Cloud Storage Architecture Diagram And Cloud Storage Pricing
Contents
Cloud Storage Architecture Diagram
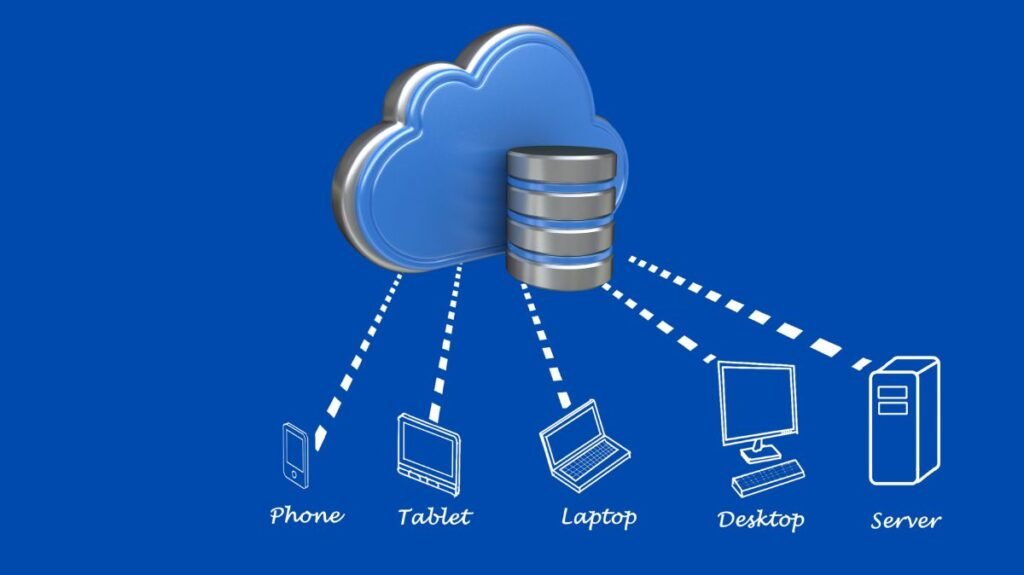
Cloud Storage Architecture
The architecture flow for cloud storage is as follows:
- Whether in a cloud architecture of cooperative or federated storage, the Cloud Storage Architecture is made up of several dispersed resources that work together as a single entity.
- long-lasting due to the production of duplicate versions.
- In the end, it often works well with the benefits of data replication.
- Businesses just have to pay for the storage they really use, which is typically around a month’s worth of usage. This does not mean that cloud storage is less expensive; rather, it means that operational costs rather than capital expenses are spent.
- Businesses that use cloud storage may reduce their energy use by as much as 70%, making them more environmentally friendly.
- The design of object storage incorporates storage and data security by design.
- Depending on the application, it may be possible to eliminate the extra infrastructure, work, and cost required to integrate accessibility and security.
- Storage management responsibilities, such acquiring more storage space, are delegated to the service provider.
- Through a web service interface, it gives consumers instant access to a large range of tools and applications stored in the infrastructure of another company.
- Cloud storage can act as a backup that is impervious to natural disasters, as there aren’t many backup servers spread out around the world.
- Cloud storage may be mapped to a local disc using the WebDAV protocol.
What Are The Types Of Cloud Storage?
Each of the three primary categories of cloud storage has unique benefits.
- Files Storage
- Blocks Storage
- Objects Storage

Files Storage
Data is saved in a hierarchical file and folder structure using file storage. Whether stored at the client where it originates or in the cloud storage system, the data maintains its format, and the hierarchy makes it simpler and more natural to locate and retrieve files when needed.
Cloud file storage is frequently utilised as a service that gives several users access to a shared collection of data kept in the cloud.
Blocks Storage
Block storage, which has historically been used in SANs, is also often used in cloud storage settings. Data is arranged using this storage strategy into “blocks,” which are substantial volumes. A distinct hard disc drive is represented by each block. Blocks are used by cloud storage companies to distribute massive volumes of data over several storage servers.
Because block storage resources have low IO latency (the time it takes for a connection to be established between the client and the system), they perform better over a network. Large databases and applications are particularly well-suited to these resources. Block storage is used for high-performance data storage in virtual private clouds (VPCs), which are public cloud services that enable an organisation to set up its own private cloud-like computing environment on shared public cloud infrastructure.
Block storage in the cloud may readily expand to accommodate the expansion of a company’s databases and apps. Block storage, for instance, enables consumer-driven websites to collect vast volumes of visitor data that can be saved and examined to enhance user experiences.
Objects Storage
Data is managed as distinct “objects” in object storage. Every object has an identification, related information, and the data contained in a file. In addition to allowing for the customisation of metadata to facilitate data access and analysis, objects keep data in the format in which it is received.
Objects are stored in repositories that offer infinite scalability rather than files or folder hierarchies. Object storage enables you to efficiently optimise storage resources since it lacks a file structure and allows for customisable metadata.
Long-term data retention is best served by cloud-based object storage. Network attached storage (NAS) and other conventional archives are being replaced by object storage in businesses.
Object storage is needed to efficiently manage unstructured data including web pages, audio and video files, and sensor data. Organisations generated 90% unstructured data in 2022.
Pricing cloud storage
The cost of cloud storage is often determined by the area, the pricing model used (on-demand, reserved, spot instances), and the resources used (compute, storage, data transport, databases).
The price of cloud storage varies. Not all cloud storage businesses charge by the gigabyte, but some do.
- 100 GB of storage costs $1.99 or $10 per month, depending on the business. Fees vary greatly. The total cost of the service typically includes extra charges for moving data from your network to the cloud storage expenses.
- In addition to the standard charges for data transit and storage, providers may impose additional fees. For example, if you move data from one location to another or access data in the cloud to make modifications or deletions, you may be charged more each time. Your expenses will increase as you carry out more of these activities each month. You pay more if you go beyond the permitted limit, even if the service provides a basic level of activity in the total cost.
- CSPs may additionally include in their prices the quantity of users who access the data, the frequency of user access, and the distance the data must travel. Depending on the kinds of data they retain and if they need extra protection for privacy and legal compliance, their prices may vary.
- A methodology known as “cloud cost optimisation” includes tactics, methods, best practices, and resources to help lower total cloud expenses (such as cloud storage) and determine the most economical approach to run your apps in the cloud while optimising business value.
- FinOps, a cloud financial management technique that helps businesses optimise business value in their hybrid and multicloud settings, is a mashup of finance and DevOps.