What Is Cloud Storage? Its Importance And How It Works?
What Is Cloud storage?
Cloud storage is stores data on off-site servers. Data on the servers is hosted, managed, and protected by the third-party source. The supplier guarantees that information stored on its servers is always available using either a private or public internet connection.
By eliminating the need for businesses to build and run their own data centres, it allows them to store, retrieve, and preserve data, shifting costs from a capital expenditure model to an operating one. Because cloud storage is scalable, businesses may adjust their data footprint to meet their needs.
How Does Cloud Storage Operate?
Cloud storage employs servers to store data, just as on-premises storage networks, except the data is transmitted to servers located offshore. Virtual machines (VMs) housed on physical servers make up the majority of these servers. The supplier builds new virtual servers to keep up with the growing demand for storage.
Through a web portal, website, or mobile application that uses an application programming interface (API), users can connect to a storage cloud over the internet or a dedicated private connection. Depending on the extent of the cloud provider’s operation, the connected server sends data to a group of computers spread throughout one or more data centres.
For redundancy, providers keep the same data across several computers as part of the service. In this manner, in the event of a server outage or being pulled down for maintenance, users may still access data.
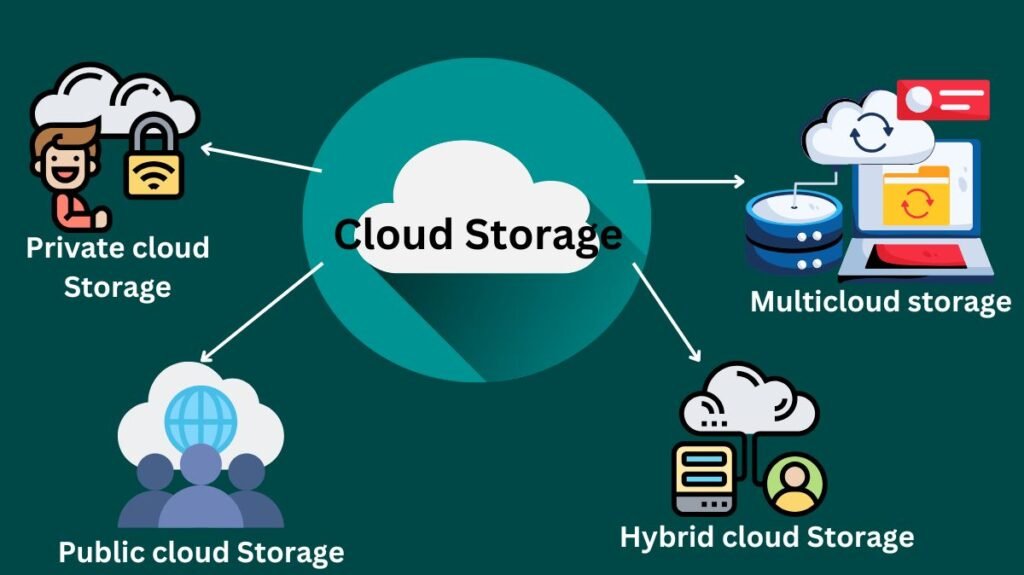
The following environments offer cloud storage:
- Private
- Public
- Hybrid
- Multicloud Storage
Private cloud Storage
The cloud concept is replicated in private cloud storage solutions, which are located within your network and boost capacity by creating instances of virtual servers on a real server.
You have the option of building a dedicated private cloud that can be accessed with a private connection or hiring a cloud storage provider to assume complete management of an on-premises private cloud. Private cloud data storage is frequently chosen by industries like banking and healthcare in order to have more control over sensitive customer data.
Public cloud Storage
With a public cloud model, you may access storage space that is utilized by other businesses and is managed by a cloud provider via the internet. Providers allow you to scale up or down as needed and make these services available from any device, including PCs and cellphones.
Hybrid cloud Storage
Businesses may choose which data to keep in which cloud by utilising a hybrid cloud architecture, which blends aspects of private and public clouds.
For example, a private cloud environment is better suitable for highly regulated data that must adhere to stringent archiving and replication criteria. On the other hand, the public cloud may be used to store less sensitive data, such emails that don’t include private company information. Some businesses employ hybrid cloud to add public cloud storage to their internal storage networks.
Multicloud storage
Utilising cloud services from many cloud vendors, or multicloud, gives businesses the freedom to maximize efficiency, manage expenses, and stay away from vendor lock-in. Multiple cloud suppliers’ storage services are combined into a single environment that customers may access via a single interface to multicloud storage.
Why Cloud Storage Important?
Scalable, affordable storage is provided via cloud storage. Operating underutilized hardware as demand declines, replacing malfunctioning devices, managing storage area networks (SANs), running out of capacity, and adding infrastructure to scale up with demand are all things you no longer have to worry about. In elastic cloud storage, you only pay for what you use and may scale up or down as needed. It lets organizations securely store data online for approved users to view at any time.
It may offer the flexibility, cost savings, security, and convenience of use you need to focus on growing your core business, regardless of size. It lets small organizations increase as they grow without spending a lot on storage management.
Large businesses with petabytes of data and billions of files may rely on cloud storage’s scalability, durability, and cost-effectiveness to build centralized data lakes that will make their data available to everyone who needs it.
Cost-effectiveness
It eliminates the need to buy gear, arrange storage, and utilise additional funds for unexpected business needs. You only pay for storage that you really need, you can instantly alter performance and retention features, and you can add or decrease storage space as needed. You can even automatically transfer data to less expensive storage when it becomes less often accessed, which will result in even greater cost savings. You may lower the total cost of ownership by shifting storage workloads from on-premises to the cloud, which eliminates overprovisioning and storage infrastructure maintenance expenses.
Enhanced agility
With cloud storage, you may click to access resources. You cut down the time it takes for your organisation to have access to those resources from weeks to minutes. Your organization’s agility is dramatically increased as a consequence. Your employees are mostly relieved of the duties associated with purchasing, setting up, managing, and maintaining. Additionally, your employees may now glean additional insights from your data to spur innovation because cloud storage interfaces with a variety of analytics tools.
Quicker deployment
Development teams should never be slowed down by infrastructure when they are prepared to start. IT can swiftly provide the precise quantity of storage required, whenever and wherever it’s needed, to cloud storage services. Instead of managing storage systems, your engineers may concentrate on resolving intricate application issues.
Effective data administration
You may carry out effective information management activities, such as automatic tiering or data locking down to satisfy compliance needs, by utilising cloud storage lifecycle management policies. Using techniques like replication, you may also leverage cloud storage to set up global or multi-region storage for your dispersed teams. Your data may be managed and arranged to support certain use cases, save costs, maintain security, and satisfy legal requirements.
Almost infinite scalability
With the nearly limitless storage capacity that cloud storage offers, you may grow up as much and as fast as you want. The limitations of on-premises storage capacity are therefore eliminated. As needed for analytics, data lakes, backups, or cloud-native apps, you may effectively scale cloud storage up and down. Without having to wait for new hardware or deal with complicated storage allocation procedures, users may access storage at any time and from any location.
Continuity of business
Cloud storage companies safeguard your data and guarantee company continuity by storing it in extremely secure data centres. Cloud storage services quickly identify and restore redundancy to manage concurrent device failure. Using versioning and replication techniques to make it easier to recover from both accidental user activities and application failures will help you further safeguard your data.
Cloud storage services allow you to:
- Protect data in the cloud at a reasonable cost without compromising functionality.
- When your data needs change, you can quickly scale up your backup resources.
- Use a data centre and network architecture designed for security-conscious enterprises to safeguard backups.