NaaS Network as a Service Architecture, Benefits And Pricing
Contents
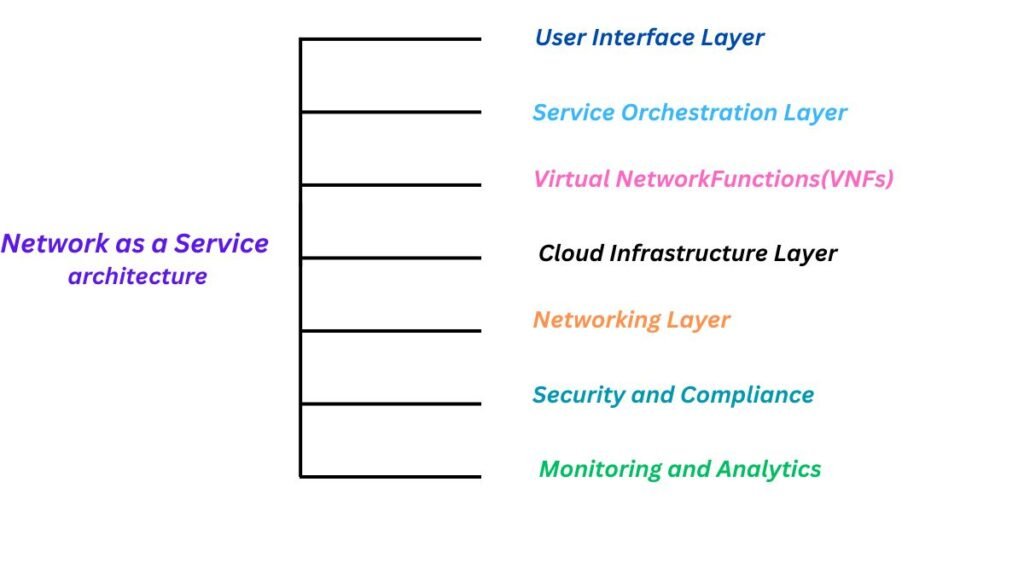
Network as a Service architecture
NaaS Network as a Service architecture uses a cloud-based concept to provide network services.
- User Interface: Network management and configuration APIs and customer portals.
- Traffic policies, scaling, and provisioning are automated by the orchestration layer.
- Virtual Network Functions (VNFs): Hardware is replaced with virtual load balancers, firewalls, and routers.
- Cloud infrastructure: Makes use of SDN controllers for dynamic routing in public or hybrid clouds.
- Networking Layer: Low-latency access via edge nodes and the physical backbone.
- Security: Tools for compliance and encryption for safe data handling.
- Monitoring: AI/ML-powered real-time analytics to maximize performance.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing, global reach for flexible networking, and scalability are key features.
Network as a Service benefits
NaaS streamlines the administration and use of software and hardware technologies. More speed, agility, and scale are made possible by it. With NaaS, SD-WAN can be implemented as a value-added service to improve application experience, security, redundancy, and performance.
Businesses can use network resources on a pay-per-use or subscription basis with the NaaS networking paradigm. It provides a platform with services, software, and hardware. Reduced technical debt, faster innovation, quicker network technology renewal lifecycles, and quicker rollouts of new features and capabilities are just a few advantages that NaaS can offer.
Automation and simplicity in IT
When companies match their expenses to their actual utilization, they gain. They can dynamically expand capacity as demands rise, and they are not required to pay for excess capacity that is not used. Upgrades, bug fixes, and security patches must be applied promptly by companies that own their own infrastructure. In order to implement improvements, IT professionals frequently have to travel to different sites. Continuous delivery of new features, fixes, and capabilities is made possible by NaaS. It offers orchestration and optimization for optimal performance, and it automates a number of tasks, including onboarding new users. The time and money spent on these procedures may be reduced as a result. Businesses depend on vendors to handle the entire lifecycle.
Accessible from any location
Employees of today can need to access the network from any location home or office on any device, without the need for a virtual private network (VPN). NaaS can offer businesses worldwide coverage, low-latency connectivity made possible by a global POP backbone, and minimal packet loss when connecting to branch offices, platform-as-a-service (PaaS)/infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) platforms, or SaaS apps.
Increased protection
Network security and the network are more tightly integrated as a result of NaaS. It is possible for certain suppliers to “piece together” network security. Network-as-a-Service solutions, on the other hand, must offer both cloud-based and on-premise security in order to satisfy modern business requirements. This will hasten the shift to a secure access service edge (SASE) architecture where and when it is required.
Awareness and perceptions
NaaS offers powerful firewall and packet inspection capabilities, proactive network monitoring, security policy enforcement, and the ability to model the performance of applications and the underlying infrastructure over time. Additionally, customers might be able to co-manage the NaaS.
A better experience with the application
Having connection that provides the same user experience as if the application were hosted in-house is essential in a multicloud environment. NaaS offers AI-powered features to assist guarantee that capacity SLAs and SLOs are fulfilled or surpassed. In order to help guarantee an exceptional user experience and to proactively handle problems that arise, NaaS offers the capability to redirect application traffic.
