The Raptor Lake S refresh, which is set to be the 14th CPU generation for desktops, is expected to launch this year. However, the true successor, Arrow Lake-S for desktops, is also taking shape alongside the new 800 series chipset. This new chipset will introduce a new processor socket, and I will soon publish the exact details, including drawings and data. It’s important to note that Meteor Lake will focus on the notebook segment and is not the subject of this article.
Recently, Videocardz.com published information about the command sets used in Arrow Lake and Lunar Lake. The information was extracted from a PDF, confirming that both series support AVX-VNNI-INT16, SHA512, SM3, and SM4. This command sets focus on Artificial Intelligence loads and hashing functions. The integration of AVX-VNNI into the Arrow Lake and Lunar Lake processors is particularly significant as it enhances the performance of inference tasks in neural networks by providing specialized capabilities for 8-bit and 16-bit integer operations.
This development suggests that applications relying on artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning algorithms can expect accelerated processing and increased efficiency. However, the specific impact on performance in individual application scenarios is not yet known.
It has been given internal performance projections that forecast the performance of a current Core i9-13900K, along with the corresponding models of Raptor Lake Refresh and Arrow Lake. Although these projections are not public relations material, they can be considered realistic. It’s important to note that the final CPU performance may vary.
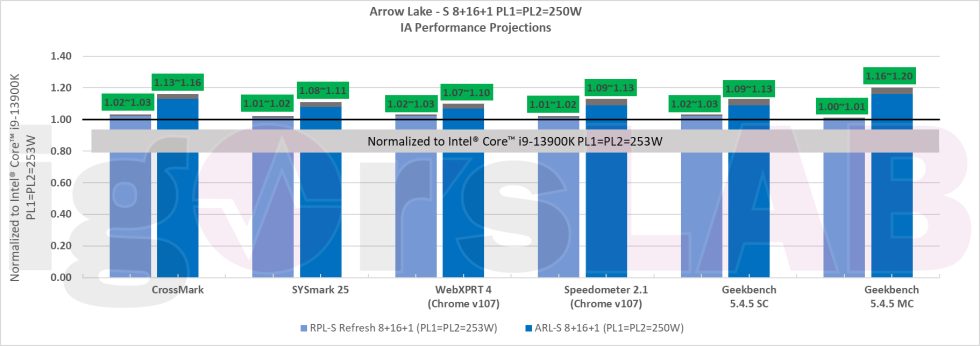
According to the projections, Intel has limited the PL1 and PL2 for the two variants of Raptor Lake S to 253 watts and for Arrow Lake to 250 watts. Interestingly, Arrow Lake is expected to have a relatively high power consumption, suggesting that power consumption is not anticipated to decrease significantly. The performance projections compare models with 8 performance cores and 16 efficiency cores, with the current Core i9-13900K as the baseline (100%).
The first graph shows that the Raptor Lake S Refresh is projected to have between a one and two percent increase in performance, primarily due to the clock speed increase. The maximum clock speed for the processor is expected to be around 6 GHz. The presence of a KS model with 6.2 GHz is uncertain. On the other hand, Arrow Lake S shows more significant performance increases, ranging from seven to 20 percent, with the largest gains expected in multi-core operations.
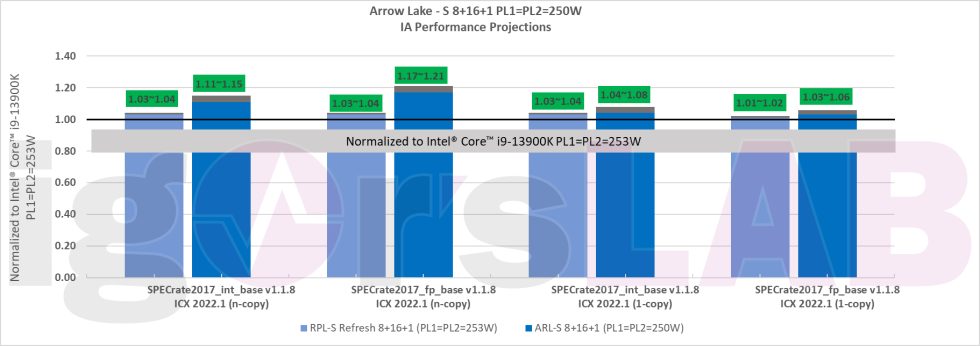
The second slide presents the SPEC CPU benchmark package, which includes standardized, CPU-intensive suites for measuring and comparing compute-intensive performance. The benchmark measures throughput or work per unit of time. The projections indicate that Raptor Lake Refresh can achieve a one to four percent increase in performance, depending on the suite, while Arrow Lake is expected to see improvements between three and a remarkable 21 percent. Arrow Lake demonstrates the most substantial increase in floating-point runs, whereas the performance of Raptor Lake Refresh remains relatively stable.
