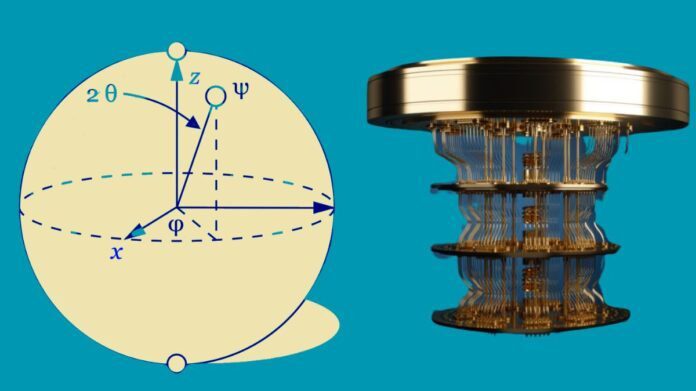
What are Qubits?
The fundamental unit of information used to encode data in quantum computing is called a qubit, or quantum bit. It is best thought of as the quantum counterpart of the conventional bit used by classical computers to encode binary data.
Benjamin Schumacher, an American theoretical physicist, is credited with coining the word “qubit.” The creation of it typically, but not always, involves working with and monitoring quantum particles the tiniest known components of the physical universe such as atoms, photons, electrons, trapped ions, and superconducting circuits.
Quantum computers, which are made possible by the special characteristics of quantum mechanics, use it to store more data than conventional bits, significantly enhance cryptography systems, and carry out extremely complex calculations that even classical supercomputers would find impossible or take thousands of years to finish.
It powered quantum computers might soon play a key role in solving many of the biggest problems facing mankind, such as machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), climate change, cancer, and other medical studies.
Different types of qubits and their advantages
Since every two-level quantum system may make a qubit, researchers are inventing numerous kinds, some superior for certain needs.
Superconducting
Superconducting qubits, controlled by microwave pulses and made of superconducting materials that operate at low temperatures, are popular among quantum computer scientists because to their great coherence.
Trapped ions
It is also possible to utilize trapped ion particles as it by using advanced laser technology. Trapped ion it are notable for high-fidelity measurements and lengthy coherence durations.
Quantum dots
One electron may be captured and used as a qubit by a tiny semiconductor called a quantum dot. Researchers are especially interested in quantum dot it because of its potential scalability and compatibility with current semiconductor technology. These it can be controlled by applying magnetic fields.
Photons
Photon qubits are now being utilized in quantum communication and quantum encryption because they can transmit quantum information over great distances via optical fiber cables by determining and measuring the directional spin states of individual light particles.
Neutral atoms
Ionic charges that are balanced between positive and negative are characteristics of common neutral atoms. These atoms may be stimulated into a variety of states by applying energy using lasers; any two of these states can be utilized to build a qubit that is ideal for operations and scaling up.
Qubit challenges
Its are quite volatile despite their ability. It need to be cooled to a temperature that is only a fraction of a degree above absolute zero which is colder than space in order to operate.
When a quantum particle is sufficiently regulated to behave like a qubit, it is said to have coherence. A qubit is said to be decoherent when it loses this capability. One of the main obstacles to quantum computing is the powerful cooling needed to produce a state of coherence for functioning qubits.
Moreover, qubit systems are often vulnerable to decoherence-driven failure, even in the coldest environments. Fortunately, previously unstable quantum systems may be stabilized by developments in the new area of algorithmic quantum error correction.
Qubits vs. bits
Bits and qubits come in a wide variety of forms, but all it must be able to exist in a quantum superposition and obey the principles of quantum physics.
There are just two possible positions for a classical bit: 0 and 1. However, it may also exist in a superposition, which is a third state. Three distinct positions are represented by a superposition, which includes 0 and 1 as well as any places in between taken simultaneously.
Despite having the ability to encode three distinct places, its are nevertheless used in binary systems to transmit data. In these systems, the word “bit” may refer to either the measurement of that bit (i.e., a 0 or a 1) or the substance or procedure utilized to represent a 0 or 1.