Adaptability
Compared to traditional infrastructure, Network-as-a-Service services provide more flexibility and customisation through a cloud-based delivery mechanism. Hardware is not used to implement changes; software is. Usually, a self-service paradigm is used to deliver this. For instance, IT teams can establish additional branch sites and change corporate networks as needed in a fraction of the time. To accommodate different consumption needs, NaaS frequently offers term-based subscriptions with usage billing and a variety of payment alternatives.
Scalability
Compared to conventional, hardware-based networks, NaaS is by nature more scalable. Rather than buying, setting up, configuring, and securing more hardware, NaaS clients just buy more capacity. This implies that they can swiftly scale up or down in response to shifting needs.
Network-as-a-Service
Disadvantages
The following are some possible disadvantages of NaaS Network as a Service:
- Dependency on outside providers: Businesses may rely on the supplier to supply network services.
- Security issues: There may be security hazards associated with NaaS.
- Restricted customization options: Network-as-a-Service might only provide a few customization choices.
- Changing providers: Changing providers might be difficult.
- Compatibility: Legacy systems, such outdated hardware or on-premise apps, might not be able to use the NaaS vendor’s infrastructure.
NaaS applications
There are numerous applications for NaaS Network as a Service, such as:
- Connecting to various cloud providers: By making private connections to numerous cloud providers easier, NaaS can establish hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
- Virtual routing: Rather of buying and maintaining actual routers, NaaS enables enterprises to implement virtual routers.
- Disaster recovery: In the event of an outage, NaaS Network as a Service can set up backup networks to guarantee constant network connectivity.
- SaaS and PaaS deployment: NaaS can swiftly roll out SaaS and PaaS across the network.
- Hardware upgrades: NaaS Network as a Service can facilitate on-demand connectivity and streamline configuration.
- Pop-up websites: Network-as-a-Service is applicable to pop-up websites.
Additionally, NaaS Network as a Service can assist enterprises with:
Flexibility in financing
NaaS Network as a Service enables businesses to pay as they expand rather than having to make large upfront commitments.
Increased protection
NaaS can contribute to improved security by swiftly implementing new features and capabilities.
Active management
NaaS’s proactive management and consulting capabilities can help reduce hazards.
Centralized management that is scalable
Coherent network domain management is possible using NaaS Network as a Service.
Sustainability
When it comes to outdated hardware resources, NaaS Network as a Service can assist allay concerns about cost and security.
Network as a Service pricing
As a Service Network Depending on the supplier, the demands of the client, and the particular services provided, (NaaS) pricing structures might differ significantly. Nonetheless, a few typical pricing schemes are as follows:
Pricing depends on subscriptions:
Fixed Monthly Fee: Regardless of consumption, a defined monthly cost for a particular set of services. Businesses with known network requirements can use this technique.
Tiered Pricing: Various price tiers according to bandwidth, service level, and other variables. This enables companies to select the package that best suits their needs.
Pricing dependent on usage:
Pay-per-Use: Users only pay for the precise resources they use, like processing power, storage, or bandwidth. For companies with varying network requirements, this strategy is perfect.
Metered Pricing: Charges are made to customers according to their actual usage, which is expressed in terms of processing time or data transmission. This gives companies flexibility and enables cost optimization.
Pricing that is hybrid:
Subscription and usage-based combined: a mix of usage-based pricing and set monthly rates. Flexibility and predictable expenses can be balanced using this model.
Network as a Service examples
NaaS Network as a Service examples include the following:
- Cloud VPNs: For safe, expandable connections, use AWS Client VPN and Cisco Meraki.
- Aryaka SmartConnect and VMware SD-WAN are two options for effective WAN management.
- Virtual networking options for hybrid/cloud networks include Google Network Connectivity Center and Azure Virtual WAN.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Akamai and Cloudflare for quick and safe content distribution.
- Internet of Things networking: AWS IoT Core and AT&T IoT NaaS for connectivity.
- Managed Functions: For cloud-managed networks, AT&T FlexWare and HPE Aruba Central.
- Global Networking: For safe worldwide connectivity, use Verizon Secure Cloud Interconnect and Cloudflare Magic WAN.
- Global Networking: Verizon Secure Cloud Interconnect and Cloudflare Magic WAN provide safe worldwide communication.
These solutions make network management for enterprises easier and more scalable.
Network as a Service companies
These are a few of the leading NaaS Network as a Service firms:
- Cisco: Provides VPNs and cloud-managed networking with Cisco Meraki and SD-WAN.
- VMware: Offers secure connection and application-aware routing for VMware SD-WAN.
- Microsoft Azure: Offers global and hybrid cloud connection with Azure Virtual WAN.
- Google Cloud: Provides a Network Connectivity Center for networking across many clouds and hybrid systems.
- AWS: Offers Transit Gateway and Client VPN for safe cloud networking.
- Cloudflare: Provides CDN and Magic WAN for network optimization and virtual wide area networks.
- AT&T: Offers IoT NaaS and FlexWare for IoT connection and virtual networking.
- Aryaka: Provides improved cloud connectivity and SmartConnect for SD-WAN.
- Juniper Networks: Offers Mist NaaS for network management powered by AI.
- Akamai: Focuses on web acceleration and CDN for worldwide content distribution.
- HPE (Aruba): Provides Aruba Central for networks that are easier to administer in the cloud.
- Verizon: Offers hybrid cloud connectivity through Secure Cloud Interconnect.
For corporations of all sizes, these firms make network administration easier and safer.