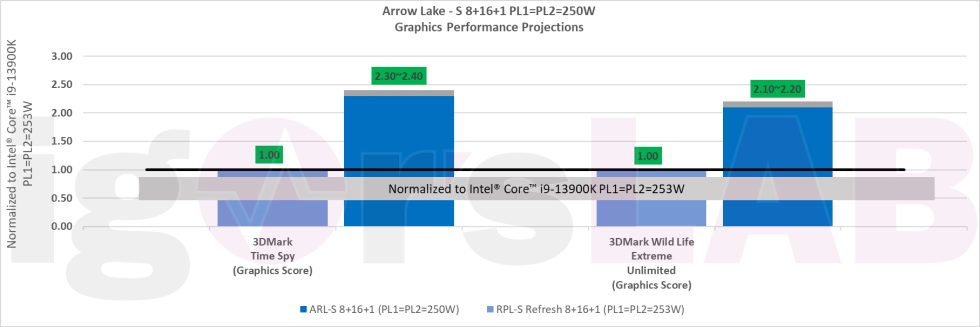
Regarding integrated graphics, Intel provides a slide that shows even larger performance increases. The Raptor Lake Refresh and Arrow Lake are equipped with the same GPU (HD700 series) as the Core i9-13900K, with a peak clock rate of 1.65 GHz. This results in similar graphics performance for both CPUs. However, the jump to Arrow Lake is significant. Arrow Lake will feature Xe LP graphics, making it the first desktop CPU to use Foveros Packaging for the integrated graphics. The slide shows an impressive 220 to 240 percent performance increase compared to Raptor Lake, which is more than a doubling. Exact details about the construction of the graphics tile are not yet available as the clock rate remains unknown.
Furthermore, Arrow Lake S will require a new socket, LGA1851. This change will impact cooler compatibility, as the Z-height and contact pressure will change. While the coolers may be somewhat compatible, they require a new mounting kit.
Raptor Lake S Refresh
This term “Raptor Lake S Refresh” describes the 14th generation of Core desktop CPUs from Intel. An incremental update of the 13th generation “Raptor Lake” CPUs is what it is.
Key attributes and details
- Architecture Hybrid: Using Intel’s performance hybrid design, these CPUs still combine:
- P-cores (performance-cores): made to handle challenging single-threaded tasks like content production and gaming.
- E-cores (efficient-cores): optimised to increase overall multitasking and power efficiency for background programs and multi-threaded operations.
- Enhanced Clock Rates: Increased clock speeds over the 13th generation are the main goal of the update. The Core i9-14900K is one of the variants that can achieve 6.0 GHz.
- A higher number of cores (on some models): The Core i7-14700K notably has more efficient cores than its predecessor.
- LGA 1700 Plug: Both motherboards using the 600 and 700 series chipsets that use the LGA 1700 socket may use them (albeit the 600 series boards probably need a BIOS upgrade).
- Assistance with Memory: They support DDR4 memory as well as DDR5 memory (up to 5600 MT/s).
- The PCIe 5.0: Fast graphics cards and other peripherals can be connected to these CPUs via PCIe 5.0 (up to 16 lanes). Additionally, PCIe 4.0 (up to 4 lanes) is supported.
- Combining Graphics: Intel UHD graphics powered by Xe architecture are found in the majority of models.
- Self-Directed Overclocking: Intel’s Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) provides one-click AI-guided overclocking on the Core i9-14900K.
- Networking: They support Bluetooth 5.3 and Wi-Fi 6/6E. There may be Thunderbolt 5 support in the future.



[…] Intel Embree Ray Tracing library has recently been updated by Intel, taking the ray-tracing performance on […]
[…] power restrictionsaa for the Intel Arrow Lake-S desktop CPUs are as follows: 125W PL1, 177W PL2, and 333W […]