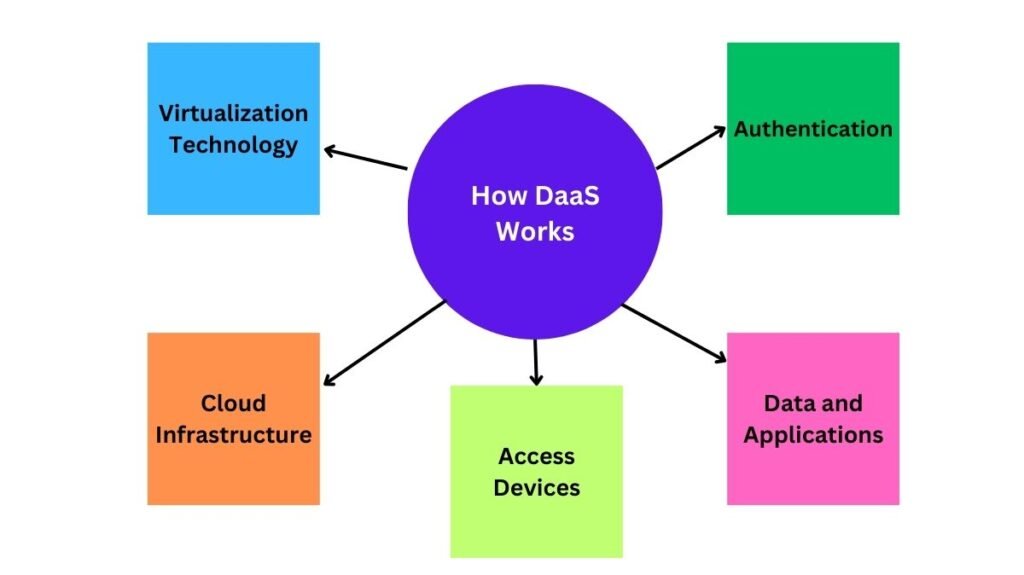
Virtualization Technology
Desktop as a Service creates and maintains virtual desktop instances through virtualization. Desktop operating systems like Windows or Linux are operated on virtual machines (VMs), which are housed on centralized cloud servers.
Cloud Infrastructure
A service provider oversees the cloud infrastructure where the desktop instances are housed. As a result, businesses no longer need to maintain hardware on-site.
Access Devices
Users use a suitable device, such as a PC, laptop, tablet, or thin client, to connect to their virtual desktops. Usually, the connection is made using a web browser or client program.
Data and Applications
Instead of being handled locally, user data, files, and apps are stored and processed on cloud servers. Central management and security are thus guaranteed.
Authentication
Users use secure login credentials to access their virtual desktops. Secure access is ensured by authentication techniques such as multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Use cases
The DaaS approach has worked well in a variety of scenarios:
- Call centers, part-time jobs, and shift work: Businesses can handle big call centers or other shift-work settings where multiple workers operate from a single workstation throughout the day. Every employee using a DaaS strategy has a different login to access their desktop.
- Software developers: Developers can simply access many different virtual desktops rather than juggling multiple PCs or running multiple operating systems on a single computer. By buying fewer devices, you may contribute to improving quality assurance and speeding up testing.
- Healthcare providers: Regardless of the computer they use in the exam room or corridor, doctors and nurses have access to programs, notes, and patient files. Patient information is protected when all data and apps are stored on a cloud that has received HIPAA certification. Instead of causing a disastrous data breach, a stolen laptop could just cause little annoyance.
- University labs: By connecting to their virtual desktop, instructors and students can access their work from any computer in a staff room, library, computer lab, or dorm room. By allowing students to share a single remote desktop, universities may make costly, limited-license applications accessible to a large number of students.
- Seasonal or contract work: There’s no need to clean out and reinstall the computer when an employee departs. In just a few minutes, the old virtual desktop can be decommissioned and a new one provisioned. Quick onboarding and offboarding of users is essential for positions with a high employee turnover rate.
- Employees who operate remotely and on the go: You can increase their productivity while strengthening data security. Your staff won’t be restricted to a physical computer in one place when you use DaaS. Instead, from any computer or mobile device, wherever in the globe, users may safely access their information.
- Acquisitions and mergers: You can expand your company’s network by adding a large number of new workers without installing more local computers if you use a DaaS model. The newly hired employees can connect to their new employer’s files and applications while still using their current equipment.
Desktop as a Service Architecture
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) lets users access cloud-based virtual desktops online. The following elements are included in the DaaS architecture:
Virtual computers
Virtual machines housed on the network, storage, and processing infrastructure of the cloud provider power DaaS desktops.
Cloud service provider
The virtual desktops are distributed and managed by the cloud provider from their datacenters.
Web browser or client software
Through this, users can access the virtual desktops and their programs.
Data storage that is centralized
The DaaS data is centrally stored by the cloud services provider, which facilitates backups.
Desktop as a Service Examples
Examples of Desktop as a Service (DaaS) in operation include the following:
Temporary employees
Seasonal employees can have their virtual desktops provisioned and deprovisioned by their organizations as needed.
Call centers
For businesses with shift workers who require the same software, DaaS can assist maximize IT resources.
Developers of software
Instead of juggling several PCs or operating systems, developers can access many virtual desktops.
Medical professionals
From any computer at a medical facility, physicians and nurses can access patient files, notes, and applications.
Labs at universities
From any computer in a university lab, library, or dorm room, instructors and students can access their work.
Institutions of finance
Financial professionals can work remotely with the support of DaaS, which guarantees data protection and adherence to industry rules.
DaaS can save expenses related to traditional desktop infrastructure, facilitate remote work, and increase IT efficiency for enterprises. Additionally, DaaS can assist companies improve sustainability, guarantee business continuity, and reduce security threats.
Desktop as a Service pricing
The cost of Desktop as a Service (DaaS) might change based on the features required, the duration of a session, and the type of virtual desktop. DaaS typically costs between $40 and $250 per virtual desktop each month. Here are a few instances of DaaS pricing from various suppliers:
Cloud Hosting by Ace
Offers individualized pricing options with plans starting at $30 per user per month.
Citrix Advanced Plus DaaS
Offers improved monitoring, session recording, and improvements to user speed and scalability, with a monthly starting price of $13 per user.
Workspaces at Kasm
Provides a free trial before offering enterprise and professional subscriptions with particular features and costs.
DinCloud
Offers a free demo and a 14-day trial, but doesn’t disclose prices without a quote request.

