Components Of VPC
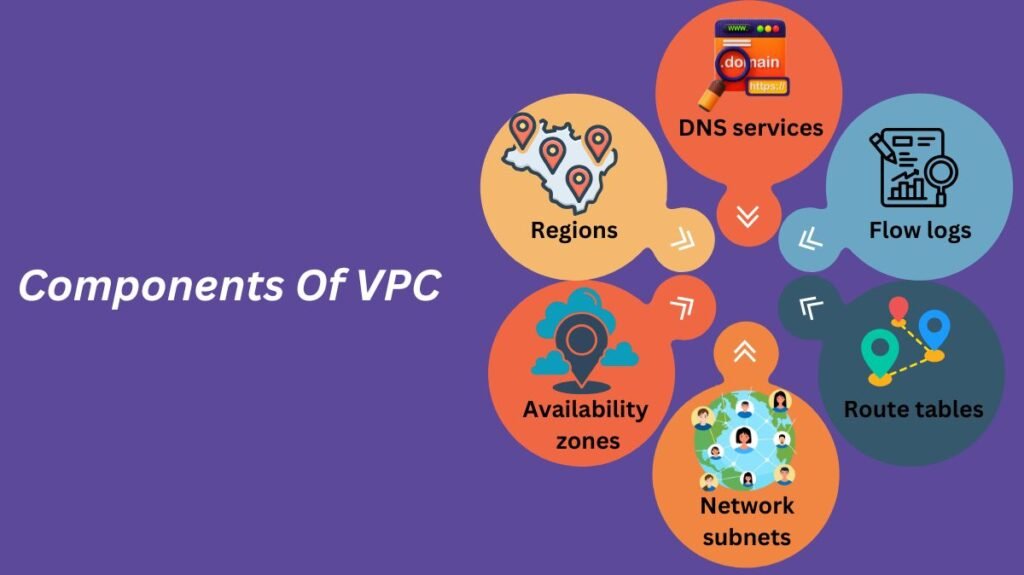
Regions
VPCs are hosted by providers in various geographies. Apps, services, and other resources can be distributed in a region, which is a specified geographic place. The computing, network, and storage resources, together with the associated cooling and electricity, for host services and applications are housed in one or more zones, which are physical data Centre’s. Because zones are segregated from one another, there is never a single point of failure in an area.
Availability zones
Within a VPC region, an availability zone is a physically and logically separated area with its own network, power, and cooling infrastructures.
Network subnets
A logical division of an IP network into smaller network pieces is called a subnet. Through the use of resource groups, routing tables, and network access control lists (ACLs), these core VPC techniques assign IP addresses to specific resources (such as virtual server instances) and provide a range of controls on these resources. Subnets function similarly to private IP addresses in a VPC context, meaning they are not publicly accessible over the Internet.
Route tables
A set of rules or routes that regulate network traffic for the subnet or gateway must be linked to each subnet in a VPC.
Flow logs
These allow you to gather, store, and display data on IP traffic entering and leaving your VPC’s network interfaces.
Domain name system (DNS) services
VPC-related DNS services let users establish their own private DNS resource records and zones. By encrypting DNS requests and prohibiting third parties from tracking online behavior, private DNS can increase online privacy and security.
Challenges Of Virtual Private Clouds
Before adopting this architecture, an organisation should take into account the issues associated with the VPC configuration. First, your in-house IT team may not be able to handle the arrangement by setting up, maintaining, and keeping an eye on a virtual private network (VPN). Furthermore, for many highly regulated sectors, the virtual private cloud may still not be sufficiently isolated because it is housed outside of an organization’s data Centre.
Virtual Private Clouds Providers
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) service providers include the following:
AWS
AWS VPC is a reputable private cloud service and one of the largest cloud providers globally. In a separate virtual network, it enables users to start other AWS resources.
Cisco
Provides a variety of private cloud solutions, such as cloud administration tools, business apps, infrastructure management packages, and data centre goods.
Google Cloud
Google Cloud’s private cloud provides a customizable environment with access to advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence technologies, making it a viable choice for small-to-midsize or big US-based businesses.
Microsoft Azure
A scalable and secure private cloud option for big businesses with Microsoft environments already in place is Azure Dedicated Host.
VMware
VMware is a well-known personal cloud provider that provides a range of cloud computing and virtualization technologies.
IBM Cloud
A REST-based API in IBM Cloud VPC facilitates integration with a user’s old toolsets and applications.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Examples
Examples of virtual private clouds (VPCs) include the following:
Amazon VPC
Amazon VPC, a key component of the AWS ecosystem, enables customers to establish separate virtual networks for their particular requirements. Subnets, routing tables, connection settings, and IP address ranges may all be defined by users.
Google Cloud
Google Cloud’s VPC Network Peering enables customers to create software as a service (SaaS) ecosystems. Users may make services privately available across many VPC networks thanks to this functionality.
VPC Peering
Clients can interconnect two VPCs and utilize private IP addresses to transport traffic between them thanks to VPC peering connection.
Virtual Private Cloud Pricing
The VPC offers from the different cloud providers may have varying pricing structures. Individual VPC resources, such storage, VSIs, and load balancers, are frequently priced differently. Some cloud providers do not charge for data transfers across private networks, while volume-based data transfer fees are also typical.
The requirements of the apps you intend to install should be taken into consideration before choosing the optimal VPC and price model to suit your company’s demands. Do they need a lot of computation? Will they need a lot of CPU power and memory? Or are their needs for CPU, storage, and memory more evenly distributed? You may estimate the possible prices while comparing solutions by answering these questions, which will help you determine your consumption demands.
Virtual Private Cloud Vs Public Cloud
| Aspect | VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) | Public Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Tenancy | Single-tenant: Private space within public cloud architecture. | Multi-tenant: Shared resources among multiple users. |
| Security | Higher security due to isolated infrastructure. | Security measures are shared but robust. |
| Flexibility | Allows customization within a private environment. | High flexibility for various workloads and use cases. |
| Scalability | May have limitations, e.g., extra storage volumes only in specific blocks. | Highly scalable without such constraints. |
| Cost | Cost-effective but generally higher than public cloud. | More affordable due to shared resources. |
| High Availability | Supported, but depends on the VPC configuration. | Extensive, with data centers across multiple regions. |
| Feature Support | Not all public cloud features are available in VPCs. | Full range of cloud features generally supported. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for businesses requiring enhanced security and compliance. | Suitable for general-purpose workloads and startups. |

