Contents [hide]
How is CloudOps works?
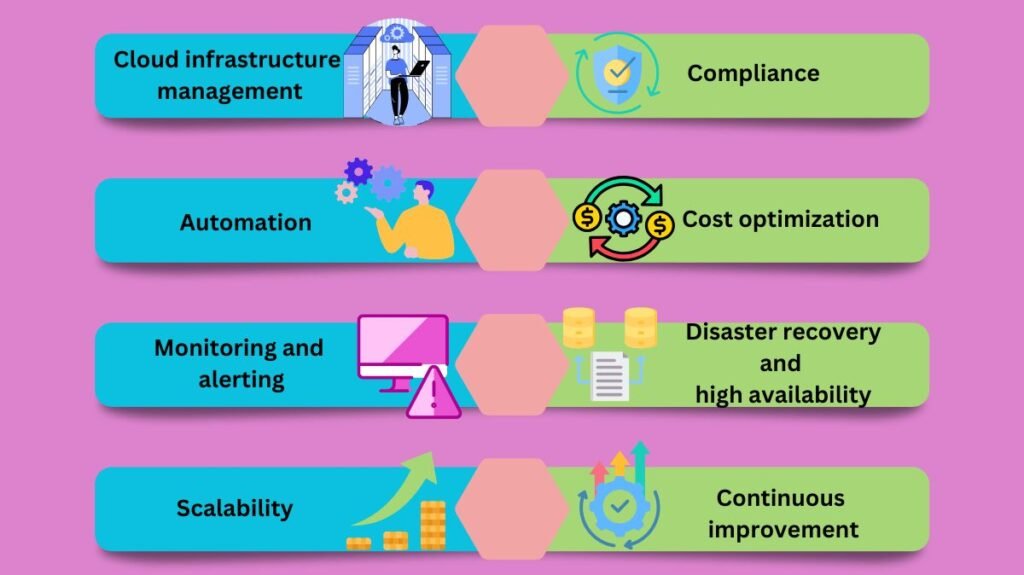
CloudOps automation manages and optimizes cloud services, apps, and infrastructure. Typical operation:
Cloud infrastructure management
CloudOps starts with AWS, Azure, or GCP infrastructure creation and administration. Virtual servers, storage, networking, and other cloud services enable enterprise applications and workloads.
Automation
CloudOps automates repetitive tasks, reduces errors, and boosts productivity. Cloud resource and application provisioning, configuration, deployment, scaling, and monitoring are often automated via Ansible, Puppet, or Terraform.
Monitoring and alerting
CloudOps monitors application performance, availability, security, and infrastructure. Google Cloud Monitoring, Amazon CloudWatch, or Azure Monitor collect metrics, logs, and events and alert for faults or anomalies.
Scalability
CloudOps lets companies scale apps and infrastructure. Cloud provider auto-scaling often involves horizontal (adding or deleting instances or nodes) and vertical scaling.
Compliance
CloudOps teams must follow corporate and industry security standards. Set up network monitoring, auditing, encryption, and access controls.
Cost optimization
CloudOps also need cost reduction. Teams can optimize cloud expenditure, find cost-saving opportunities, and monitor resource utilization and spending trends by rightsizing instances, employing reserved instances, or using spot instances for non-essential work.
Disaster recovery and high availability
CloudOps uses DR and HA to reduce downtime and data loss. Cloud backup and restore, data replication across several sites, and disaster recovery testing may be needed.
Continuous improvement
CloudOps teams improve cloud infrastructure and application reliability, efficiency, and performance. This covers incident post-mortems, metrics and performance data analysis, automation, optimization, and upgrades.
CloudOps helps businesses use cloud computing‘s scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness while guaranteeing infrastructure and application dependability, security, and performance.
Advantages of CloudOps
There are numerous advantages that CloudOps provides to businesses, such as:
Increased automation
A wide range of routine chores, such as provisioning servers and storage, application testing, monitoring and reporting, application builds, and security incident remediation, can be made easier with the help of cloud operations tools.
Increased safety
To assist guard against cybercrime or data exfiltration, major hyperscale cloud providers use the finest physical security available and continuously monitor their infrastructure. Considering that cloud security is as much the responsibility of the organisation as it is of the cloud provider, almost all businesses experience security enhancements when they move to the cloud.
Enhanced RPO/RTO
The first use case for the public cloud was backup and data recovery, which is still a major factor in cloud migration. By reducing the recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO) to almost zero, backup and replication techniques can help guarantee availability for a user and customer base that is becoming more and more global.
Total savings on IT
Pay-as-you-go cloud services reduce the need for significant capital investments, service contracts, and ongoing data centre infrastructure upgrades to accommodate evolving customer needs. Additionally, facility expenses like power, cooling, and even real estate are reduced when data centre infrastructure is removed.
Scalability on demand
Instant capacity expansions can be made to accommodate growing or seasonal demands, typically through a self-service portal. The ability to quickly provide new virtual machines, physical servers, storage, and even network bandwidth allows businesses to be more flexible and respond quickly to demands.
Access from anywhere
From any location with an internet connection, businesses may use almost any device to access cloud apps and resources at any time.
Non-disruptive upgrades
Both software and infrastructure can be updated or upgraded without affecting service, allowing for the addition of new features or the application of corrections while regular business activities continue.
Disadvantages of CloudOps
Increased dangers to data security
Despite cloud platforms’ constant improvements to their security protocols, you’re still vulnerable to hacks and attacks. Because cloud systems’ networks are accessible from a distance, they continue to be the target of various cyberattacks.
Possible budget overruns
The issue with growing cloud resources is that you may inadvertently overprovision with unused space and inactive assets. Your bill would incur additional fees as a result, which over time might become extremely high. Wasted spending accounts for a third of what organizations spend on the cloud already, and by the end of the year, that percentage is expected to rise to 47%.
What difficulties does CloudOps present?
The following are some of the different CloudOps challenges:
- Complexity: Cloud infrastructures can be complex due to their many services and tools, which makes resource management and optimization challenging.
- Security: Because attackers target cloud settings, cloud infrastructure security is different from IT security.
- Governance: Managing cloud resources across teams and departments while complying can be tough.
- Capabilities gaps: CloudOps demands different capabilities than typical IT operations, making it hard to locate candidates.
- Cost control: Cloud services are expensive, and it can be hard to analyze spending across providers, services, and usage trends.
- Integration: Linking cloud services to on-premises infrastructure and other clouds is difficult and time-consuming.
- Change management: Cloud systems introduce new services and capabilities frequently, making change management difficult.
- Vendor lock-in: Switching cloud providers is expensive and complicated, so businesses may become dependent on one.
The organisation may struggle to deploy CloudOps and use cloud services due to these issues. Businesses may solve these problems by creating rules and processes to manage and optimize cloud resources while maintaining security, compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
Read more on CloudOps Definition, Simplifying Cloud Control With CloudOPs

